在前幾篇,我們深入了 Scheduler 的基本運作、記憶體與圖管理、優先級與分層、以及 Time-Slicing 與協作式排程。
這些都是讓 reactivity 系統「內部正確運作」的基礎。
然而,光有正確的內部機制還不夠。
對開發者來說,更重要的是 如何觀察與診斷 這個系統,才能除錯、優化,並建立直覺的心智模型。
這就是 DevTools 與診斷工具 存在的價值。
在開發過程中,最常見的需求之一就是「我現在這個 signal / computed 的值到底是多少?」。
如果我們只能透過 console.log,會非常不方便,甚至破壞程式結構。
value
deps / subs)stale 或 disposed 狀態// devtools.ts
// type 沿用前面章節的 graph.ts
import type { Node } from "./graph.js";
// 以 WeakMap 發 ID,不污染 Node 結構
const ids = new WeakMap<Node, string>();
let seq = 0;
function getId(n: Node) {
let id = ids.get(n);
if (!id) {
id = `${n.kind}#${++seq}`;
ids.set(n, id);
}
return id;
}
export type InspectSnapshot = {
id: string;
kind: Node["kind"];
inDegree: number; // deps.size
outDegree: number; // subs.size
deps: { id: string; kind: Node["kind"] }[];
subs: { id: string; kind: Node["kind"] }[];
};
// 取得單一節點的扁平快照(不遞迴)
export function inspect(node: Node): InspectSnapshot {
return {
id: getId(node),
kind: node.kind,
inDegree: node.deps.size,
outDegree: node.subs.size,
deps: [...node.deps].map(n => ({ id: getId(n), kind: n.kind })),
subs: [...node.subs].map(n => ({ id: getId(n), kind: n.kind })),
};
}
// 友善輸出:上游 / 下游各一張表 + 概要
export function logInspect(node: Node) {
const snap = inspect(node);
// 概要
console.log(`[inspect] ${snap.id} (${snap.kind}) in=${snap.inDegree} out=${snap.outDegree}`);
// 上游
if (snap.deps.length) {
console.log(" deps ↑");
console.table(snap.deps);
} else {
console.log(" deps ↑ (none)");
}
// 下游
if (snap.subs.length) {
console.log(" subs ↓");
console.table(snap.subs);
} else {
console.log(" subs ↓ (none)");
}
}
// 小範圍遞迴展開(避免循環):向上/向下各走 depth 層
export function inspectRecursive(root: Node, depth = 1) {
const seen = new Set<Node>();
type Row = { from: string; to: string; dir: "deps" | "subs" };
const rows: Row[] = [];
const queue: Array<{ node: Node; dUp: number; dDown: number }> = [{ node: root, dUp: depth, dDown: depth }];
seen.add(root);
while (queue.length) {
const { node, dUp, dDown } = queue.shift()!;
const fromId = getId(node);
if (dUp > 0) {
for (const dep of node.deps) {
rows.push({ from: getId(dep), to: fromId, dir: "deps" });
if (!seen.has(dep)) {
seen.add(dep);
queue.push({ node: dep, dUp: dUp - 1, dDown: 0 }); // 向上繼續
}
}
}
if (dDown > 0) {
for (const sub of node.subs) {
rows.push({ from: fromId, to: getId(sub), dir: "subs" });
if (!seen.has(sub)) {
seen.add(sub);
queue.push({ node: sub, dUp: 0, dDown: dDown - 1 }); // 向下繼續
}
}
}
}
return {
center: getId(root),
nodes: [...seen].map(n => ({ id: getId(n), kind: n.kind })),
edges: rows,
};
}
//(加碼)輸出 Mermaid,用於文件示意
export function toMermaid(root: Node, depth = 1) {
const g = inspectRecursive(root, depth);
const lines = ["graph TD"];
for (const n of g.nodes) {
lines.push(` ${n.id.replace(/[^a-zA-Z0-9_#]/g, "_")}["${n.id}"]`);
}
for (const e of g.edges) {
const a = e.from.replace(/[^a-zA-Z0-9_#]/g, "_");
const b = e.to.replace(/[^a-zA-Z0-9_#]/g, "_");
lines.push(` ${a} --> ${b}`);
}
return lines.join("\n");
}
inspect(node):最快,拿到單點的入/出度與鄰居清單。logInspect(node):調試友好,上游/下游各一張 console.table。inspectRecursive(node, depth):小範圍展開,避免依賴圖太大或循環卡死。toMermaid(node, depth):文件/DevTools 顯示,把目前的子圖輸出成 Mermaid。當應用變大,單純的文字 inspect 已經不夠了。
這時就需要 依賴圖 (graph) 的可視化。
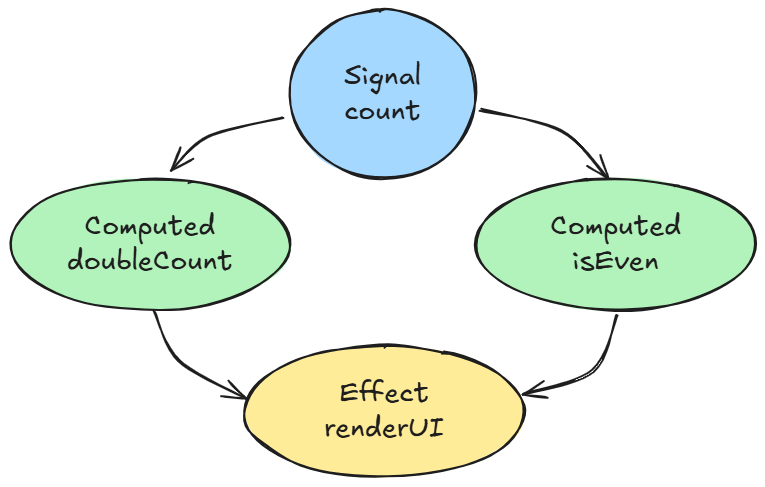
在 DevTools 裡,我們可以:
stale 節點,觀察資料流動unlink/link 與 auto-unlink 過程這能讓開發者清楚看到「哪個狀態觸發了哪個更新」。
在 UI 框架中,最常見的效能瓶頸是 過度渲染 (over-rendering)。
例如:某個 component 不斷 re-render,卻沒有實際變化。
在大型應用中,光知道「誰被更新過」還不夠。
我們需要知道「誰更新得最多」,也就是 效能熱點 (hotspot)。
hotspot.ts// hotspot.ts
// 型別一樣沿用之前的 graph.ts
import type { Node } from "../graph.js";
export type HotspotStats = {
updates: number;
lastTs: number;
freqPerMin: number;
durTotal: number;
durCount: number;
};
let stats = new WeakMap<Node, HotspotStats>();
const liveNodes = new Set<Node>(); // 登記活躍節點,方便列出排行榜
const alpha = 0.2;
const now = () => (globalThis.performance?.now?.() ?? Date.now());
function getStats(n: Node): HotspotStats {
let s = stats.get(n);
if (!s) {
s = { updates: 0, lastTs: now(), freqPerMin: 0, durTotal: 0, durCount: 0 };
stats.set(n, s);
}
return s;
}
// ── 對外 API ───
export function registerNode(n: Node) { liveNodes.add(n); }
export function unregisterNode(n: Node) { liveNodes.delete(n); }
export function recordUpdate(node: Node) {
const s = getStats(node);
const t = now();
const dt = Math.max(1, t - s.lastTs);
const instFreqPerMin = (1000 / dt) * 60;
s.freqPerMin = alpha * instFreqPerMin + (1 - alpha) * s.freqPerMin;
s.updates += 1;
s.lastTs = t;
}
export function withTiming<T>(node: Node, fn: () => T): T {
recordUpdate(node);
const t0 = now();
try {
return fn();
} finally {
const d = now() - t0;
const s = getStats(node);
s.durTotal += d;
s.durCount += 1;
}
}
export function allNodes(): Iterable<Node> { return liveNodes; }
export function topHotspots(
n = 5,
by: "freq" | "updates" | "avgTime" = "freq",
nodes: Iterable<Node> = liveNodes
) {
const rows = [] as Array<{
kind: Node["kind"];
updates: number;
freqPerMin: number;
avgMs: number;
inDegree: number;
outDegree: number;
}>;
for (const nd of nodes) {
const s = stats.get(nd);
if (!s) continue;
rows.push({
kind: nd.kind,
updates: s.updates,
freqPerMin: Number(s.freqPerMin.toFixed(2)),
avgMs: s.durCount ? Number((s.durTotal / s.durCount).toFixed(2)) : 0,
inDegree: nd.deps.size,
outDegree: nd.subs.size,
});
}
switch (by) {
case "updates": rows.sort((a, b) => b.updates - a.updates); break;
case "avgTime": rows.sort((a, b) => b.avgMs - a.avgMs || b.updates - a.updates); break;
default: rows.sort((a, b) => b.freqPerMin - a.freqPerMin || b.updates - a.updates);
}
return rows.slice(0, n);
}
export function logTopHotspots(
n = 5,
by: "freq" | "updates" | "avgTime" = "freq",
nodes: Iterable<Node> = liveNodes
) {
const rows = topHotspots(n, by, nodes).map(r => ({
kind: r.kind,
updates: r.updates,
"freq (/min)": r.freqPerMin,
"avg ms": r.avgMs,
"in-degree": r.inDegree,
"out-degree": r.outDegree
}));
console.table(rows);
}
export function resetHotspots() {
stats = new WeakMap<Node, HotspotStats>(); // 重新建立即可,相當於「清空」
liveNodes.clear();
}
signal.ts(只加註冊+記錄)// signal.ts
export function signal<T>(initial: T, equals: Comparator<T> = defaultEquals) {
const node: Node & InternalNode<T> & { kind: 'signal'; equals: Comparator<T> } = {
kind: 'signal',
deps: new Set(),
subs: new Set(),
value: initial,
equals,
};
// 登記活節點(供 Hotspot 列表使用)
registerNode(node); // 新增
const get = () => {
track(node);
return node.value;
};
const set = (next: T | ((prev: T) => T)) => {
const prev = node.value;
const nxtVal = typeof next === 'function' ? (next as (p: T) => T)(node.value) : next;
if (node.equals(node.value, nxtVal)) return;
if (inAtomic()) recordAtomicWrite(node, prev);
node.value = nxtVal;
// 記錄更新事件(signal 寫入最常見)
recordUpdate(node); // 新增
if (node.subs.size === 0) return;
for (const sub of node.subs) {
if (sub.kind === 'effect') {
Effects.get(sub)?.schedule();
} else if (sub.kind === 'computed') {
markStale(sub);
}
}
};
const subscribe = (observer: Node) => {
if (observer.kind === 'signal') {
throw new Error('A signal cannot subscribe to another node');
}
link(observer, node);
return () => unlink(observer, node);
};
return { get, set, subscribe, peek: () => node.value };
}
computed.ts(只加註冊 + withTiming 包 recompute)// computed.ts
export function computed<T>(fn: () => T, equals: Comparator<T> = defaultEquals) {
const node: Node & {
kind: "computed";
value: T;
stale: boolean;
equals: Comparator<T>;
computing: boolean;
hasValue: boolean;
} = {
kind: "computed",
deps: new Set(),
subs: new Set(),
value: undefined as unknown as T,
stale: true,
equals,
computing: false,
hasValue: false,
};
registerNode(node); // ← 新增
function recompute() {
// 用 withTiming 包住重算,收集更新次數與耗時
withTiming(node, () => { // ← 新增(外層)
if (node.computing) throw new Error("Cycle detected in computed");
node.computing = true;
for (const d of [...node.deps]) unlink(node, d);
const next = withObserver(node, fn);
if (!node.hasValue || !node.equals(node.value, next)) {
node.value = next;
node.hasValue = true;
}
node.stale = false;
node.computing = false;
});
}
const get = () => {
track(node);
if (node.stale || !node.hasValue) recompute();
return node.value;
};
const peek = () => node.value;
const dispose = () => {
for (const d of [...node.deps]) unlink(node, d);
for (const s of [...node.subs]) unlink(s, node);
node.deps.clear();
node.subs.clear();
node.stale = true;
node.hasValue = false;
// 這裡不強制 unregister,因為 computed 可能被重用/復活
};
return { get, peek, dispose };
}
effect.ts(只加註冊、withTiming 包 run、dispose 時註銷)// effect.ts
export class EffectInstance implements EffectInstanceLike {
node: Node = { kind: 'effect', deps: new Set(), subs: new Set() };
cleanups: Cleanup[] = [];
disposed = false;
constructor(private fn: () => void | Cleanup) {
Effects.set(this.node, this);
registerNode(this.node); // 新增:登記活節點
}
run() {
if (this.disposed) return;
drainCleanups(this.cleanups);
for (const dep of [...this.node.deps]) unlink(this.node, dep);
// 用 withTiming 包住 effect 執行(收集更新與耗時)
withTiming(this.node, () => { // 新增
activeEffect = this;
try {
const ret = withObserver(this.node, this.fn);
if (typeof ret === 'function') this.cleanups.push(ret);
} finally {
activeEffect = null;
}
});
}
schedule() { scheduleJob(this); }
dispose() {
if (this.disposed) return;
this.disposed = true;
drainCleanups(this.cleanups);
for (const dep of [...this.node.deps]) unlink(this.node, dep);
this.node.deps.clear();
unregisterNode(this.node); // 新增:從活節點中移除
Effects.delete(this.node);
}
}
import { allNodes, logTopHotspots, topHotspots, resetHotspots } from "./devtools/hotspot";
// 任意時刻:印出前 5 大熱點(以頻率排序)
logTopHotspots(5, "freq", allNodes());
// 也可看「平均耗時」或「總次數」
logTopHotspots(5, "avgTime", allNodes());
logTopHotspots(5, "updates", allNodes());
// 如果你想要資料而非列印:
const topByTime = topHotspots(10, "avgTime", allNodes());
// resetHotspots(); // 需要時重置統計
signal.set、computed.recompute、effect.run)。recordUpdate 統計更新頻率,withTiming 才統計耗時(適合 computed/effect)。registerNode / unregisterNode / allNodes 讓你隨時列出排行榜;不會洩漏內部 WeakMap。equals、markStale、Effects.schedule()、scheduleJob 等流程。DevTools 並不只是除錯工具,它還能幫助:
透過 inspect 節點、依賴圖可視化、render 計數器、熱點追蹤,
我們不僅能把 reactivity 系統從「黑箱」變成「透明可觀測」,
更能在實際應用中有效除錯與優化。
這不僅是開發者的利器,也能推進框架本身的演進。
到這裡,我也和大家分享了我透過實作得到的大部分知識,後續進階內容的展開,還有更多未知的差異存在,這些差異也造成許多 library 對於特定場景使用上的優劣。
下一篇,我想要分享一下我寫這系列文章的心得與一些個人觀點。
