因為tuple內建比較規則是固定的字典序 (lexicographic order),如果今天要以字串長度為排序依據,要自定義結構和比較方法。
在Day16有看到Ord,比大小會用lexicographic order,我們來看實際source code,看Day 15堆積插入在Rust BinaryHeap怎麼做的。
插入新值會放在最後一個節點,接著開始sift_up
#[stable(feature = "rust1", since = "1.0.0")]
#[rustc_confusables("append", "put")]
pub fn push(&mut self, item: T) {
let old_len = self.len();
self.data.push(item);
// SAFETY: Since we pushed a new item it means that
// old_len = self.len() - 1 < self.len()
unsafe { self.sift_up(0, old_len) };
}
sift_up中比較是否比父節點的值大if hole.element() <= unsafe { hole.get(parent) ,這裡會使用到Ord,比較字典序
unsafe fn sift_up(&mut self, start: usize, pos: usize) -> usize {
// Take out the value at `pos` and create a hole.
// SAFETY: The caller guarantees that pos < self.len()
let mut hole = unsafe { Hole::new(&mut self.data, pos) };
while hole.pos() > start {
let parent = (hole.pos() - 1) / 2;
// SAFETY: hole.pos() > start >= 0, which means hole.pos() > 0
// and so hole.pos() - 1 can't underflow.
// This guarantees that parent < hole.pos() so
// it's a valid index and also != hole.pos().
if hole.element() <= unsafe { hole.get(parent) } {
break;
}
// SAFETY: Same as above
unsafe { hole.move_to(parent) };
}
hole.pos()
}
order實作cmp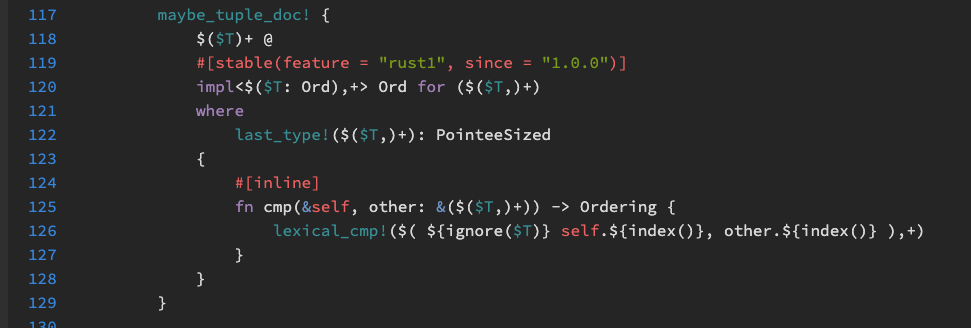
參考來源:https://doc.rust-lang.org/src/core/tuple.rs.html#110
從上面可以知道tuple型別定義好cmp方式了,所以我們只能自定義結構和比較方法。
Entry結構比較方法Ord、PartialOrd
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use std::cmp::Reverse;
use std::collections::BinaryHeap;
#[derive(Eq, PartialEq,Debug)]
struct Entry {
freq: i32,
word: String,
}
// 假設我們要:頻率小長度短的放堆頂
impl Ord for Entry {
fn cmp(&self, other: &Self) -> Ordering {
// 讓頻率少的勝出
match self.freq.cmp(&other.freq).reverse() {
Ordering::Equal => self.word.len().cmp(&other.word.len()).reverse(), // 讓長度短的勝出
ord => ord,
}
}
}
impl PartialOrd for Entry {
fn partial_cmp(&self, other: &Self) -> Option<Ordering> {
Some(self.cmp(other))
}
}
fn main() {
let mut heap = BinaryHeap::new();
heap.push(Entry{ freq: 2, word: String::from("i") });
heap.push(Entry{ freq: 2, word: String::from("love") });
heap.push(Entry{ freq: 1, word: String::from("leetcode") });
heap.push(Entry{ freq: 1, word: String::from("coding") });
for i in 0..heap.len(){
println!("top={:?}",heap.pop().unwrap());
//top=Entry { freq: 1, word: "coding" }
//top=Entry { freq: 1, word: "leetcode" }
//top=Entry { freq: 2, word: "i" }
//top=Entry { freq: 2, word: "love" }
}
}
#[derive(Eq, PartialEq,Debug)]為屬性 (attribute),讓編譯器替這個型別自動生成某些特徵(trait)的實作,你不用自己寫一大堆樣板程式碼。
PartialEq提供 == 和 != 運算子。
代表「部分相等 (partial equality)」:有些型別,並不是所有值都能正確定義「相等」。
EqEq 是 marker trait (標記 trait),沒有任何方法。
表示這個型別的相等性是「全序 (total equality)」
Debug允許用 {:?} 輸出值。
1.如何自定義Ord特徵,把字典序改成依長度排序
2.Rust attribute
