如果覺得文章對你有所啟發,可以考慮用 🌟 支持 Gthulhu 專案,短期目標是集齊 300 個 🌟 藉此被 CNCF Landscape 採納 [ref]。
今天來講一下搶佔式任務處理對 Gthulhu 為何重要?以及我們如何實作。
scx_rustland 和 Gthulhu 都是 vtime-based 的 scheduler,大家可以把 vtime 想像成 virtual deadline。而 Gthulhu 的 deadline 是這樣決定的:
func updatedEnqueueTask(t *models.QueuedTask) uint64 {
// Check if we have a specific strategy for this task
strategyApplied := ApplySchedulingStrategy(t)
if !strategyApplied {
// Default behavior if no specific strategy is found
if minVruntime < t.Vtime {
minVruntime = t.Vtime
}
minVruntimeLocal := util.SaturatingSub(minVruntime, SLICE_NS_DEFAULT)
if t.Vtime == 0 {
t.Vtime = minVruntimeLocal + (SLICE_NS_DEFAULT * 100 / t.Weight)
} else if t.Vtime < minVruntimeLocal {
t.Vtime = minVruntimeLocal
}
t.Vtime += (t.StopTs - t.StartTs) * t.Weight / 100
}
return 0
}
ApplySchedulingStrategy 嘗試查找 API server 提供的 policy 中有沒有對的當前任務調整。對於時間敏感的任務,如:5G 在 Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communications 場景的要求是:
如果只靠預設的排程器,很難保證在各種負載下滿足這樣的水準。
更甚者,即使將最高優先度的任務的 virtual deadline 設為 0,在系統有高負載的情況下,等到任務被排程也需要幾十個 ms。
解決辦法也很簡單,就是靠 preemption!
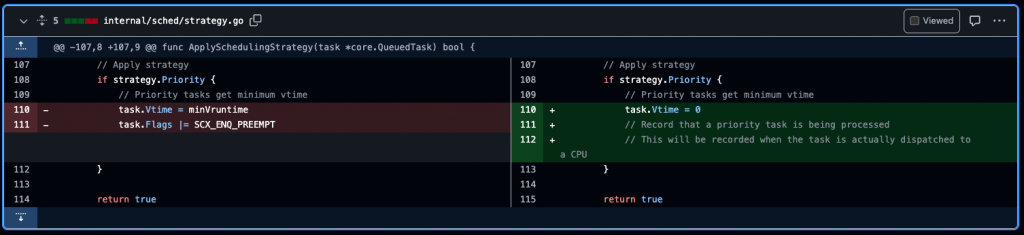
假設任務是高優先度的任務,我們先在 user space 將他的 vtime 設置為 0。我們會將 vtime 為 0 的任務的 pid 存入 priority_tasks 這個 eBPF MAP:
/*
* Helper function to update priority tasks map based on vtime.
* If vtime == 0, add PID to map. If vtime != 0, remove PID from map.
*/
static void update_priority_task_map(u32 pid, u64 vtime)
{
if (vtime == 0) {
u8 val = 1;
bpf_map_update_elem(&priority_tasks, &pid, &val, BPF_ANY);
} else {
bpf_map_delete_elem(&priority_tasks, &pid);
}
}
接著在 .enqueue 時直接處理高優先度的任務:
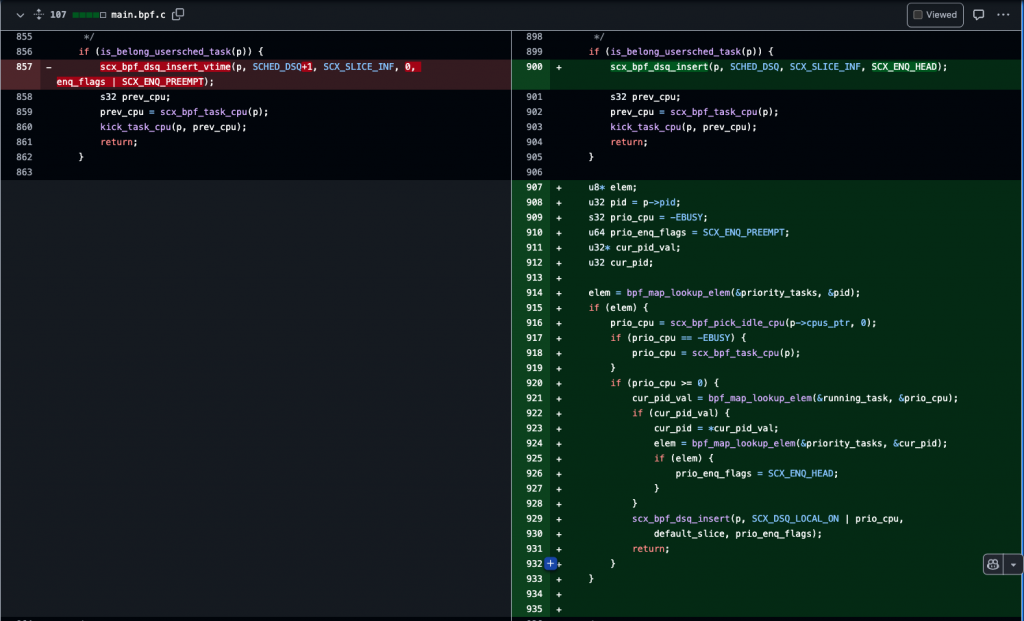
首先,先為需要排程的任務尋找一個 idle cpu,如果找不到,就選擇前一次服務該任務的 cpu。
接著我們會看這個 cpu 上正在執行的任務:
SCX_ENQ_PREEMPT 觸發 preemption。詳細的更動請參考 PR #15
讓 Gthulhu 支援 preemption 之後,我們就有能力對延遲敏感的任務進行最佳調整。但是,下一個挑戰來了,我們要如何挑選出 The One(需要被調整的 Process)呢?讓我們在未來兩篇文章揭曉。
