上次介紹用來辨識的CNN,這次要介紹影像風格轉換,而這裡使用[2]所介紹到的VGG19模型來訓練,順便練習一下如何載入訓練好的模型。而使用訓練好的模型特徵也稱為遷移學習。
首先先了解VGG19的結構,如下圖的E即是VGG19結構,可知道每一層都是使用3X3捲積,池化則是2X2。接著使用Tensorflow讀取已訓練好的VGG19資料。(mat格式)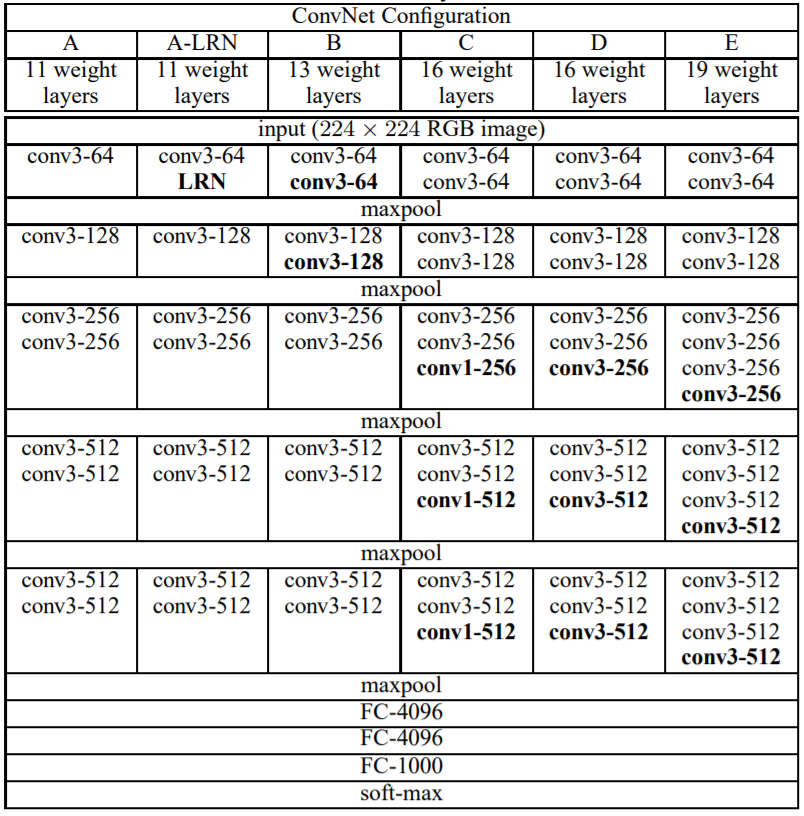
圖來源:[3]。
這裡要注意的地方則是np.transpose(weights, [1, 0, 2, 3]),因為mat儲存格式為[width, height, in_channels, out_channels]而Tensorflow計算格式為[height, width, in_channels, out_channels]所以必須要轉置矩陣到對應位置。
layers為每一層名稱。VGG19_build為讀取資料函數,參數vgg19_path為mat檔案路徑,image_data為影像資料,回傳權重型態為Tensor的陣列。conv2d為回傳計算3X3捲積。max_pool為回傳計算2X2池化。relu為回傳relu活化函數。import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import scipy.io
layers = (
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1',
'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'conv3_3',
'relu3_3', 'conv3_4', 'relu3_4', 'pool3',
'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'conv4_3',
'relu4_3', 'conv4_4', 'relu4_4', 'pool4',
'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'conv5_3',
'relu5_3', 'conv5_4', 'relu5_4'
)
def VGG19_build(vgg19_path, image_data):
mat_data = scipy.io.loadmat(vgg19_path)
layers_data = mat_data['layers'][0]
nets = {}
output = image_data
for index, name in enumerate(layers):
kind = name[:4]
if kind == 'conv':
weights, biases = layers_data[index][0][0][0][0]
# mat: weights 格式依序為[width, height, in_channels, out_channels]
# tensorflow: weights 格式依序為[height, width, in_channels, out_channels]
weights = np.transpose(weights, [1, 0, 2, 3])
biases = biases.reshape(-1)
output = conv2d(output, weights, biases)
elif kind == 'relu':
output = relu(output)
elif kind == 'pool':
output = max_pool(output)
nets[name] = output
return nets
def conv2d(input, weights, biases):
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input, tf.constant(weights), strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
return tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
def max_pool(input, k=2):
return tf.nn.max_pool(input, ksize=[1, k, k, 1], strides=[1, k, k, 1], padding='SAME')
def relu(input):
return tf.nn.relu(input)
首先要先介紹一些數學公式,而這公式主要用來計算影像特徵的損失函數。主要參考[5]。
在上一章提到離均差,而之前[筆記]深度學習(Deep Learning)-神經網路學習的優化提到分散量數是在表達目前數據分散數值(離散值),公式為向量X每個x扣掉平均的平方,如下圖。。
協方差與方差的差別在於,一個是計算本身,一個是計算兩者差異,而協方差公式為向量X和Y每個x和y扣掉各自平均的平方,如下圖。
看公式能得知方差是計算自己的離散程度,而協方差則是計算兩個向量的離散程度(相似性)。
將協方差公式輸入帶入垂直行向量與水平列向量,兩者扣除平均相乘則會變為矩陣相乘。公式(E代表平均)帶入為。接著以下舉個較明瞭的實例。
假設,
帶入cov公式,
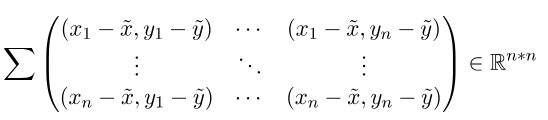
可看到所產生的結果為R^n*n大小(R為線性代數的向量次方則是維度),更明瞭來說就是計算X向量的每一個元素與Y向量每一個元素的差距,最後總和即是差異值。
在影像風格處理當中,風格損失函數使用格拉姆矩陣來計算目前的損失量,而格拉姆矩陣與協方差矩陣類似,差別在於格拉姆矩陣無扣掉均值。它所使用公式為,,從公式可以得知
格拉姆矩陣是在計算每個元素和每個元素之間的影響大小的總和。
這時你可能會疑惑為何不用原始影像做處理,主要因為原始影像是包含了顏色、紋理和位置等等特徵(所以主要影像的損失會用原始影像計算),而格拉姆矩陣則單純計算元素與元素的影響,所以位置不一定要在原來位置也能計算出相同結果,然而結果就會變為新風格加入主要影像。
以下為X矩陣大小1*N的格拉姆矩陣公式,由公式能得知它所產生出來的是一個對稱的三角矩陣,而三角矩陣特性在計算特徵值時候是非常快速的,三角矩陣還有其他特性但這裡沒使用到先暫時略過。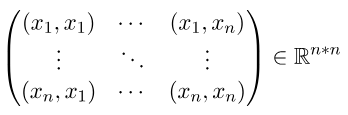
影像風格依照[2]輸入影像所使用層為['relu4_1'],風格輸入影像所使用層數為['relu1_1', 'relu2_1', 'relu3_1', 'relu4_1', 'relu5_1'],公式依照[4]所發表的公式實作。
使用均方誤差函數,目前輸入資料與主要影像輸入比較。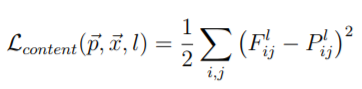
content_feature為原始影像權重。vgg_layer為目前訓練的權重。def content_loss(content_feature, vgg_layer):
return tf.nn.l2_loss(vgg_layer - content_feature)
轉置矩陣乘上原始矩陣。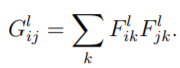
將計算後的格拉姆矩陣使用均方誤差函數,目前輸入資料與主要影像輸入比較。而作者在這裡定義的損失函數的除法MN是要計算使用格拉姆矩陣後的平均,1/4則是方便微分。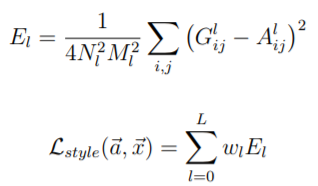
style_feature為風格影像權重的格拉姆矩陣。vgg_layer為目前訓練的權重。vgg_feats為展開成二維陣列。vgg_gram為計算格拉姆矩陣。def style_loss(style_feature, vgg_layer):
K, height, width, channel = map(lambda i: i.value, vgg_layer.get_shape())
vgg_feats = tf.reshape(vgg_layer, (-1, channel))
vgg_gram = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(vgg_feats), vgg_feats)
#M = K * height * width, N = channel
loss_base = ((K * height * width) ** 2) * (channel ** 2) * 2
return tf.nn.l2_loss(vgg_gram - style_feature) / loss_base
將主要影像損失函數加上風格影像損失函數即是總損失函數。跑迴圈計算每一層的損失函數並加總。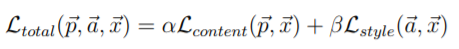
content_feature為原始影像權重。style_feature為風格影像權重的格拉姆矩陣。vgg_layer為目前訓練的權重。def loss(content_features, style_features, vgg_layers):
content_loss_total = 0.0
for name in CONTENT_LAYERS:
content_loss_total += content_loss(content_features[name], vgg_layers[name])
style_loss_total = 0.0
for index in range(len(STYLE_PATH)):
for name in STYLE_LAYERS:
style_loss_total += style_loss(style_features[index][name], vgg_layers[name])
style_loss_total /= len(STYLE_LAYERS)
loss_total = CONTENT_WEIGHT * content_loss_total + STYLE_WEIGHT * style_loss_total
return loss_total
CONTENT_WEIGHT內容影像權重。STYLE_WEIGHT風格影像權重。CONTENT_LAYERS內容影像特徵網路層。STYLE_LAYERS風格影像特徵網路層。LEARNING_RATE訓練率。TRAIN_TIMES訓練次數。CONTENT_WEIGHT = 7.0
STYLE_WEIGHT = 400.0
CONTENT_LAYERS = ['relu4_1']
STYLE_LAYERS = ['relu1_1', 'relu2_1', 'relu3_1', 'relu4_1', 'relu5_1']
LEARNING_RATE = 10.0
TRAIN_TIMES = 1000
論文使用白化處理,這裡偷懶一點直接扣除一半的像素。
def imsave(path, img):
img = np.clip(img + 128, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
scipy.misc.imsave(path, img)
def imread(path):
return scipy.misc.imread(path).astype(np.float) - 128
content_image讀取後扣掉RGB均值或VGG預設均值(扣128)。content_image轉為四維。CONTENT_LAYERS層內的權重。style_image也是相同只是多計算格拉姆。# init
content_features = {}
style_features = [{} for _ in STYLE_PATH]
with tf.Session() as session:
content_image = imread(CONTENT_PATH)
#content_mean = np.mean(np.mean(content_image, axis=0), axis=0)
#content_image -= content_mean
content_4d_shape = (1,) + content_image.shape
content_image = np.reshape(content_image, content_4d_shape)
vgg_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=content_4d_shape)
nets = vgg19.VGG19_build(VGG_PATH, vgg_input)
for name in CONTENT_LAYERS:
content_features[name] = session.run(nets[name], feed_dict={vgg_input: content_image})
with tf.Session() as session:
for index in range(len(STYLE_PATH)):
style_image = imread(STYLE_PATH[index])
#style_mean = np.mean(np.mean(style_image, axis=0), axis=0)
#style_image -= style_mean
style_4d_shape = (1,) + style_image.shape
style_image = np.reshape(style_image, style_4d_shape)
vgg_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=style_4d_shape)
nets = vgg19.VGG19_build(VGG_PATH, vgg_input)
for name in STYLE_LAYERS:
style_feature = session.run(nets[name], feed_dict={vgg_input: style_image})
style_feats = np.reshape(style_feature, (-1, style_feature.shape[3]))
style_gram = np.matmul(style_feats.T, style_feats)
style_features[index][name] = style_gram
initial為隨機初始化影像權重,並存入Tensor型態的image。nets為初始化要訓練的神經網路。loss_op為計算目前損失。train_op為使用Adam訓練。TRAIN_TIMES次即可。initial = None
with tf.Graph().as_default():
if initial is None:
initial = tf.random_normal(content_4d_shape) * 1
else:
initial = np.array([initial])
initial = initial.astype('float32')
image = tf.Variable(initial)
nets = vgg19.VGG19_build(VGG_PATH, image)
loss_op = loss(content_features, style_features, nets)
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(LEARNING_RATE).minimize(loss_op)
min_loss = 10000000000000
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for time in range(TRAIN_TIMES):
train_op.run()
now_loss = loss_op.eval()
print(time, ":", now_loss)
if now_loss < min_loss:
min_loss = now_loss
save_image = image.eval()
imsave('Image/' + str(time) + '.jpg', save_image[0])
imsave('Image/final.jpg', save_image[0])

內容影像。

風格影像。

結果。
在[2]中有修改一些公式,訓練出來的資料也不錯,這也代表損失函數可以加入自己的公式和想法,並創造出不同的風格,其實延伸至其他網路也是如此,但要做出屬於真正可用的公式我想要有一定的數學知識,否則也很難達到真正所需的效果。
[1] https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf
[2] 籃子軒(譯者)(2018)。Deep Learning深度學習基礎|設計下一代人工智慧演算法。台灣:歐萊禮。
[3]Karen Simonyan, Andrew Zisserman,"Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition".arXiv:1409.1556, 2015
[4]Leon A. Gatys, Alexander S. Ecker, Matthias Bethge,"A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style".arXiv:1508.06576, 2015
[5] https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/37609917
[6] https://upmath.me/
