今天要介紹的是Avg以及Weighted Avg
Avg就是平均值大家應該都知道哈哈,那我們這邊直接用範例做給大家看應該會比較快
我們用以下的資料進行測試,假設用以下的csv匯入學生的成績
csv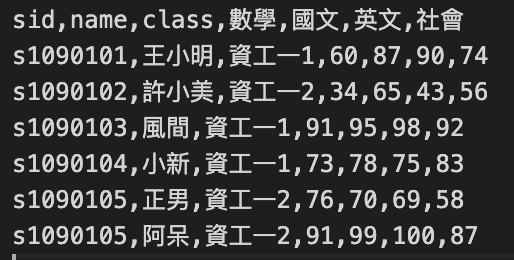
匯入index內部每個文檔的樣子:
{
"grades" : {
"math" : "91",
"mand" : "99",
"eng" : "100",
"soc" : "87"
},
"name" : "阿呆",
"class" : "資工一2",
"sid" : "s1090105"
}
先訂個目標,今天如果我想算出資工一2的數學總成績
term query:
"query": {
"term": {
"class": "資工一2"
}
}
aggregations query:
"aggs": {
"math_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "grades.math"
}
}
}
結合起來
query:
{
"query": {
"term": {
"class": "資工一2"
}
},
"aggs": {
"math_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "grades.math"
}
}
}
}
出來的結果再aggregations的math_avg(一開始aggs query取的name):
結果:
資工一2數學平均是67分
如果學生沒有成績,預設會被忽略掉,如果想要預防這種事情的話可以加上missing變成以下
"aggs": {
"math_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "grades.math",
"missing": 30
}
}
}
這樣的話如果沒有成績就會給一個初始成績30分
如果覺得學生考太低也可以寫個腳本幫學生加分
經典的開平方*10
aggs query:
"aggs": {
"math_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "grades.math",
"script": {
"lang": "painless", # 指定使用的腳本語言有painless及expression兩種,預設是painless
"source": "Math.sqrt(_value) * 10"
}
}
}
}
結果: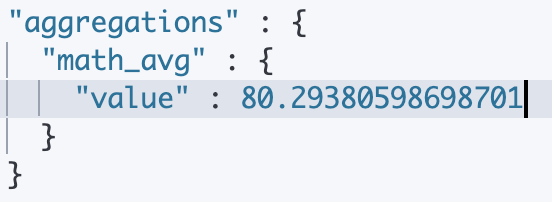
從67分變成了80分
或者也可以給定一個參考數值直接乘上數值
aggs query:
"aggs": {
"math_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "grades.math",
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "_value * params.correction",
"params": {
"correction": 1.1
}
}
}
}
}
結果:
加權公式:
∑(value * weight) / ∑(weight)
這種聚合方式需要一個字段提供加權的數值,所以我們在原本的文檔上加上weight,如下面這樣
{
"grades" : {
"math" : "91",
"mand" : "99",
"eng" : "100",
"soc" : "87"
},
"name" : "阿呆",
"class" : "資工一2",
"sid" : "s1090105",
"weight" : "1.4"
}
{
"grades" : {
"math" : "34",
"mand" : "65",
"eng" : "43",
"soc" : "56"
},
"name" : "許小美",
"class" : "資工一2",
"sid" : "s1090102",
"weight" : "0.6"
}
阿呆成績比較好所以讓阿呆的權重高一點,小美成績比較不好所以權重低一點
aggs query:
"aggs": {
"math_avg": {
"weighted_avg": {
"value": { #指定要計算數值的字段
"field": "grades.math"
"missing": 60 #一樣可以使用missing在數值為空時給預設值
},
"weight": { #指定加權數值的字段
"field": "weight"
"missing": 1
}
}
}
}
結果:
有了加權之後從原本的67變成了83.5
這種聚合方法也可以使用腳本,想了解更多可以看官方文件
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/search-aggregations-metrics-weight-avg-aggregation.html
今天的文章就到這邊,明天再繼續吧!
