大部分的系統都會有帳戶機制,其中涉及的部分不外乎就是註冊、登入與驗證,這部分內容較多,我會拆成上下兩篇,這篇會先實作註冊帳號的部分。
不曉得大家還記不記得前面有一張圖裡面有一個 ? Route,那正是驗證機制所需要的路由,我們叫它 Auth Route,又因為一個應用可能會有多種驗證機制,舉例來說:可以用本地帳戶、Google 或 Facebook 進行登入,所以這裡可以再將路由切細一點,切出一個 LocalAuthRoute 來實作本地帳戶,如下圖: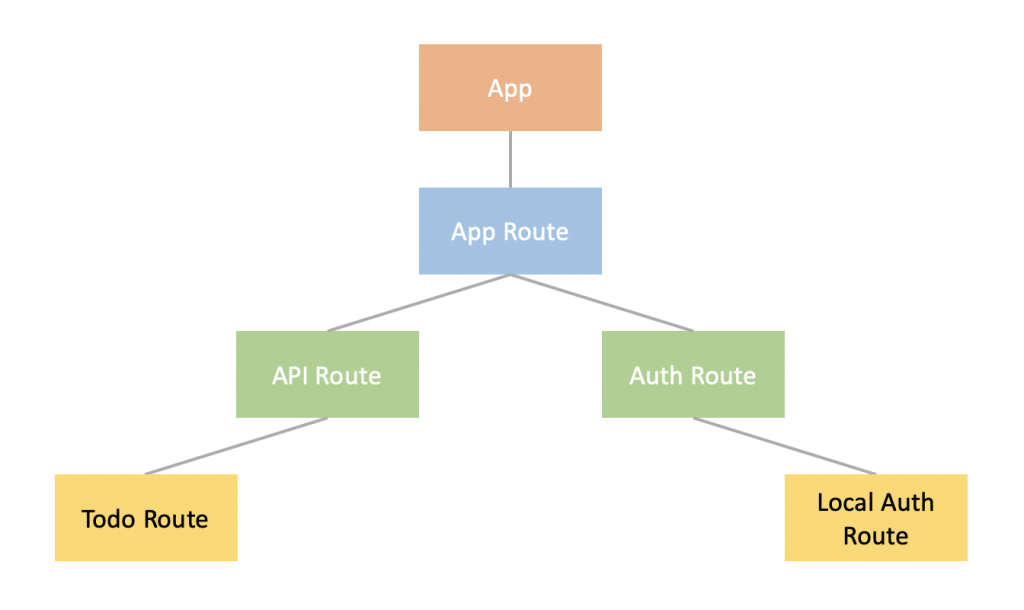
實作本地帳戶驗證機制一定會依賴資料庫,所以我們來規劃 Schema 與製作 Model。下方為 local-auth.model.ts 的程式碼:
import { model, Schema } from 'mongoose';
import { CoreDocument } from '../types/model.type';
import { EmailValidator } from '../validators';
const LocalAuthSchema = new Schema(
{
username: {
type: String,
required: true,
minlength: 3,
maxlength: 12
},
password: {
salt: {
type: String,
required: true
},
hash: {
type: String,
required: true
}
},
email: {
type: String,
required: true,
validate: {
validator: EmailValidator
}
}
}
);
export interface LocalAuthDocument extends CoreDocument {
username: string;
password: {
salt: string;
hash: string;
};
email: string;
}
export const LocalAuthModel = model<LocalAuthDocument>('User', LocalAuthSchema);
可以看到 password 的欄位並不是直接儲存的,而是有 salt 與 hash 兩個欄位,原因是密碼屬於較敏感的資訊,必須加密再儲存進資料庫當中,而 salt 就是替密碼加鹽,能夠大幅提升被攻破的難度!
在設計完 LocalAuthModel 後,就來新增 LocalAuthRepository 吧!新增一個 local-auth.repository.ts 並實作 addUser 與 getUser 方法:
import crypto from 'crypto';
import { LocalAuthModel, LocalAuthDocument } from '../models/local-auth.model';
export class LocalAuthRepository {
public async addUser(
username: string,
password: string,
email: string
): Promise<LocalAuthDocument> {
const { salt, hash } = this.hashPassword(password);
const user = new LocalAuthModel({
username,
password: { salt, hash },
email
});
const document = await user.save();
return document;
}
public async getUser(
options: { username?: string, email?: string }
): Promise<LocalAuthDocument | null> {
const params = Object.keys(options)
.filter(key => !!(options as any)[key])
.map(key => {
return { [key]: (options as any)[key] };
});
const getCondition = () => {
if ( params.length > 1 ) {
return {
$or: params
};
}
return params[0];
};
const user = await LocalAuthModel.findOne(getCondition());
return user;
}
public hashPassword(
password: string,
salt = crypto.randomBytes(16).toString('hex')
): { salt: string, hash: string } {
const hash = crypto.pbkdf2Sync(password, salt, 1000, 64, 'sha256').toString('hex');
return { salt, hash };
}
}
可以看到 addUser 方法有使用到 hashPassword,這就是替密碼加鹽,我的實作方法是沒有指定 salt 的情況下會是隨機字串,並把傳入的 password 與 salt 用 sha256 進行迭代,最後再傳回結果。另外,getUser有 username 與 email 兩種查詢方式,這樣就能更有彈性地找出使用者資訊。
整理一下資料夾結構,並將路由相關的檔案也一併列上來:
├── src
| ├── index.ts
| ├── app.ts
| ├── app.routing.ts
| ├── + bases
| ├── + common/resonse
| ├── + exceptions
| ├── main
| | ├── + api
| | └── auth
| | ├── auth.routing.ts //本篇新增
| | └── local
| | ├── local-auth.service.ts //本篇新增
| | ├── local-auth.controller.ts //本篇新增
| | └── local-auth.routing.ts //本篇新增
| ├── models
| | ├── local-auth.model.ts //本篇新增
| | └── todo.model.ts
| ├── repositories
| | ├── local-auth.repository.ts //本篇新增
| | └── todo.repository.ts //本篇新增
| ├── + dtos
| ├── + types
| ├── + environments
| ├── + database
| └── + validators
├── package.json
└── tsconfig.json
下方為 local-auth.service.ts 的程式碼:
import { LocalAuthRepository } from '../../../repositories/local-auth.repository';
import { HttpStatus } from '../../../types/response.type';
export class LocalAuthService {
private readonly localAuthRepo = new LocalAuthRepository();
public async addUser(username: string, password: string, email: string) {
const isUsed = await this.localAuthRepo.getUser({ username, email });
if ( isUsed ) {
const error = new Error('使用者名稱或電子信箱已被使用');
(error as any).status = HttpStatus.CONFLICT;
throw error;
}
const user = await this.localAuthRepo.addUser(username, password, email);
return user;
}
}
下方 local-auth.controller.ts 的程式碼:
import { Request } from 'express';
import { ControllerBase } from '../../../bases/controller.base';
import { LocalAuthService } from './local-auth.service';
import { ResponseObject } from '../../../common/response/response.object';
import { HttpStatus } from '../../../types/response.type';
export class LocalAuthController extends ControllerBase {
protected readonly localAuthSvc = new LocalAuthService();
public async signup(req: Request): Promise<ResponseObject> {
const { username, password, email } = req.body;
const user = await this.localAuthSvc.addUser(username, password, email);
return this.formatResponse(user, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
}
下方為 local-auth.routing.ts 的程式碼:
import express from 'express';
import { RouteBase } from '../../../bases/route.base';
import { LocalAuthController } from './local-auth.controller';
export class LocalAuthRoute extends RouteBase {
protected controller!: LocalAuthController;
protected initial(): void {
this.controller = new LocalAuthController();
super.initial();
}
protected registerRoute(): void {
this.router.post('/signup',
express.json(),
this.responseHandler(this.controller.signup)
);
}
}
使用 Postman 進行帳號註冊: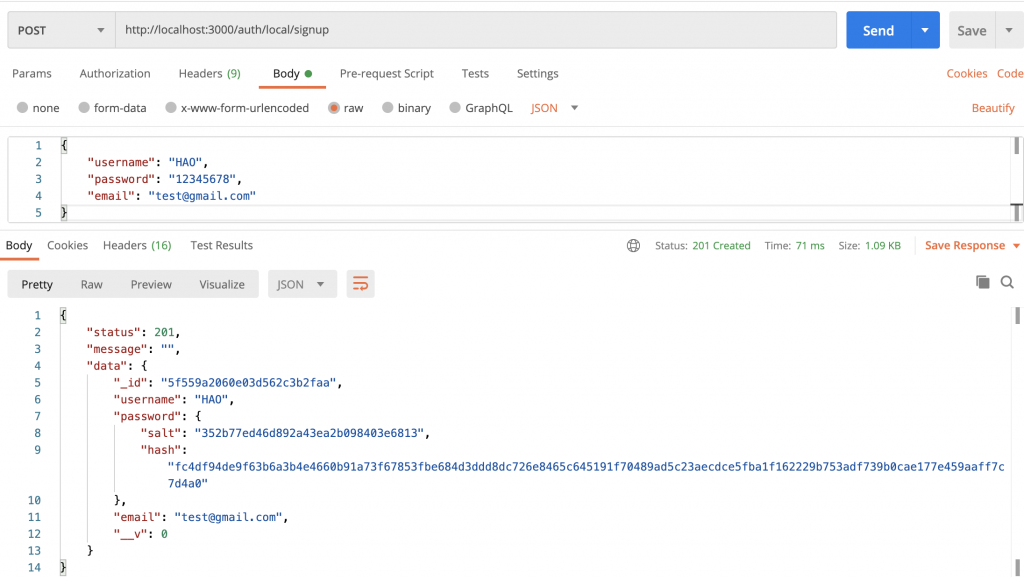
可以看到 User 的資料表示成功!
本篇實作了註冊帳戶的部分,下篇會開始實作登入與驗證機制,並實現 token 的機制,敬請期待!
