(這其實是一個很複雜且相對較進階的主題,本篇文章僅供認識這個概念,相關實作範例都是終極簡化版)
在海量資料的儲存情境下,DB 的效能會受到影響,此時透過垂直擴充架構也許是無法滿足的,因此會需要資料分片(shard),以水平擴展的方式來提升效能(可以想像成多個公路比起一條道路,可以達到分流,減緩堵塞)。
水平擴展方式一般來說又可以分為 Horizontal Partitioning 與 Sharding,前者是在同一個資料庫中將 table 拆成數個小 table,後者則是將 table 放到數個資料庫中。Horizontal Partitioning 的 table 與 schema 可能會改變,Sharding 的 schema 則是相同,但分散在不同資料庫中。
既然要做 sharding,如何決定哪些資料要到哪個資料庫就顯得非常重要了,常見的 Sharding 方式有以下兩種:
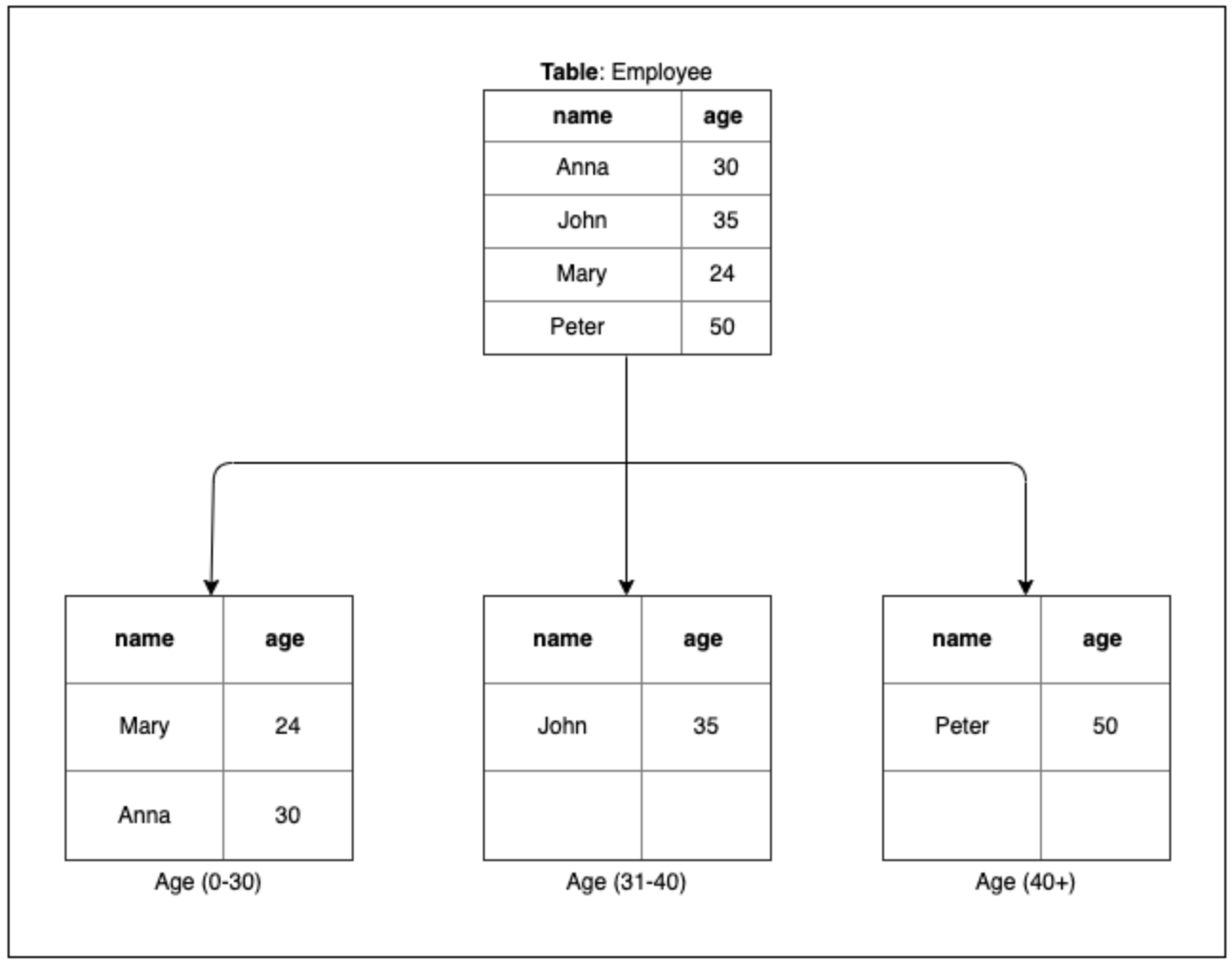
用區間來判斷,以上圖為例,年齡 0–30 會被分配到第一個資料庫中, 31–41 會到第二個,40歲以上會到第三個資料庫。實際區分的欄位可以自己決定。
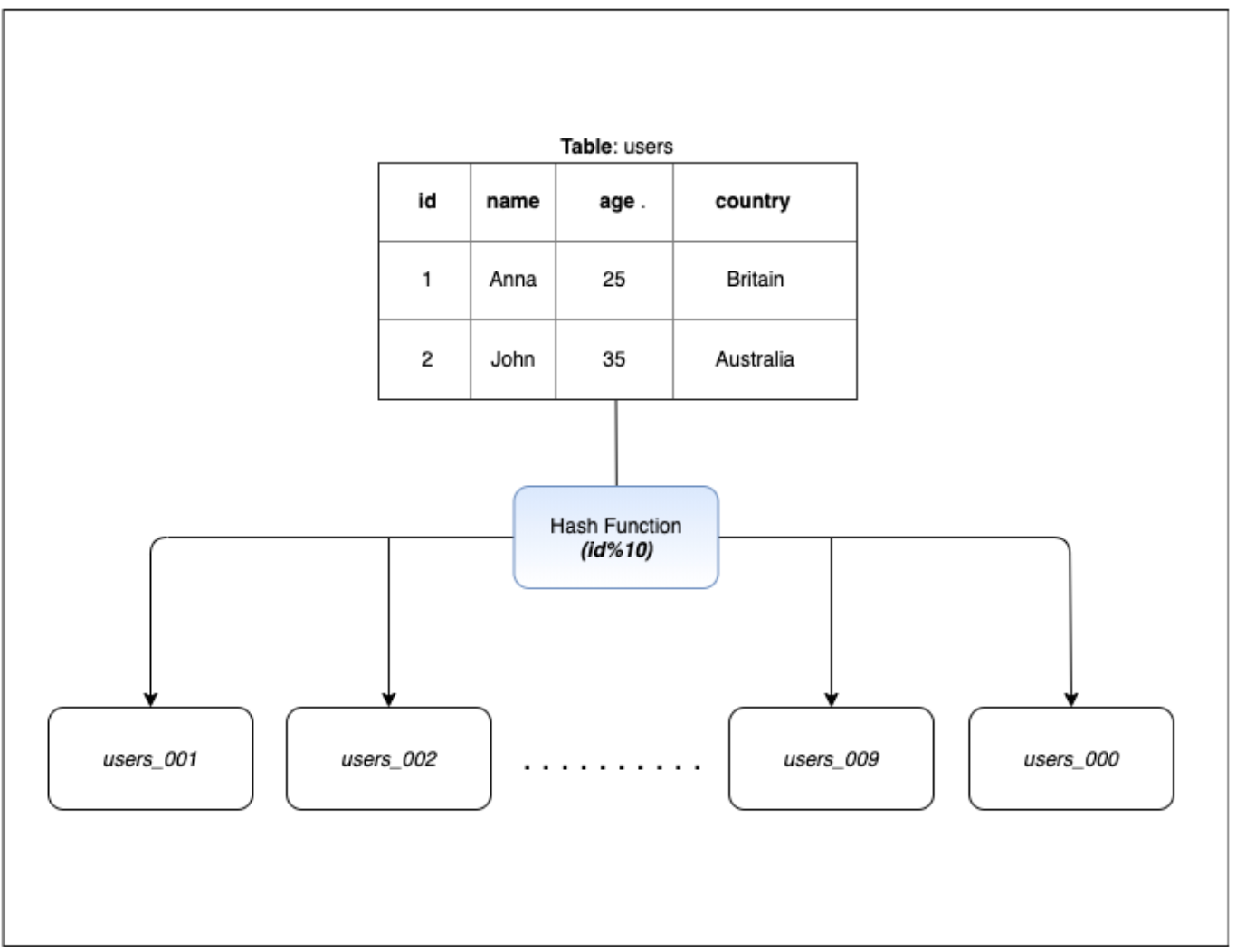
將特定 key (ex: id) 丟到 hash 中,得出目標要存取的資料庫。
(使用 docker 啟動多個 postgres 容器)
const app = require("express")();
const {Client} = require("pg");
const crypto = require("crypto");
const HashRing = require("hashring");
const hr = new HashRing();
hr.add("5433")
hr.add("5434")
const clients = {
"5433" : new Client ({
"host": "localhost",
"port": "5433",
"user": "postgres",
"password": "postgres",
"database": "postgres"
}),
"5434" : new Client ({
"host": "localhost",
"port": "5434",
"user": "postgres",
"password": "postgres",
"database": "postgres"
})
}
connect();
async function connect() {
await clients["5433"].connect();
await clients["5434"].connect();
}
app.get("/:urlId", async (req, res) => {
const urlId = req.params.urlId;
const server = hr.get(urlId)
const result = await clients[server].query("SELECT * FROM URL_TABLE WHERE URL_ID = $1", [urlId]);
if (result.rowCount > 0) {
res.send({
"urlId": urlId,
"url": result.rows[0],
"server": server
})
}
else
res.sendStatus(404)
})
app.post("/", async (req, res) => {
const url = req.query.url;
const hash = crypto.createHash("sha256").update(url).digest("base64")
const urlId = hash.substr(0, 5);
const server = hr.get(urlId)
await clients[server].query("INSERT INTO URL_TABLE (URL, URL_ID) VALUES ($1,$2)", [url, urlId]);
res.send({
"urlId": urlId,
"url": url,
"server": server
})
})
app.listen(8088, () => console.log("Listening 8088") )
hr.add("5433")
hr.add("5434")
使用 HashRing 套件,讓丟進 hash 的值最終都會得到 5433 或 5434,藉此達成 Hash Partitioning。
優點:
缺點:
https://medium.com/@oldmo860617/%E7%AD%86%E8%A8%98-database-sharding-22e22f0809c0
