在 C# 中,支持三类循环:
do...while 循环的语法格式:
do
{
code to loop
} while (<condition>);
循环体内的代码,是重复执行的代码,每次执行完代码都会检查一下条件,是否满足退出循环的条件,只要条件满足,即退出循环,执行循环后面的代码。
让我们来看一下 do...while 循环的示例:计算 1 到 100 之间所有整数的和,
using System;
namespace doWhile
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int sum = 0, i = 0;
do
{
sum = sum + i;
i = ++i;
} while (i <= 100);
Console.WriteLine($"The sum is {sum}.");
}
}
}
运行结果: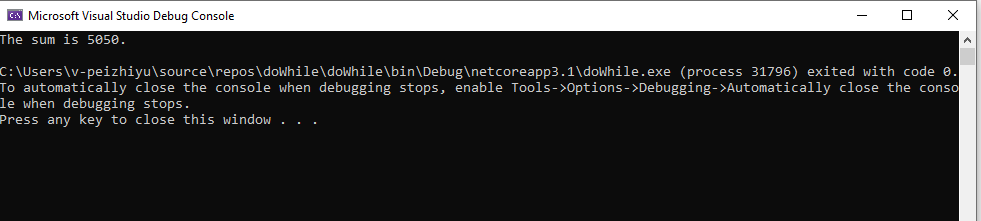
while 循环的语法格式:
while (<condition>)
{
code to loop
}
while 和 do...while 很类似,除了循环测试条件的位置,其他的几乎没有区别;
while 循环和 do...while 循环很类型,区别在于结束循环的条件,在循环体前面。
下面我们来看一下 while 循环的示例:100以内所有偶数的个数。
using System;
namespace whileTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int i = 1, j = 0;
while (i < 100)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
j = ++j;
}
i = ++i;
}
Console.WriteLine($"{j}");
}
}
}
运行结果: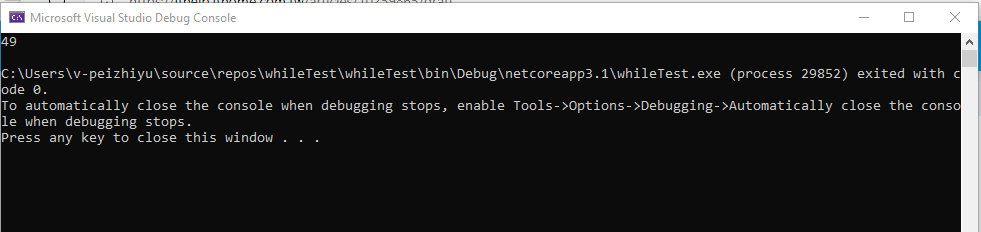
for 循环也被称为遍历循环,它可以遍历一个序列内的所有内容。由于它可以遍历一个序列的所有内容,我们可以使用 for 循环来遍历一组有序的数字,从而实现指定次数的循环。
for 循环的语法格式:
for ( <initialization>; <condition>; <operation>)
{
code to loop
}
下面看一个 for 循环的示例: 通过 for 循环的方式求 1 到 100 之间的整数和
using System;
namespace forTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int a = 1; a <= 100; a++)
{
sum = sum + a;
}
Console.WriteLine($"{sum}");
}
}
}
运行结果: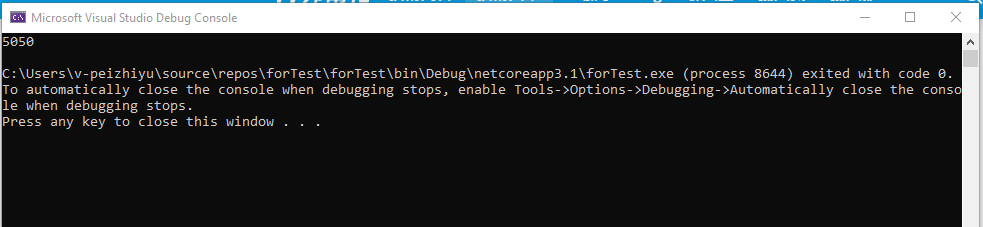
我们再来看看 for 的另外一种用法:
下面我们来看一个示例:找出一个数组中的所有偶数(关于数组,可以查看最后的补充说明。)
using System;
namespace forTest2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] num = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 }; // 声明一个数组
for (int i = 0; i < num.Length; i++)
{
if (num[i] % 2 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine(num[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
运算结果: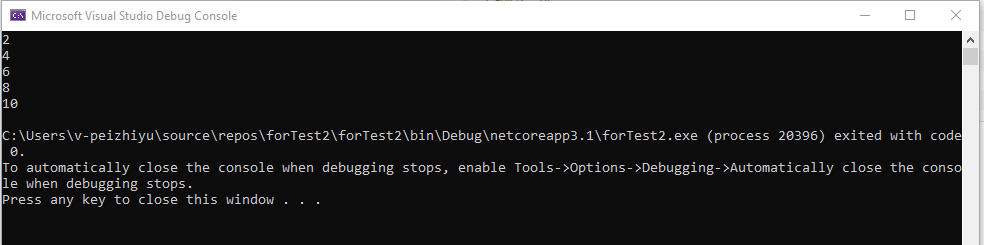
其实我们还可以通过 foreach 来实现这种遍历,并且更加简单:
using System;
namespace foreachTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] num = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
foreach (int i in num)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{i}");
}
}
}
}
}
运行结果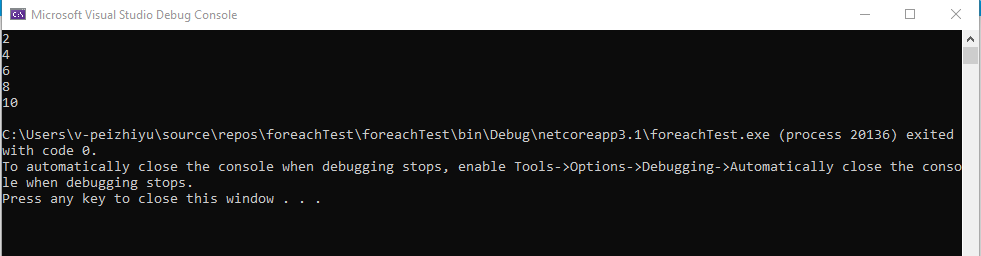
数组是一个存储相同类型元素的有序的集合。
数组的声明格式:
type[] arrayName;
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/csharp/programming-guide/arrays/
C# 中的注释:
// 单行注释
/*
多行
注释
/*
