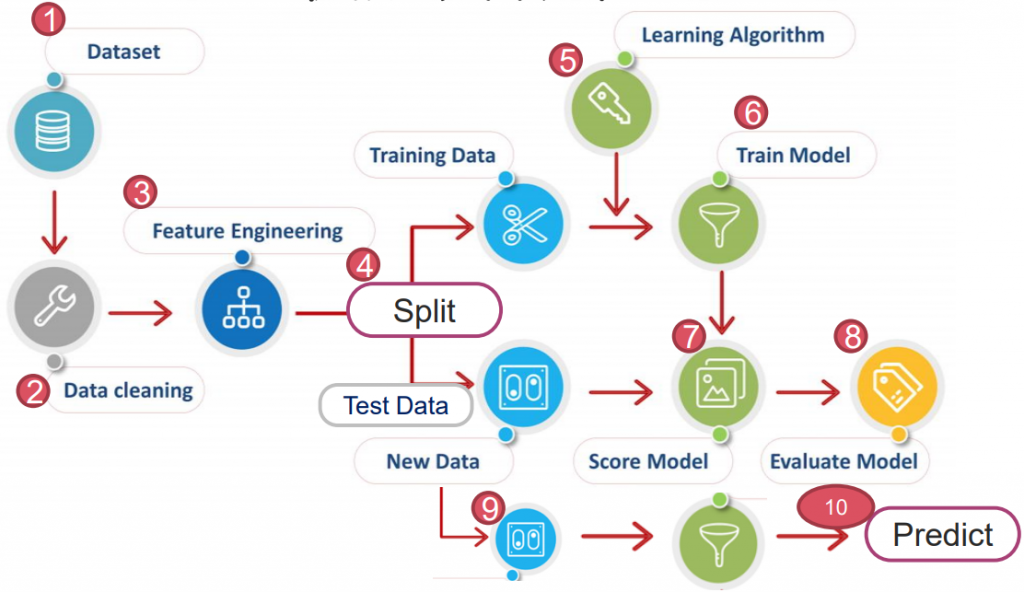
https://yourfreetemplates.com/free-machine-learning-diagram/
將「縮放」「降維」「演算法」等規劃進管線,方便一次性調校超參數,找出最佳效能。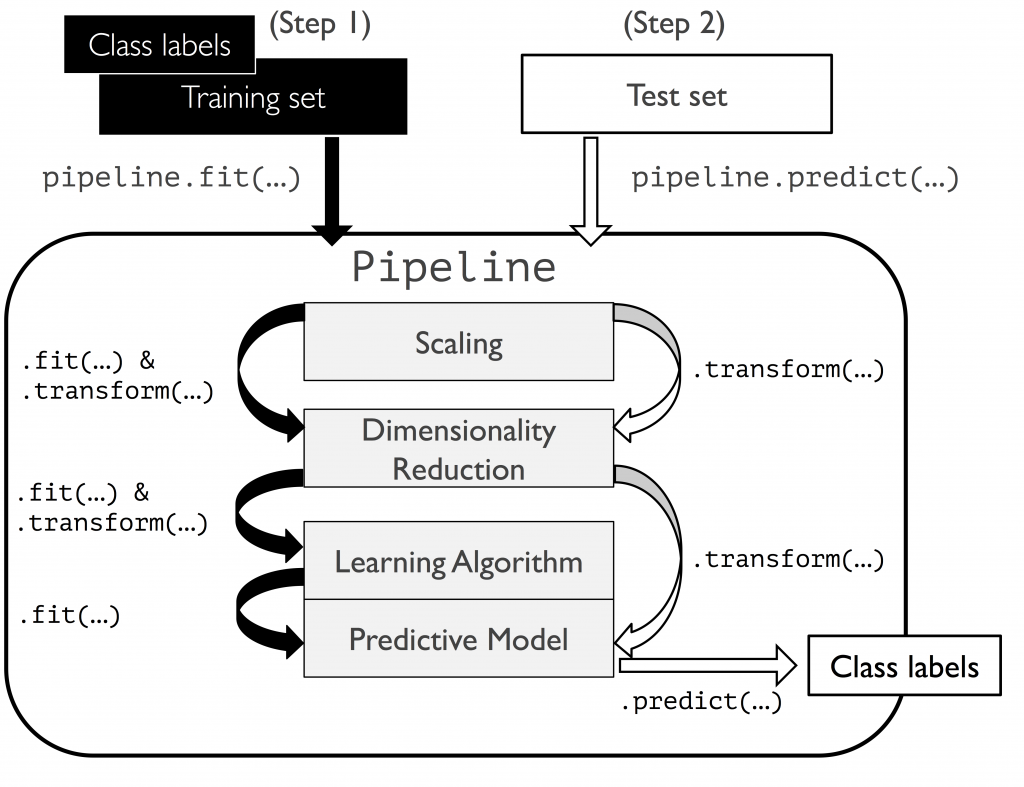
以乳癌為例:
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3)
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier as RFC
rfc_PL = make_pipeline(
StandardScaler(),
PCA(n_components=2),
RFC(n_estimators=100, criterion='gini', max_depth=3)
)
rfc_PL.fit(X_train, y_train)
rfc_PL.score(X_test, y_test)
>> 0.9239766081871345
我們使用 make_pipeline 中省去了轉換資料放入標準化、PCA 與演算法等時間。
GridSearchCV
對當前影響模型最大的參數調校直到最優,接著調校下個參數,至調整完畢。
優點:省時。
缺點:可能會調整模型為局部最優,而不是全局最優。
以鳶尾花為例:
from sklearn import svm, datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
ds = datasets.load_iris()
parameters = {'kernel':('linear', 'rbf', 'poly'), 'C':[0.1, 1, 10]}
svc = svm.SVC()
clf = GridSearchCV(svc, parameters, n_jobs=-1)
clf.fit(ds.data, ds.target)
# clf.best_params_
clf.best_estimator_
>> SVC(C=0.1, kernel='poly')
超參數
訓練資料再次切成 Training & Validation,且在訓練過程中不停用驗證資料交叉驗證。
優點:獨立資料,驗證與訓練資料互不相干,僅需運算一次故成本低。
缺點:若切割不當,易造成效能評估不穩定。(可用 K 折交叉驗證法解決)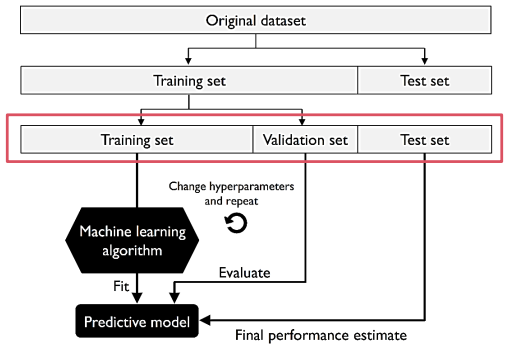
以阿拉伯數字為例:
import tensorflow as tf
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
X_train_n, x_test_n = X_train / 255.0, X_test / 255.0
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
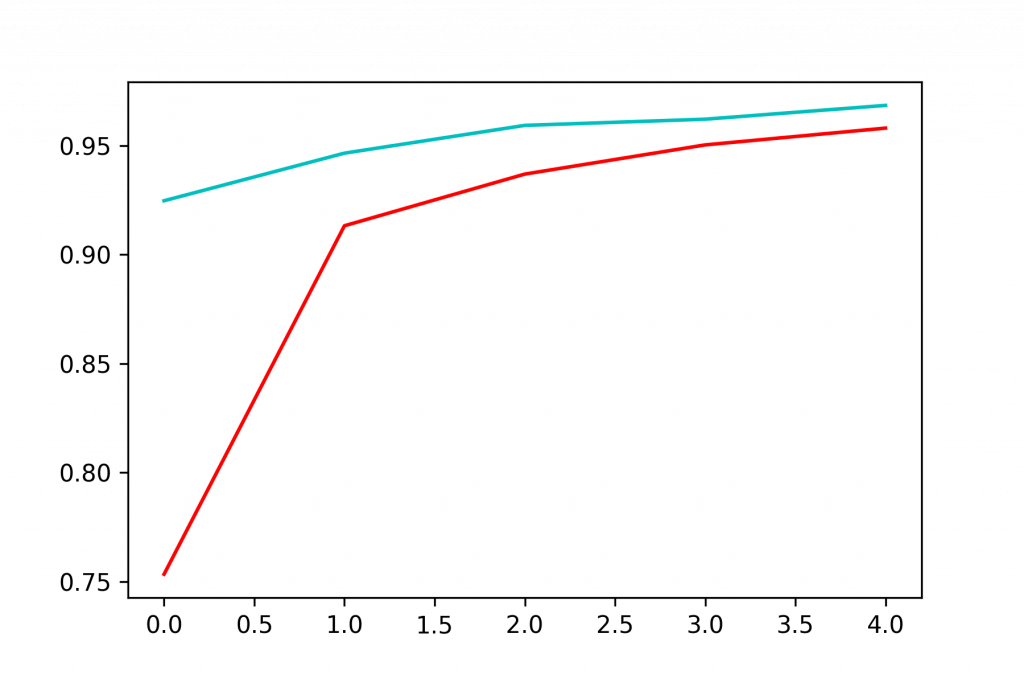
his = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=5, validation_split=0.2)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(his.history['accuracy'], 'r', label='train')
plt.plot(his.history['val_accuracy'], 'c', label='validate')
plt.show()
將資料切割成 K 份,以 K-1 做訓練,1 做驗證資料。
重複演算 K 次以得到 K 個模型與效能,最終把效能取平均值,作為模型的效能評估。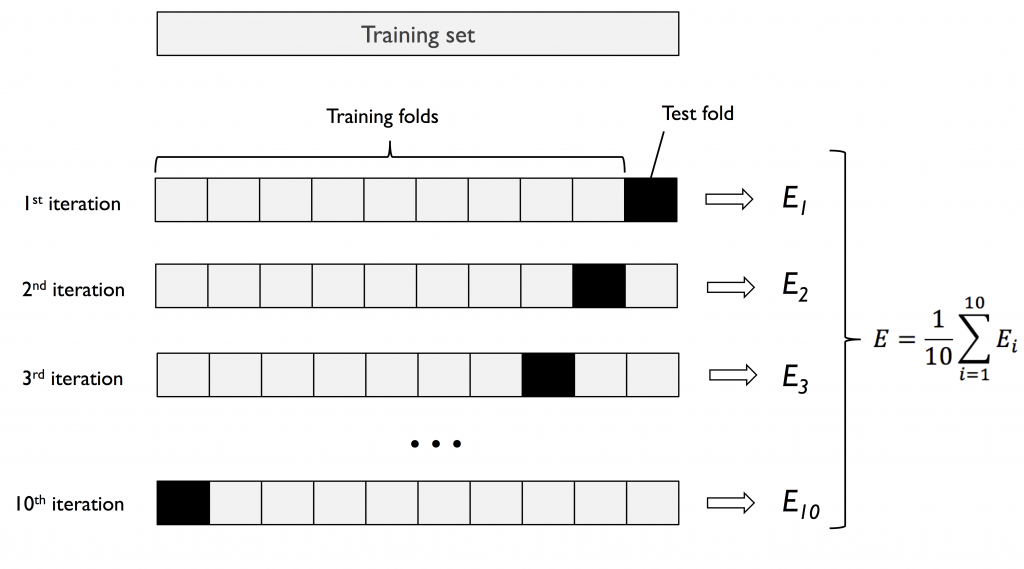
優點:K 值大,模型做效能評估時「偏差」小。可針對差異大類型資料做演算。
缺點:因重複數據多,運算時間長。且模型間非常類似可能造成「變異」大。
原始數據小:K 值大,以獲得較準的效能評估。
原始數據大:K 值小(如 k=5),仍能獲得不錯的效能評估,最小化變異。
以乳癌為例:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/'
'machine-learning-databases'
'/breast-cancer-wisconsin/wdbc.data', header=None)
X = df.loc[:, 2:].values
y = df.loc[:, 1].values
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
le = LabelEncoder()
le.transform(['M', 'B'])
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.20,
stratify=y,
random_state=1
)
製作管線:
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
lr_PL = make_pipeline(
StandardScaler(),
PCA(n_components=2),
LogisticRegression(random_state=1)
)
比起一般 K 折,分層 K 折可以將原樣本中數據依照比例拆分。
例如:台北市長投票人中,有 60% 是年長者 40% 是年輕人。
StratifiedKFold 會依 6:4 比例,盡量使每個分拆資料中皆含有年長者 & 年輕人。
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
kf = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=10).split(X_train, y_train) # , random_state=1
score_list = []
for k, (train, test) in enumerate(kf):
# 把 train/test 形狀印出
print(train.shape, test.shape)
# 切割資料丟入演算法
lr_PL.fit(X_train[train], y_train[train])
# 計算每一折的分數
score = lr_PL.score(X_train[test], y_train[test])
score_list.append(score)
print(f'Fold: {k+1:2d}, Class dist.: {np.bincount(y_train[train])}, Acc: {score:.3f}')
print(f'\nCV accuracy: {np.mean(score_list):.3f} +/- {np.std(score_list):.3f}')

超參數:
n_splits: 拆成幾份
顧名思義,就是簡單版的 K 折
# cross_val_score 簡化 K 折
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
# 這邊也可以把超參數 'cv' 的位置,用原本的 K 折取代。
scores = cross_val_score(lr_PL, X, y, cv=10)
scores
>> array([0.96491228, 0.89473684, 0.96491228, 0.94736842, 0.94736842,
0.94736842, 0.92982456, 0.98245614, 0.98245614, 0.98214286])
print(f'CV accuracy: {np.mean(scores):.3f} +/- {np.std(scores):.3f}')
>> CV accuracy: 0.954 +/- 0.026
使用內建 wine,試著用 pipeline、Cross Validation,寫個迴圈以操作演示過的演算法。
