Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
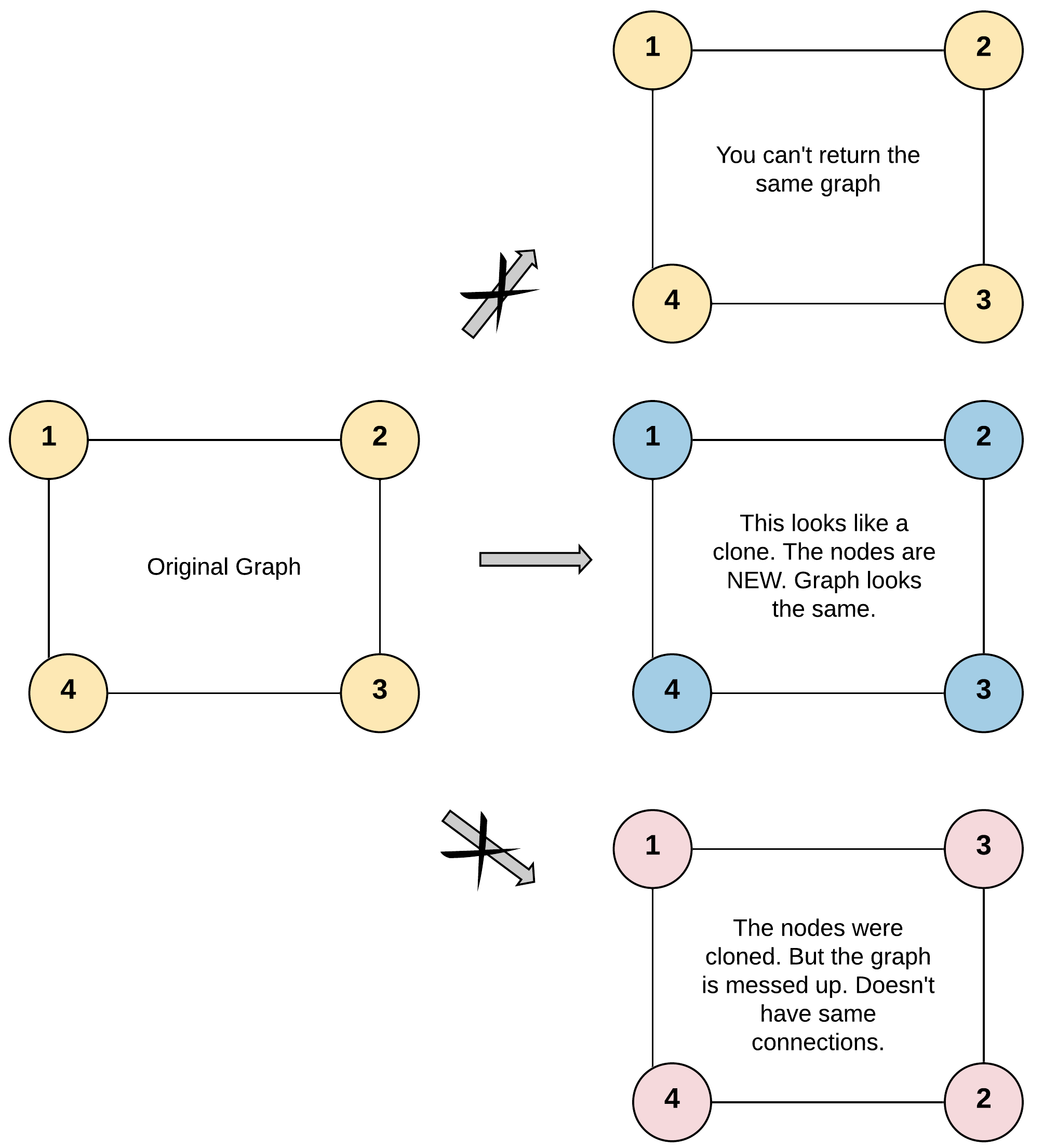
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity, each node's value is the same as the node's index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph.
1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
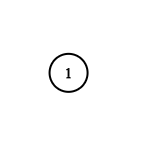
Input: adjList = [[]]
Output: [[]]
Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = []
Output: []
Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Constraints:
[0, 100].1 <= Node.val <= 100
Node.val is unique for each node.一個資料結構 Node 裏面紀錄了該點的值 Val 還有透過陣列 Neighbor 來紀錄相連的 Node 參造 如下
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
透過這種結構可以紀錄一個連結的 Graph
題目給定了一個 Graph 的起始 Node 參造
要求寫一個演算法來把這個 Graph 結構複製
直覺的作法是從最開始的點透過 BFS 逐個複製
特別要注意的是因為是無向連結,所以必須標注已經走過的結點,避免重複拜訪已走過的 neighbor
如下圖

第2種作法是透過 DFS
每次先建立當下的 copyNode 然後把新舊對應的透過 hashmap 紀錄下來
然後當作完一輪後原本的 reference 就會自動建立好了

package sol
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Neighbors []*Node
* }
*/
func cloneGraph(node *Node) *Node {
if node == nil {
return nil
}
visit := make(map[int]*Node)
created := make(map[int]*Node)
var result *Node
var bfs = func(node *Node) {
queue := []*Node{node}
for len(queue) != 0 {
top := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
// mark as visited
visit[top.Val] = top
// create top if no existed
var cur *Node
if found, ok := created[top.Val]; ok {
cur = found
} else {
cur = &Node{Val: top.Val}
created[cur.Val] = cur
}
// assign to result if cur.Val = 1
if cur.Val == 1 {
result = cur
}
// copy Neighbors if exists
nLen := len(top.Neighbors)
if nLen != 0 {
cur.Neighbors = make([]*Node, nLen)
for idx := range top.Neighbors {
n := top.Neighbors[idx]
var newNode *Node
if find, ok := created[n.Val]; ok {
newNode = find
} else {
newNode = &Node{Val: n.Val}
created[n.Val] = newNode
}
cur.Neighbors[idx] = newNode
// check if not visited push to queue
if _, ok := visit[n.Val]; !ok {
queue = append(queue, n)
}
}
}
}
}
bfs(node)
return result
}
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Neighbors []*Node
* }
*/
func cloneGraphDFS(node *Node) *Node {
if node == nil {
return nil
}
oldToNew := make(map[*Node]*Node)
var dfs func(node *Node) *Node
dfs = func(node *Node) *Node {
if found, ok := oldToNew[node]; ok {
return found
}
newNode := &Node{Val: node.Val}
oldToNew[node] = newNode
for _, nei := range node.Neighbors {
newNode.Neighbors = append(newNode.Neighbors, dfs(nei))
}
return newNode
}
return dfs(node)
}
