HTML先設定出3個Box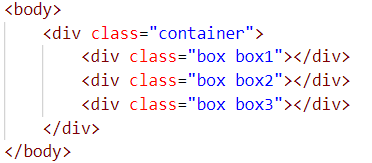
Box的顏色分別為:
box1
box2
box3
div.container{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: rgb(244, 251, 230);
}
.box{
width: 125px;
height: 125px;
}
.box1{
background-color: aquamarine;
}
.box2{
background-color: rgb(255, 240, 127);
}
.box3{
background-color: rgb(127, 200, 255);
}
不會被特別定位,元素會依據文檔的正常流程來定位
在這裡top、right、bottom、left、z-index屬性是無效的
元素會依據文檔的正常流程來定位,沒設定屬性跟Static是相同的
這邊可以設定Box擺放的相對位置
所以top、right、bottom、left、z-index屬性是有效的
範例:
將box2定位設為 relative ,設定相對移動位置left: 250px; top: 125px;
.box2{
background-color: rgb(255, 240, 127);
position: relative;
left: 250px;
top: 125px;
}
實作結果: box2相對於原本的位置,下移125px,右移250px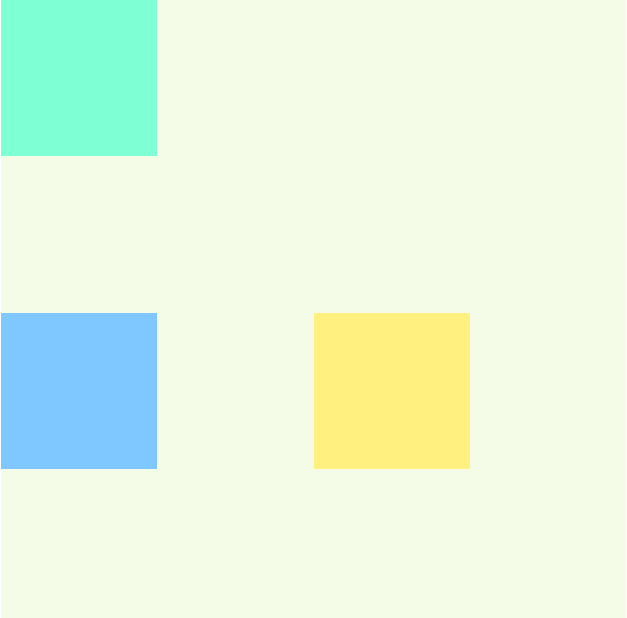
z-index屬性應用
.box1{
background-color: aquamarine;
position: relative;
z-index: 1;
}
.box2{
background-color: rgb(255, 240, 127);
position: relative;
left: 50px;
bottom: 75px;
z-index: 3;
}
.box3{
background-color: rgb(127, 200, 255);
position: relative;
left: 100px;
bottom: 150px;
z-index: 2;
}
實作結果:
重疊時數字越大將會覆蓋數字越小的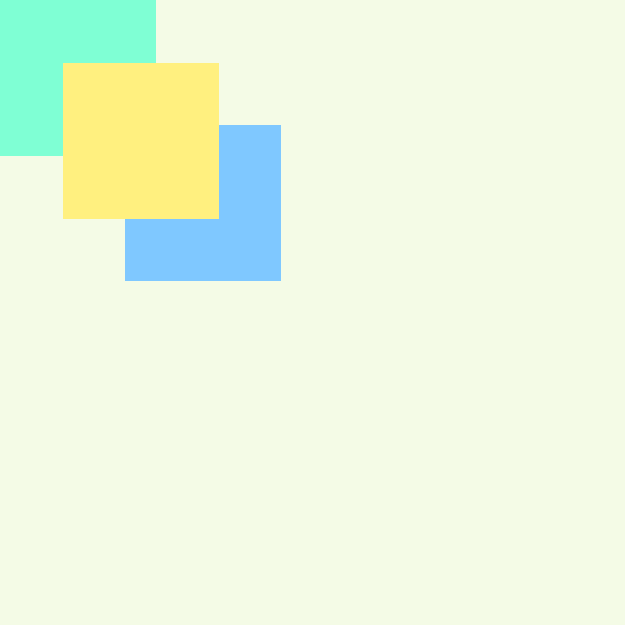
absolute的定位是所處上層容器的相對位置
如果上層容器沒有可以被定位的元素的話,那麼這個元素的定位會直接參考 body 元素的絕對位置
範例:
將box2定位設為 absolute ,設定left: 0px; bottom: 0px;
.box2{
background-color: rgb(255, 240, 127);
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
bottom: 0px;
}
實作結果:
box2沒有父元素,因此定位直接參考 body 元素的絕對位置
如果我們將上層容器(也就是div.container)定位設為relative
實作結果:
會發現它就盯喂在上層容器中的left: 0px; bottom: 0px;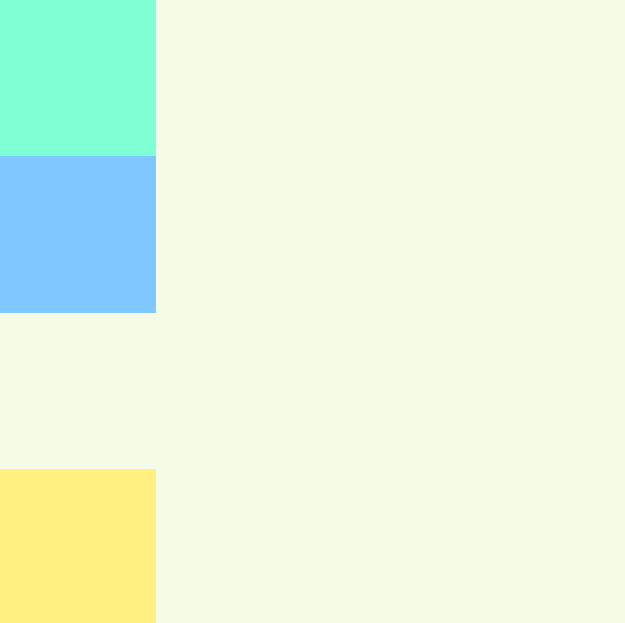
fixed的元素會相對於瀏覽器視窗來定位,如果頁面捲動,它還是會固定在同樣的位置
不會保留它原本在頁面應有的空間,所以不會跟其他元素的配置互相干擾
範例:
將box2定位設為 fixed ,設定left: 100px; top: 100px;
.box2{
background-color: rgb(255, 240, 127);
position: fixed;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
}
實作結果: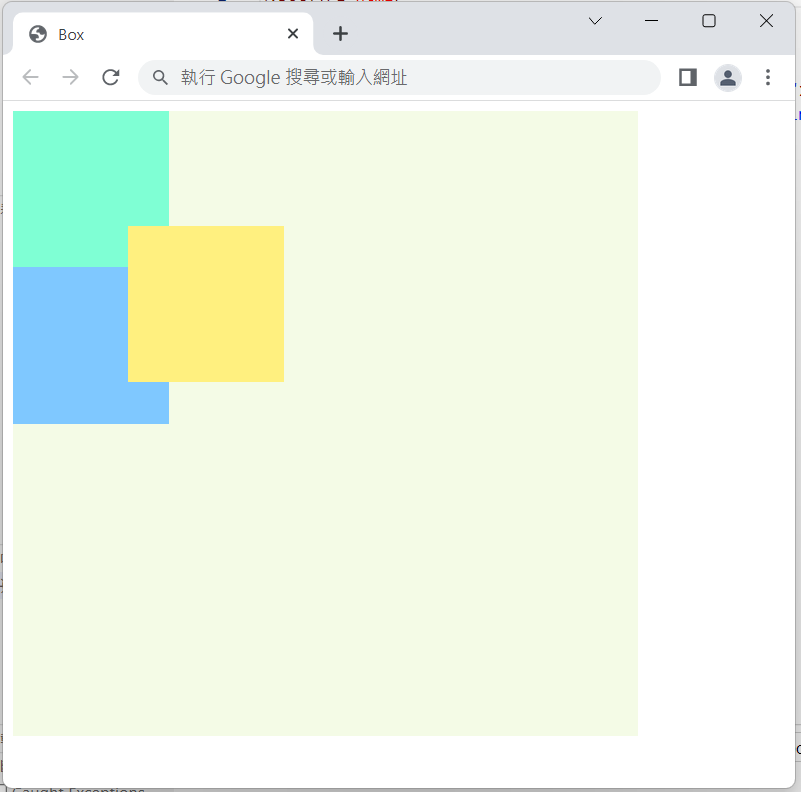
當畫面捲動到超過畫面時就會讓元素固定在容器之中的位置
範例可看position: sticky
讓我們來看看實際的網頁版面配置幫助我們更加理解 position 的用法~
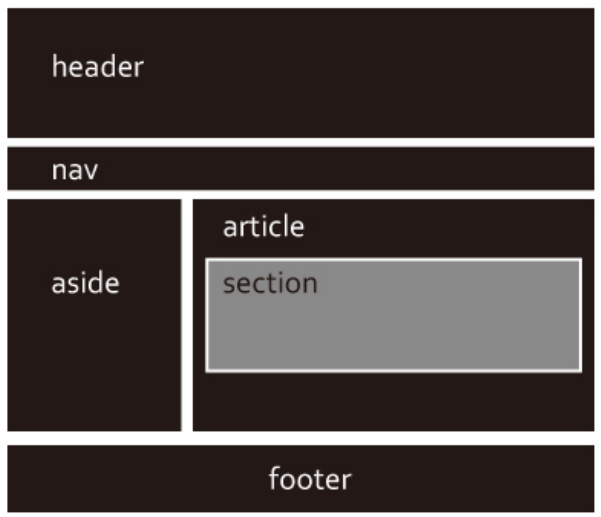
學會定位了!明天我們就來讓這些箱子動起來吧~
