簡單介紹一下什麼是 thread (執行緒)
process 一定會有一個 thread,所以也可以有很多個 thread
thread 自己的記憶體空間 stack 只有自己可以使用無法與別的 thread 共用process 底下的 heap 區塊可以使用 std::thread::spawn 來建立一個 thread
use std::thread;
fn main() {
let thread = thread::spawn(move || {
// do something
});
}
假設一個情境,我們需要計算出所有出所有出現過字母的次數
const CASE: [&str; 8] = [
"freude schöner götterfunken",
"tochter aus elysium,",
"wir betreten feuertrunken,",
"himmlische, dein heiligtum!",
"deine zauber binden wieder",
"was die mode streng geteilt;",
"alle menschen werden brüder,",
"wo dein sanfter flügel weilt.",
];
可以使用最簡單的 for 迴圈來達成
fn frequency(input: &[&str]) -> HashMap<char, usize> {
let mut map = HashMap::new();
for line in input {
for c in line.chars().filter(|c| c.is_alphabetic()) {
*map.entry(c.to_ascii_lowercase()).or_default() += 1;
}
}
map
}
這邊的結果會是下圖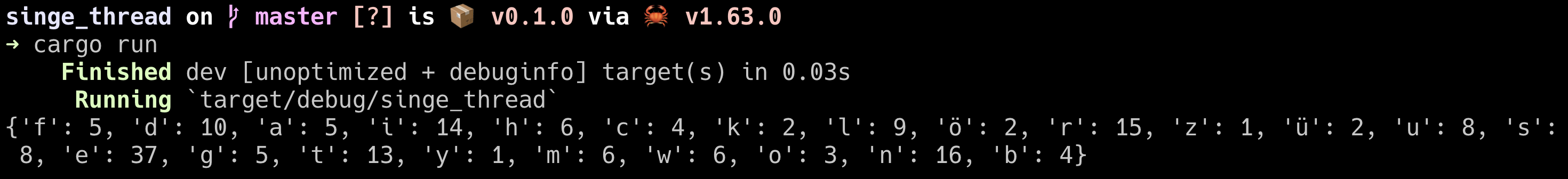
使用multithreading來實作
pub fn frequency(input: &[&str], worker_count: usize) -> HashMap<char, usize> {
let mut result: HashMap<char, usize> = HashMap::new();
let chunks = input.chunks((input.len() / worker_count).max(1)); // 使用chunk拆分
let mut handles = Vec::new();
for chunk in chunks {
let string = chunk.join(""); // 轉成string
let handle = thread::spawn(move || { // 一個chunk 一個thread
let mut map: HashMap<char, usize> = HashMap::new();
for c in string.chars().filter(|c| c.is_alphabetic()) {
*map.entry(c.to_ascii_lowercase()).or_default() += 1;
}
map
});
handles.push(handle);
}
for handle in handles {
let map = handle.join().unwrap();
for (key, value) in map {
*result.entry(key).or_default() += value;
}
}
result
}
這邊先介紹筆者用的壓測工具, criterion,這是一個非官方提供的工具,那不用Rust自己提供工具的原因是因為必需要使用Nightly版本以外顯示的資訊也沒有比這個criterion還詳細。
Single thread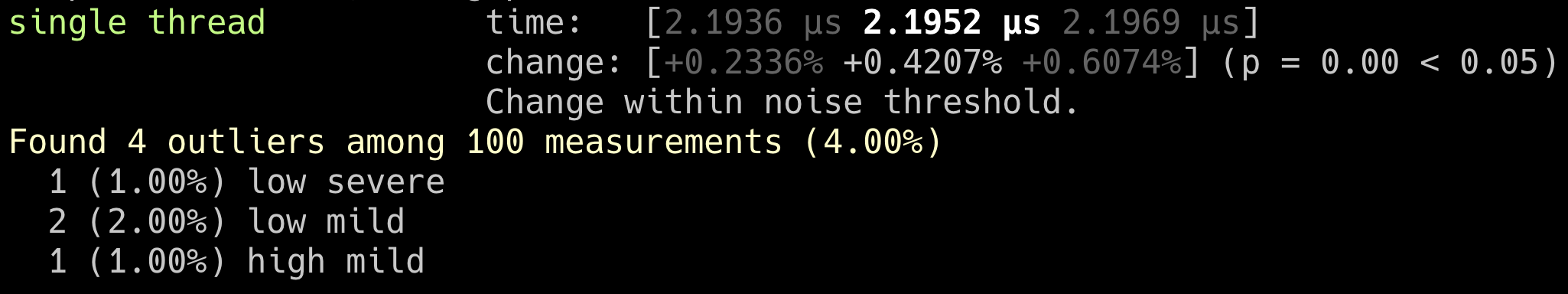
multi thread (2 thread)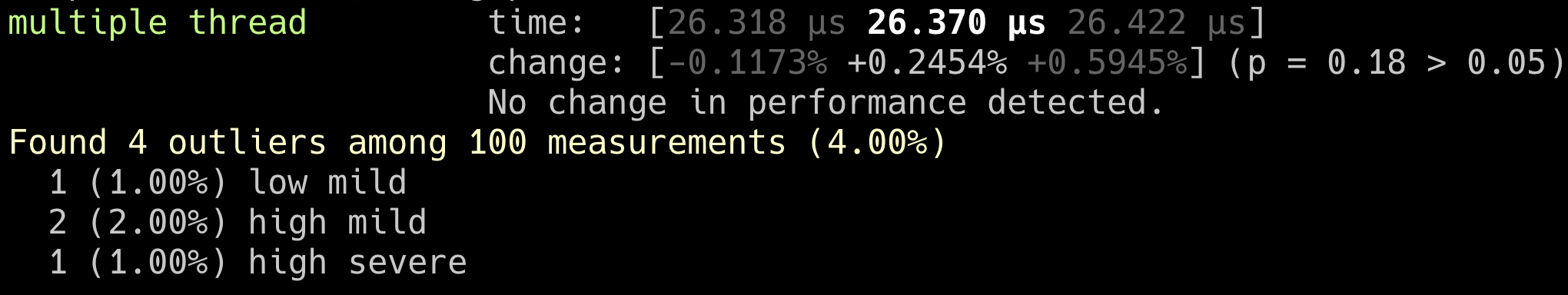
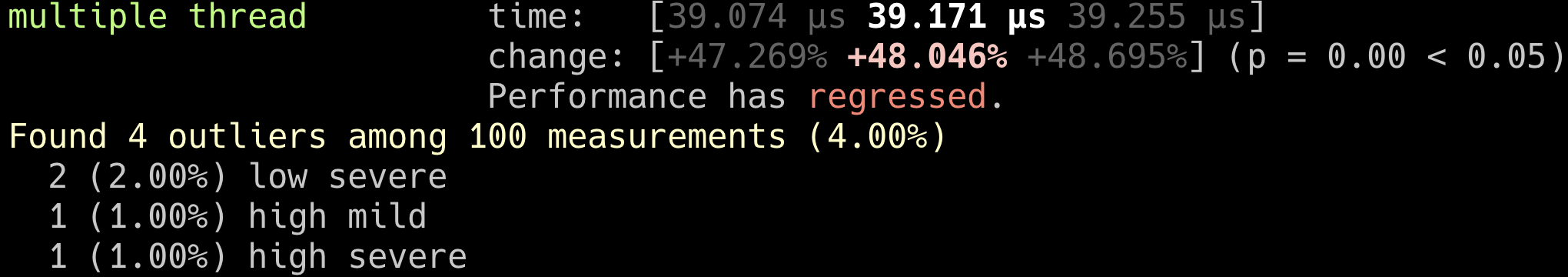
這邊可以發現其實使用兩個thread的速度是比單個的還慢很多的,原因是因為multithreading比較適合跑在需要大量I/O的情境底下。舉個實際例子,大量發送EDM信件就很適合。
建立多個thread的缺點
如果把thread數量往上加會越來越慢
multi thread (4 thread)