昨天我們聊到 Polynomial Regression 是一種希望透過數據使用多項式預測函數來建模,並且未知的模型參數也是通過數據來估計的回歸模型。
今天我們來一起實做吧
在這個部分,我們可以先使用 scikit-learn 的 library 來先試試看
如果尚未安裝,使用 pip install scikit-learn 來安裝 package
首先們先建立 3 團隨機產生數值的 cluster
# Number of data points in each cluster
num_points = 500
# Generate data for three clusters
cluster1 = np.random.normal(loc=[2, 2], scale=[0.5, 0.5], size=(num_points, 2))
cluster2 = np.random.normal(loc=[6, 6], scale=[0.7, 0.7], size=(num_points, 2))
cluster3 = np.random.normal(loc=[4, 8], scale=[0.4, 0.6], size=(num_points, 2))
# Combine the clusters
x = np.concatenate((cluster1[:, 0], cluster2[:, 0], cluster3[:, 0]))
y = np.concatenate((cluster1[:, 1], cluster2[:, 1], cluster3[:, 1]))
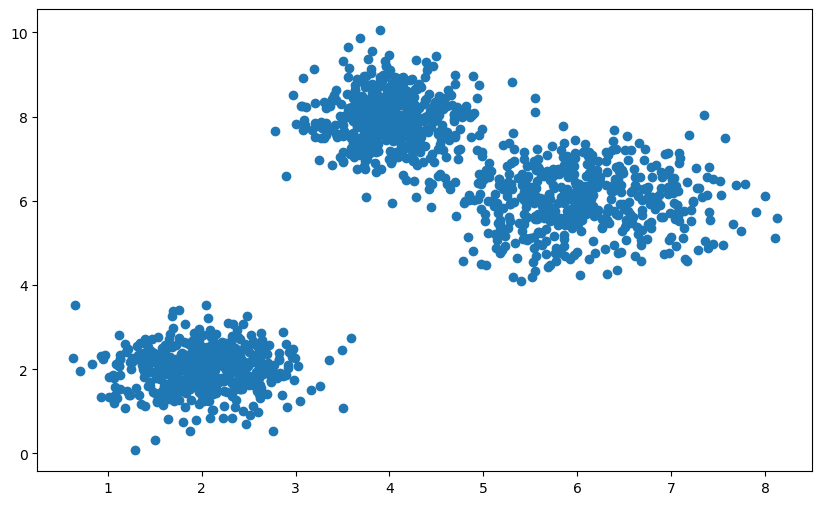
接著定義 polynomial features 的維度
degree = 1
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree, include_bias=True)
poly_features = poly.fit_transform(x.reshape(-1, 1)) # x.reshape(-1, 1) is a 2D array with one column
透過建立 LinearRegression 來預測有哪一個參數可以來代表這些 cluster 的分佈
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
poly_reg_model = LinearRegression()
poly_reg_model.fit(poly_features, y)
y_predicted = poly_reg_model.predict(poly_features)
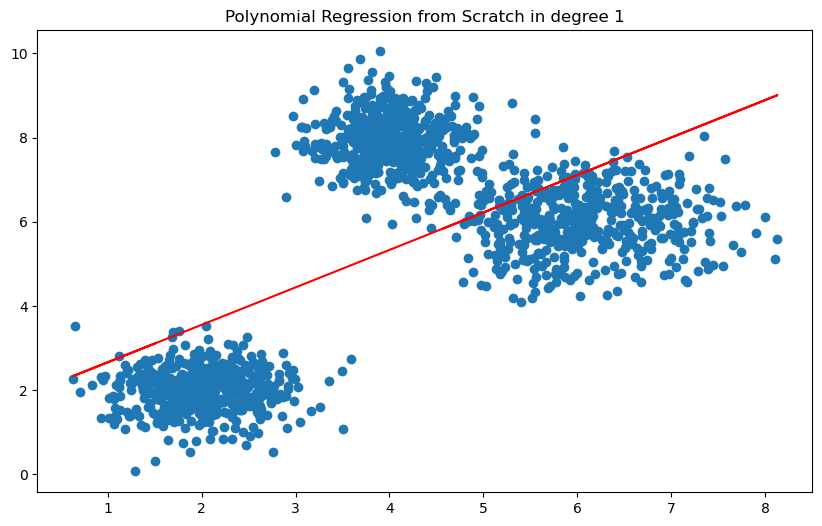
如昨天提及,我們可以透過 MSE 和 MAE 的 loss function 來判斷模型好壞
# calculate loss, MSE, MAE
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
print("Accuracy: ", poly_reg_model.score(poly_features, y))
print("MSE: ", mean_squared_error(y, y_predicted))
print("MAE: ", mean_absolute_error(y, y_predicted))
Accuracy: 0.3770748813271505
MSE: 4.092465875195728
MAE: 1.791307625621191
在 From Scratch 的部分僅使用 numpy
這裡 code 定義 CustomFeatureTransformer 用於進行特徵轉換
class CustomFeatureTransformer:
def __init__(self, degree, is_bias=True):
self.is_bias = is_bias
self.degree = degree
def transform(self, x = None):
if x is None:
raise ValueError('x is None')
if self.is_bias:
x = np.c_[np.ones(x.shape[0]), x]
for i in range(2, self.degree + 1):
x = np.c_[x, x[:, 1] ** i]
return x
def fit_transform(self, x):
return self.transform(x)
__init__(self, degree, is_bias)degree(次數):這是一個整數,表示要對特徵進行多少次方轉換。is_bias(偏差):這是一個布林值,表示是否要添加偏差項(常數項)到特徵中。transform(self, x)這個用於對輸入的特徵進行轉換,它有一個參數x,表示輸入的特徵數據。這個方法執行以下步驟:
x是否為None,如果是,則拋出ValueError異常is_bias為True,則在特徵x的左側添加一列全為1的常數項,以添加偏差項degree指定的次數x
這裡 code 定義 CustomLinearRegression 的自定義線性回歸類別,用於執行簡單的線性回歸模型
class CustomLinearRegression:
def __init__(self):
self.w = None
def fit(self, x, y):
self.w = np.linalg.inv(x.T.dot(x)).dot(x.T).dot(y)
def predict(self, x):
return x.dot(self.w)
def score(self, x, y):
y_pred = self.predict(x)
return 1 - ((y - y_pred)**2).sum() / ((y - y.mean())**2).sum()
fit(self, x, y)這是訓練模型的方法
這裡使用兩個參數 x 和 y,分別代表輸入特徵和目標變數
x.T
x.T 與 x 的矩陣乘積 x.T.dot(x)
np.linalg.inv(x.T.dot(x))
(x.T.dot(x)).dot(x.T),然後再與 y 相乘,得到最終的權重 self.w
predict(self, x)這是用於進行預測的方法
這裡使用輸入特徵 x,並使用模型的權重 self.w 對輸入進行線性組合,返回預測值
class MAE:
def __call__(self, y, y_pred):
return np.mean(np.abs(y - y_pred))
def gradient(self, y, y_pred):
return np.sign(y - y_pred)
class MSE:
def __call__(self, y, y_pred):
return np.mean((y - y_pred)**2)
def gradient(self, y, y_pred):
return 2 * (y_pred - y)
在判斷 From scratch 是否實做成功,可以用 Evaluation 來觀察兩者輸出是否接近或相同
詳細 Notebook 可以參考 Github
明天要進入真實實戰部份,會透過 Kaggle competition 來演練
![]()
