在7.11版本後ES推出了runtime這個新功能,在以往都是
Schema on Write:寫入時就已經定義好資料的數據結構
現在新增Runtime後,導入了
Schema on Read:在讀取時才決定要怎麼解析資料
Runtime field也就是在執行query的當下,才對資料進行解析
優點:
缺點:
mapping設定:
例如原本的欄位只有存身分證字號,但是我們想透過runtime來整合出哪幾個縣市的人有多少
PUT /test-runtime
{
"mappings": {
"runtime": {
"city": {
"type": "keyword",
"script": {
"source": "emit(doc['TW-id'].value.substring(0, 1))"
}
}
},
"properties": {
"TW-id": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
接著輸入我們的資料,使用bulk API
雖然之前沒提過,但是我覺得都能到這天的可以直接看官方文檔了,我就不額外補充了
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/8.9/docs-bulk.html
POST /_bulk
{"index": {"_index": "test-runtime", "_id": 1}}
{"TW-id": "R123456789"}
{"index": {"_index": "test-runtime", "_id": 2}}
{"TW-id": "B123456789"}
{"index": {"_index": "test-runtime", "_id": 3}}
{"TW-id": "A123456789"}
{"index": {"_index": "test-runtime", "_id": 4}}
{"TW-id": "A123456769"}
{"index": {"_index": "test-runtime", "_id": 5}}
{"TW-id": "A123456719"}
接著我們直接看結果:
GET /test-runtime/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}

結果中沒有我們的runtime field
還記得我們一開始說的嗎~ runtime field出來的欄位不索引,那_source當然沒東西
我們使用fields API
GET /test-runtime/_search
{
"fields": ["*"],
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
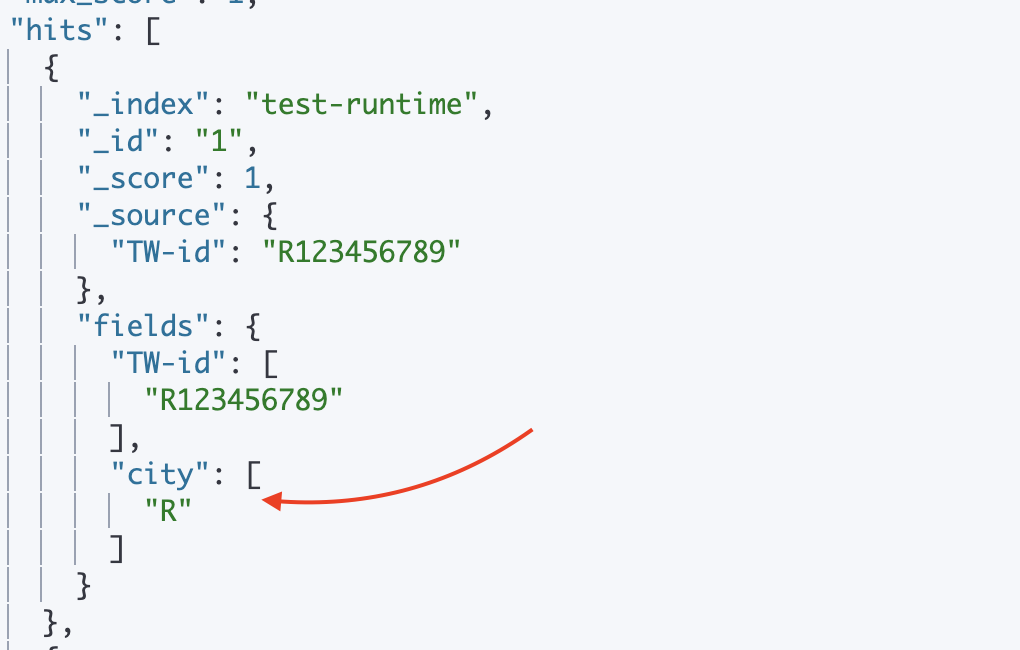
就能找到資料了
那如果要刪除也很簡單:
PUT /test-runtime/_mapping
{
"runtime": {
"city": null
}
}
另外在前面的Dynamic也提過可以設定成runtime
此時產出的欄位type有稍微不同,所以要注意:
| 偵測類型 | dynamic: true | dynamic: runtime |
|---|---|---|
| float | float | double |
| json | object | 不會產生 |
| string(但內容都是數字) | float或long | double或long |
接下來我們說一下search的runtime,這邊因為還沒提過search
所以不會用太難的語法,並且因為runtime的核心就是在執行query時才執行
所以避不開search,而search那邊內容也很多,再拉一個runtime比較難統整
畢竟他還是跟我們前一天的內容還是有很高關聯性的
此時我們先把剛剛的索引刪掉,然後創一個新的
PUT /test-runtime
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"TW-id": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
並且再次輸入資料(跟上面一模一樣)
接著輸入查詢語與聚合
GET /test-runtime/_search
{
"runtime_mappings": {
"city": {
"type": "keyword",
"script": {
"source": "emit(doc['TW-id'].value.substring(0, 1))"
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"city": {
"terms": {
"field": "city"
}
}
}
}

我們就能看到,針對這個runtime欄位所做的聚合
而這也是使用runtime field相比於script的優勢,能對欄位再作進一步的處理
接著來說明與runtime同時推出的Async search
Async search:
async API可以用非同步的方式送出搜尋請求,並且可以監控它的進程並在部分結果能夠取得時獲取
使用方式如下,並且請求體跟一般_search沒什麼差別
POST /index_name/_async_search
送出請求後會返回以下範例:
{
"id" : "FmRldE8zREVEUzA2ZVpUeGs2ejJFUFEaMkZ5QTVrSTZSaVN3WlNFVmtlWHJsdzoxMDc=",
"is_partial" : true,
"is_running" : true,
"start_time_in_millis" : 1583945890986,
"expiration_time_in_millis" : 1584377890986,
"response" : {
"took" : 1122,
"timed_out" : false,
"num_reduce_phases" : 0,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 562,
"successful" : 3,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 157483,
"relation" : "gte"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}
}
// 獲取
GET /_async_search/id
// 刪除
DELETE /_async_search/id
可以設置的參數:
今天介紹了runtime field,這個可以在開發初期多加利用的好工具
並且如果搜尋量大,可以使用async API在背景執行,不影響其他排程使用
但是如果開發方向已經確定了,還是制定好mapping或是reindex等操作才是最佳解
參考資料
runtime field:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/runtime.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/runtime-mapping-fields.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/runtime-search-request.html
async API:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/async-search.html#async-search
