在設計稍為複雜的對話系統時,常會遇到資料來源需經過特定處理元件的轉換或預先處理。LangChain 框架的核心元件 - Chain(也可稱為執行鏈或動作鏈)正是為了簡化這類作業需求而生。
本文將以「例句推薦」作為案例,來詳細介紹 LangChain 的 Chain 與 LLMChain 的基礎概念。在進入這兩個主題之前,我們先探討例句推薦的整體運作流程。
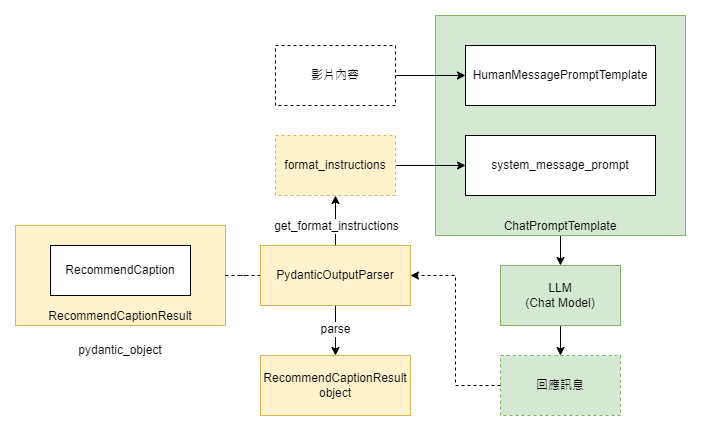
例句推薦處理單元在收到影片內容後,會透過語言模型隨機選出三個推薦的教學例句。除此之外,我們也利用 PydanticOutputParser 來生成結構化指令的公司訊息,並且在得到語言模型的回應訊息後,再將訊息透過 PydanticOutputParser 來做結構化資料的轉換。
以下是相關程式碼,首先我們的 pydantic_object 的結構定義:
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import List
# Define your desired data structure.
class RecommendCaption(BaseModel):
line_no: int = Field(description="教學例句的原始行數")
text: str = Field(description="教學例句")
# langchain pydantic parser 目前不支援 list of pydantic model 的輸出,所以要再包一層 List Object
class RecommendCaptionResult(BaseModel):
captions: List[RecommendCaption] = Field(description="所有的教學例句")
當我們完成解析目標的結構定義後,就能將其指派給 PydanticOutputParser 類別,並進行物件的創建。對於那些對 parser 生成的指令細節感到好奇的讀者,您也可以自行列印相關程式碼進行深入研究:
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
# 建立 PydanticOutputParser 案例
output_parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=RecommendCaptionResult)
print(output_parser.get_format_instructions())
在我們的上一篇文章中,我們已經介紹過 LangChain OutputParser 的一個核心設計理念:一旦你成功定義了 Parser 物件,就可以使用 get_format_instructions 方法來獲取格式化訊息的相關指令。另外,在收到語言模型的回應後,你也可以使用 parse 方法來進行資料解析。接下來,我們將來示範如何透過這一設計來取得推薦例句,以及如何轉化這些信息為結構化的資料:
from langchain.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
PromptTemplate,
SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
)
template = """你是一個專業的外語老師,你有一個特殊專長,能夠在影片的內容找出值得教學的內容,你也很擅長做課程的規劃。
接下來我會提供給你影片內容,請你在影片內容裏面,隨機且使用均勻分佈的原則挑選出 3 句左右值得教學的句子(教學例句),
同時也請記下你挑選的教學例句的原始內容以及行數。
{format_instructions}
"""
system_message_prompt = SystemMessagePromptTemplate(
prompt=PromptTemplate(
template = template,
input_variables=[],
partial_variables={"format_instructions": output_parser.get_format_instructions()}
)
)
human_template = "影片內容:\n{text}"
human_message_prompt = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_template)
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([system_message_prompt, human_message_prompt])
response = chat_model(chat_prompt.format_messages(text=line_data))
print(response)
--- 下方則是實際的輸出結果 ---
>> content='{\n "captions": [\n {\n "line_no": 2,\n "text": "no matter where in the world they live. We begin today’s program with a story. Kwesuka sukela - once upon a time - there lived"\n },\n {\n "line_no": 8,\n "text": "a gift to a mother long ago. Stories are important to"\n },\n {\n "line_no": 29,\n "text": "teach good advice or give a moral lesson. Even simple stories can have big lessons. Usually these stories are called fables. This is the story of the Wise Old Man In a village, there was a very old man. Every day, people came to the old man"\n }\n ]\n}' additional_kwargs={} example=False
透過 parse 指令解析的結果:
output_parser.parse(response.content)
--- 下方則是實際的輸出結果 ---
>> RecommendCaptionResult(captions=[RecommendCaption(line_no=2, text='no matter where in the world they live. We begin today’s program with a story. Kwesuka sukela - once upon a time - there lived'), RecommendCaption(line_no=8, text='a gift to a mother long ago. Stories are important to'), RecommendCaption(line_no=30, text='complaining about the same problems. One day the old man told them a joke. Everyone laughed and laughed. After a few minutes, the old')])
在 LangChain 中,所謂的 Chain 是一種預先設計好的基礎元件類別,透過這類元件的實例,我們非但能夠將它按順序逐一執行。這些元件同時也內建了狀態管理和記憶單元的界面,能夠方便我們將單元做模組化設計,它的基礎界面設計如下:
class Chain(BaseModel, ABC):
"""所有鏈都應實現的基礎介面。"""
memory: BaseMemory
callbacks: Callbacks
def __call__(
self,
inputs: Any,
return_only_outputs: bool = False,
callbacks: Callbacks = None,
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
...
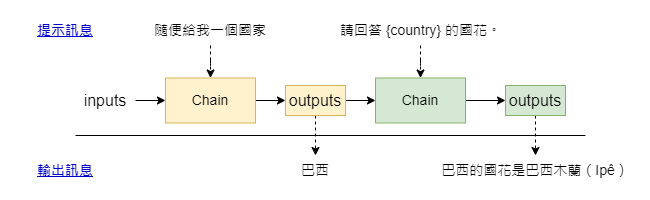
接著,我們將通過 LangChain 提供的其中一種 Chain 類別—LLMChain,來展示如何將多個任務單元有效串聯。
在下面的示例中,我們將首先利用語言模型生成一個國家名稱,然後將這個輸出作為下一個 Chain 結構的輸入,用以獲取該國的國花,首先,我們先讓語言模型隨機生成一個國家:
from langchain import PromptTemplate, OpenAI, LLMChain
llmchain_template = "隨便給我一個國家。"
#llmchain_template = "What is a good name for a company that makes {product}?"
chain1 = LLMChain(
llm=chat_model,
prompt=PromptTemplate.from_template(llmchain_template)
)
# 執行方法一
chain1({})
--- 我們這裏會得到如下的輸出 ---
>> {'text': '巴西'}
然後我們再將第一個 LLMChain 的訊息,提供給第二個 LLMChain 來取得它的國花::
llmchain_template2 = "請回答 {country} 的國花。"
chain2 = LLMChain(
llm=chat_model,
prompt=PromptTemplate.from_template(llmchain_template2)
)
chain2({
"country": chain1({})
})
--- 下方則是 chain2 最後給我們的回覆 ---
>> {'country': {'text': '巴西'}, 'text': '巴西的國花是巴西木蘭(Ipê)'}
更複雜一點的串接方式,我們甚至也可以在一個 Chain 結構,接受多個輸入參數,例如下方這樣:
llmchain_template3 = "請提供給我 {country} 的 {infor} 資訊。"
chain3 = LLMChain(
llm=chat_model,
prompt=PromptTemplate.from_template(llmchain_template3)
)
chain3({"country": chain1({})["text"],
"infor": "建國時間"})
--- 以下是實際輸出結果 ---
>> {'country': '巴西',
'infor': '建國時間',
'text': '巴西的建國時間是1822年9月7日。在這一天,巴西宣布獨立,從葡萄牙王國獨立出來,成為一個獨立的帝國。'}
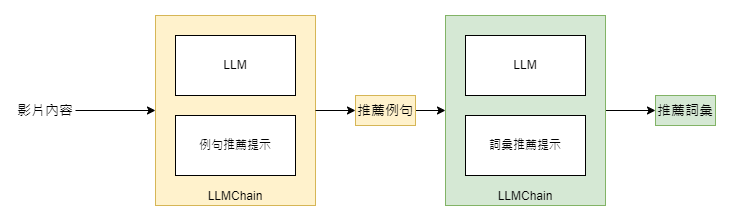
熟悉了 LLMChain 的基本操作後,我們將著手將例句推薦功能用 LLMChain 來實做。這次,我們不僅會利用 LLMChain 來獲取語言模型的回應,還會將這些回應連接到我們先前示範過的詞彙推薦功能上,首先是例句推薦的部分:
# LLMChain 版本的 例句推薦
from langchain.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
PromptTemplate,
SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
)
template = """你是一個專業的外語老師,你有一個特殊專長,能夠在影片的內容找出值得教學的內容,你也很擅長做課程的規劃。
接下來我會提供給你影片內容,請你在影片內容裏面,隨機且使用均勻分佈的原則挑選出 3 句左右值得教學的句子(教學例句),
同時也請記下你挑選的教學例句的原始內容以及行數。
{format_instructions}
"""
system_message_prompt = SystemMessagePromptTemplate(
prompt=PromptTemplate(
template = template,
input_variables=[],
partial_variables={"format_instructions": output_parser.get_format_instructions()}
)
)
human_template = "影片內容:\n{text}"
human_message_prompt = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_template)
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([system_message_prompt, human_message_prompt])
chain_caption = LLMChain(
llm=chat_model,
prompt=chat_prompt
)
chain_caption(line_data)
--- 以下是實際的輸出 ---
>> {'text': '{\n "captions": [\n {\n "line_no": 2,\n "text": "no matter where in the world they live. We begin today’s program with a story. Kwesuka sukela - once upon a time - there lived"\n },\n {\n "line_no": 8,\n "text": "a gift to a mother long ago. Stories are important to"\n },\n {\n "line_no": 29,\n "text": "teach good advice or give a moral lesson. Even simple stories can have big lessons. Usually these stories are called fables. This is the story of the Wise Old Man In a village, there was a very old man. Every day, people came to the old man"\n }\n ]\n}'}
接下來則是詞彙推薦的部分:
from langchain.output_parsers import CommaSeparatedListOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
PromptTemplate,
SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
)
output_parser_lex = CommaSeparatedListOutputParser()
system_template_lex = """你是一個專業的外語老師,你有一個特殊專長是在能夠以影片的內容找出值得教學的內容,你也很擅長做課程的規劃。
接下來我會提供給挑選出來的教學例句,請在所有教學例句裏面隨機找出 10 個詞彙。
{lex_format_instructions}
"""
system_message_prompt_lex = SystemMessagePromptTemplate(
prompt=PromptTemplate(
template = system_template_lex,
input_variables=[],
partial_variables={"lex_format_instructions": output_parser_lex.get_format_instructions()}
)
)
human_template_lex = "教學例句:\n{captions}"
human_message_prompt_lex = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_template_lex)
chat_prompt_lex = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([system_message_prompt_lex, human_message_prompt_lex])
chain_lex = LLMChain(
llm=chat_model,
prompt=chat_prompt_lex
)
最後,對於例句推薦和詞彙推薦這兩個處理單元,我們可以利用 LLMChain 將它們如下所示地連結在一起:
chain_lex({
"captions": chain_caption(line_data)["text"]
})
--- 下方是實際的輸出結果 ---
>> {'captions': '{\n "captions": [\n {\n "line_no": 2,\n "text": "no matter where in the world they live. We begin today’s program with a story. Kwesuka sukela - once upon a time - there lived"\n },\n {\n "line_no": 8,\n "text": "a gift to a mother long ago. Stories are important to"\n },\n {\n "line_no": 29,\n "text": "teach good advice or give a moral lesson. Even simple stories can have big lessons. Usually these stories are called fables. This is the story of the Wise Old Man In a village, there was a very old man. Every day, people came to the old man"\n }\n ]\n}',
'text': 'world, program, story, live, gift, mother, important, teach, lesson, village'}
我們也可以進行更細緻的操作,比如在流程中間以及最終階段都運用 output parser,將收到的訊息轉換成結構化的資料:
caption_parse_result = output_parser.parse(chain_caption(line_data)["text"])
chain_lex_response = chain_lex({
"captions": caption_parse_result
})
output_parser_lex.parse(chain_lex_response['text'])
--- 以下為輸出結果 ---
>> ['world',
'program',
'story',
'gift',
'mother',
'stories',
'important',
'complaining',
'problems',
'joke']
希望這篇文章能讓大家更深刻地體驗到 LangChain 框架在大型語言模型應用開發上的便利性。如有任何不清楚的地方,歡迎在下方留言提問。
對於有興趣實際操作的讀者,我們也提供了相關的程式碼,可前往以下連結進行實驗: D18. LangChain 專案實做 - 例句推薦與 LLMChain 介紹.ipynb。
透過 LLMChain 這種設計模式,你不僅能更有效地組織和管理程式碼,還能更容易地進行除錯和維護,從而大大提升開發效率。
