Given the heads of two singly linked-lists headA and headB, return the node at which the two lists intersect. If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
For example, the following two linked lists begin to intersect at node c1:
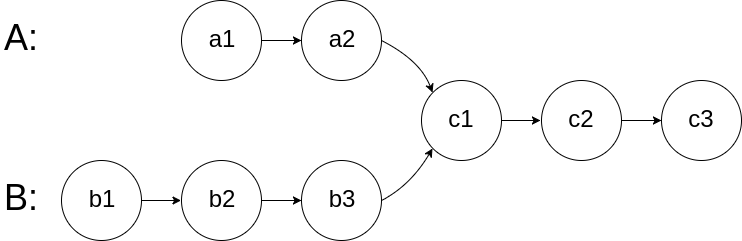
The test cases are generated such that there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
Note that the linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
Custom Judge:
The inputs to the judge are given as follows (your program is not given these inputs):
intersectVal - The value of the node where the intersection occurs. This is 0 if there is no intersected node.listA - The first linked list.listB - The second linked list.skipA - The number of nodes to skip ahead in listA (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.skipB - The number of nodes to skip ahead in listB (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.The judge will then create the linked structure based on these inputs and pass the two heads, headA and headB to your program. If you correctly return the intersected node, then your solution will be accepted.
Example 1:
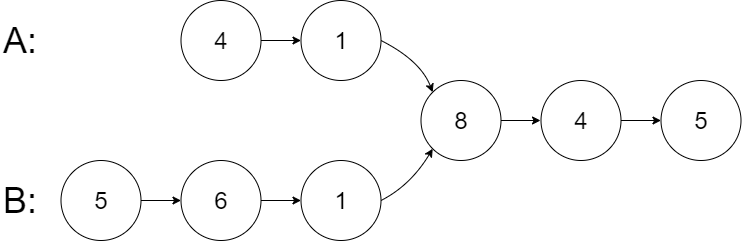
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Intersected at '8'
Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
- Note that the intersected node's value is not 1 because the nodes with value 1 in A and B (2nd node in A and 3rd node in B) are different node references. In other words, they point to two different locations in memory, while the nodes with value 8 in A and B (3rd node in A and 4th node in B) point to the same location in memory.
Example 2:
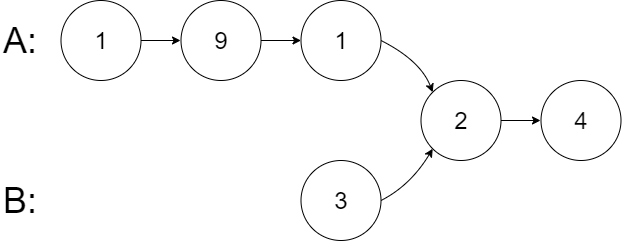
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Intersected at '2'
Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:
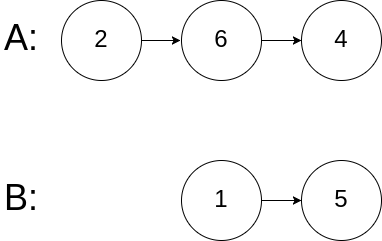
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: No intersection
Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Constraints:
listA is in the m.listB is in the n.1 <= m, n <= 3 * 10^4
1 <= Node.val <= 10^5
0 <= skipA < m
0 <= skipB < n
intersectVal is 0 if listA and listB do not intersect.intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB] if listA and listB intersect.Follow up:
Could you write a solution that runs in O(m + n) time and use only O(1) memory?
這題的解法要求時間複雜度O(m+n)以及空間複雜度O(1),但這題我實在想不出怎麼在這條件下解題,只好暴力一點使用Set集合去記憶看過的節點,如果發現看過的就直接回傳,在Memory Usage 感覺表現很好,但在Runtime 上就差很多了...
Runtime: 6 ms (16.25%)
Memory Usage: 46 MB (98.98%)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> seen = new HashSet<>();
seen.add(headA);
if (!seen.add(headB)) {
return headB;
}
while (headA.next != null || headB.next != null) {
if (headA.next != null) {
headA = headA.next;
if (!seen.add(headA)) {
return headA;
}
}
if (headB.next != null) {
headB = headB.next;
if (!seen.add(headB)) {
return headB;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
Example 1:
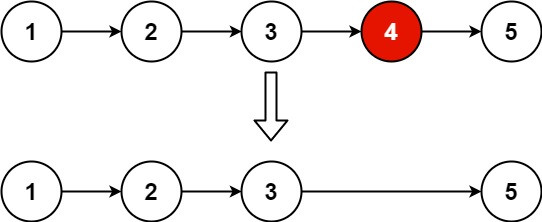
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints:
sz.1 <= sz <= 30
0 <= Node.val <= 100
1 <= n <= sz
Follow up: Could you do this in one pass?
這題寫了兩個解法,效果意外的還不錯?
第一個是暴力解,利用遞迴方法去找要刪除的節點位置,最後再到那個節點前的位置去執行傳操作。
Runtime: 0 ms (100%)
Memory Usage: 40.1 MB (91.69%)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode temp = head;
while (!checkReachTail(temp, n)) {
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp == head) return head.next;
ListNode result = head;
while (temp != head.next) {
head = head.next;
}
head.next = head.next.next;
return result;
}
private boolean checkReachTail(ListNode node, int n) {
if (node != null && n != 0) {
return checkReachTail(node.next, n - 1);
} else if (node != null && n == 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
第二個是參考了其他人的做法,使用快慢指針的方法,先讓快指針往前n的節點,然後兩個指針同時前進,當快指針到達尾端時,慢指針的節點就是要刪除的節點。
Runtime: 0 ms (100%)
Memory Usage: 40.9 MB (19.84%)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (n > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
n--;
}
if (fast == null) {
return head.next;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return head;
}
}
不管是在陣列還是鏈結陣列,雙指針演算法的技巧是真的蠻實用的,多刷題多看其他解法是真的很有幫助,不過第二題是讓我有點意外的,沒想到暴力一點的解法速度上沒變,記憶體用量反而比較少。
