這次要結合的地方是RecyclerView的點擊事件,當點擊了RecyclerView中的某一個項目後就執行跳轉頁面,將資料跟著傳入到目的地頁面,再將傳入的資訊顯示出來,這次實作預計會結合前幾篇講到的Api資料,將資料丟進RecyclerView顯示點擊某個選項後,就跳到下個頁面將所有資訊顯示出來。
implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.9.0'
implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.9.0'
//Retrofit
implementation 'com.squareup.retrofit2:adapter-rxjava3:2.9.0'
implementation 'io.reactivex.rxjava3:rxjava:3.1.6'
implementation 'io.reactivex.rxjava3:rxandroid:3.0.0'
//RxJava
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
這次的實作除了原本的主畫面外,還有新增一個給Intent跳轉的頁面
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Space
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="0.2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/search"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="0.1"
android:text="搜尋"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recyclerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="0.7"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
tools:listitem="@layout/recycleritem"/>
</LinearLayout>
主畫面設定了一個搜尋按鈕,按下後就會將資料填入下方的RecyclerView。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="@drawable/border"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="0.2"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:text="Name :" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_name"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="0.8"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:text="TextView" />
</LinearLayout>
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="@color/black" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="0.2"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:text="Email :" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_email"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="0.8"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:text="TextView" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
item的設計也很簡單,就是把每一筆資料附的name跟email顯示出來。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity2">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/result"
android:layout_width="374dp"
android:layout_height="496dp"
android:layout_marginStart="19dp"
android:layout_marginTop="132dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="18dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="103dp"
android:background="@drawable/border"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="TextView"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.0"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/back"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="17dp"
android:layout_marginTop="55dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="304dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="30dp"
android:text="返回"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/result"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
這個介面我新增了一個TextView將接收到的資料顯示出來,並且增加了一個按鈕,用來將現在這個介面返回到前一頁。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item>
<shape>
<stroke android:width="3dp"
android:color="#2EA9DF"/>
</shape>
</item>
</selector>
這個部分跟之前的寫法一樣,這邊就跳過不重講一次,詳情可以看之前的文章Day15。
這次我在要取資料用了比較不一樣的方式將資料加進我的ArrayList,因此這裡就單獨將這個部分拉出來講
private void searchCommentData() {
getApi.getCommentData()
.observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread())
.subscribeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread())
.subscribe(new DisposableObserver<List<DataResponse>>() {
@Override
public void onNext(@NonNull List<DataResponse> dataResponses) {
for (DataResponse data : dataResponses){
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("postId",data.postId);
hashMap.put("id",data.id);
hashMap.put("name",data.name);
hashMap.put("email",data.email);
hashMap.put("body",data.body);
mArrayList.add(hashMap);
}
setRecyclerView(mArrayList);
}
@Override
public void onError(@NonNull Throwable e) {}
@Override
public void onComplete() {}
});
}
在onNext的部分我使用了for迴圈走訪抓下來的資料,然後再將資料給丟進我建立好的ArrayList裡面,最後再將資料傳進我的RecyclerView裡面
for (DataResponse data : dataResponses){
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("postId",data.postId);
hashMap.put("id",data.id);
hashMap.put("name",data.name);
hashMap.put("email",data.email);
hashMap.put("body",data.body);
mArrayList.add(hashMap);
}
setRecyclerView(mArrayList);
首先我設定了一個DataResponse的變數data,這樣我的data就會代表DataResponse裡面的元素,這麼做最大的原因是因為得到的資料也是屬於DataResponse的元素,這麼做就可以順利地走訪得到的資料,接著下面在將每次的資料用HashMap存起來,在放進ArrayList裡面。
最後在設定RecyclerView,像這樣將程式的先後順序用呼叫函式的方法分開,不讓他一次執行,就可以降低讓程式報錯的機率。
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Button;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import io.reactivex.rxjava3.android.schedulers.AndroidSchedulers;
import io.reactivex.rxjava3.annotations.NonNull;
import io.reactivex.rxjava3.observers.DisposableObserver;
import io.reactivex.rxjava3.schedulers.Schedulers;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>> mArrayList;
private MyListAdapter myListAdapter;
private RecyclerView recyclerView;
private Button search;
private ApiClient apiClient;
private GetApi getApi;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
search = findViewById(R.id.search);
recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.recyclerView);
apiClient = new ApiClient();
getApi = apiClient.getCommentApi().create(GetApi.class);
mArrayList = new ArrayList<>();
search.setOnClickListener(view -> searchCommentData());
}
private void searchCommentData() {
getApi.getCommentData()
.observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread())
.subscribeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread())
.subscribe(new DisposableObserver<List<DataResponse>>() {
@Override
public void onNext(@NonNull List<DataResponse> dataResponses) {
for (DataResponse data : dataResponses){
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("postId",data.postId);
hashMap.put("id",data.id);
hashMap.put("name",data.name);
hashMap.put("email",data.email);
hashMap.put("body",data.body);
mArrayList.add(hashMap);
}
setRecyclerView(mArrayList);
}
@Override
public void onError(@NonNull Throwable e) {}
@Override
public void onComplete() {}
});
}
private void setRecyclerView(ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> mArrayList) {
myListAdapter = new MyListAdapter(mArrayList);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(getApplicationContext()));
recyclerView.setAdapter(myListAdapter);
}
}
基本設定的部分這邊一樣也跳過,詳細可以看之前的文章Day8
這邊會講解怎麼設定RecyclerView的點擊事件,以及怎麼跟Intent跳轉頁面做結合
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull MyListAdapter.ViewHolder holder, int position) {
holder.name.setText(mArrayList.get(position).get("name"));
holder.email.setText(mArrayList.get(position).get("email"));
holder.itemView.setOnClickListener(view -> {
HashMap data = mArrayList.get(position);
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.putExtra("data",data);
intent.setClass(view.getContext(), MainActivity2.class);
view.getContext().startActivity(intent);
});
}
RecyclerView點擊事件要用到itemView裡面的點擊事件,並且設定在點擊到某個選項後,就將點擊到的資料都存進一個HashMap,接著就可以將資料用putExtra的方式把資料丟給Intent,然後在將本地的Context以及目的地的Class填好,最後就可以呼叫startActivity將Intent傳入,讓他執行跳轉頁面的指令。
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MainActivity2 extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView result;
private Button back;
private ArrayList data;
@SuppressLint("MissingInflatedId")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2);
result = findViewById(R.id.result);
back = findViewById(R.id.back);
data = new ArrayList();
Intent intent = getIntent();
if (intent != null){
data.add(intent.getSerializableExtra("data"));
}
result.setText(data.get(0).toString());
back.setOnClickListener(view -> finish());
}
}
首先看到這個部分
Intent intent = getIntent();
if (intent != null){
data.add(intent.getSerializableExtra("data"));
}
result.setText(data.get(0).toString());
因為這次的資料型態較複雜所以要用到getSerializableExtra,填入傳入資料時設定的key,就能將資料丟給ArrayList去存取,最後在將資料丟給TextView去顯示。
接著看到按鈕的設定
back.setOnClickListener(view -> finish());
這邊要說明一下,可以想像一下有一個容器用來存取每個開啟的頁面,當使用Intent跳轉頁面時,就是在一個容器中將目的地的頁面也加進一個容器中,大概就像這樣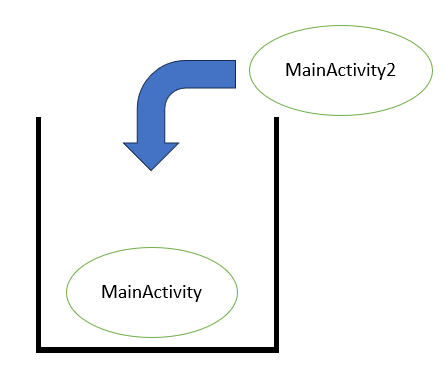
接著我設定了,當點擊這個按鈕後就執行finish()這個指令,finish可以把當前的這個頁面給關掉,可以想像成將後面添加的頁面給丟掉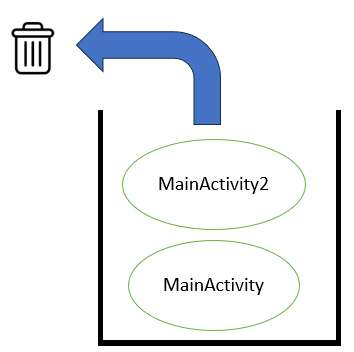
最後就會剩下MainActivity這個頁面,也就會自動跳回上一頁囉~
