昨天我們介紹了多元二次多項式系統,並提到雙極構造法:
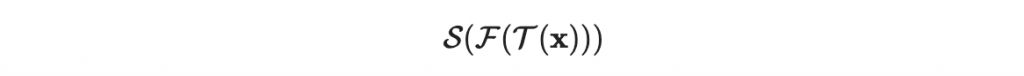
其中 S 與 T 是兩個隨機的仿射變換、F 是很好算反函數的多元二次多項式系統。密碼學上,S, F, T 皆當作私鑰;S(F(T(x)) 則為公鑰。
今天我們來討論這個「很好算反函數的」F 該怎麼被構造?
在 Day6 的時候,我們介紹了多項式商環的概念: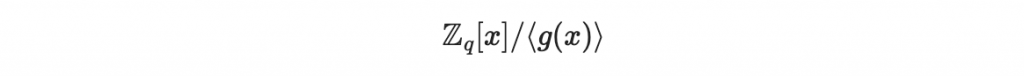
這個集合收集了所有次數比 g(x) 的次數還小的多項式,其中這些多項式的係數都在 Z_q 內。這個環的加法與乘法都是在原本多項式乘法做完後模除 g(x) ,也就是取除以 g(x) 的餘數。
那因為這個集合裡面的多項式次數都比 g(x) 的次數還小,如果 g(x) 的次數是 n ,那麼這個集合裡面的多項式都小於 n 次:
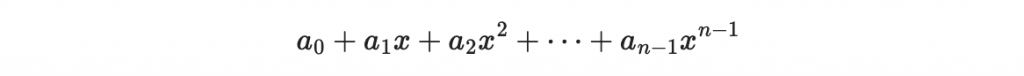
意思是,我們可以用一個 n 維度向量來表達這個集合裡面的多項式
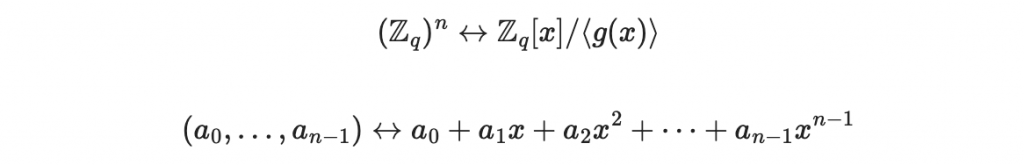
好!既然有了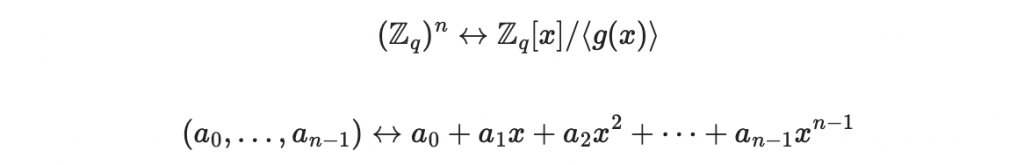
就可以開始思考一件事:
如果有一個多項式 a(x) 在這兩個表示法下分別是
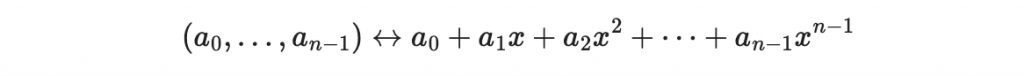
那麼我們可以計算 a(x) 的平方:
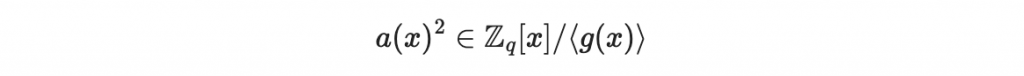
因為 a(x) 的平方結果還在右手邊的商環裡面,所以我們可以用向量表示法來表示 a(x) 的平方
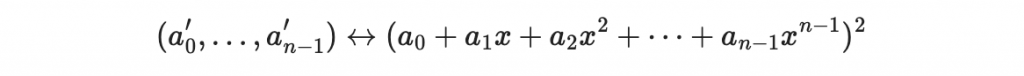
(提醒:在這個商環計算裡面,都需要模除 g(x) ,所以最後的次數仍然小於 g(x) 的次數)
從這裡我們發現:把 a(x) 做平方的這個操作,其實是以下兩個 n 維度向量的操作:
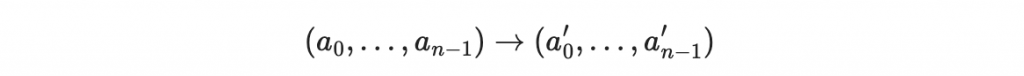
現在用 SageMath 來建構這樣的計算:
首先建立好多項式商環:
R = quotient(ZZ,7*ZZ);
R_poly = PolynomialRing(R,x);
g = R_poly(6*x^5 + 6*x^3 + 5*x^2 + 3)
# 建立多項式商環
R_poly_quotient = quotient(R_poly, g)
print(R_poly_quotient)
# Outputs:
# Univariate Quotient Polynomial Ring in xbar over Finite Field of size 7 with modulus x^5 + x^3 + 2*x^2 + 4
找一個隨機的 a(x) ,並印出他的向量表示法
a = [R(randint(0,7)) for i in range(5)]
a = R_poly_quotient(a)
print(a)
print(a.list())
# Outputs:
# xbar^4 + 6*xbar + 6
# [6, 6, 0, 0, 1]
計算平方,並輸出最後的向量表示法
a_square = a^2
print(a_square)
print(a_square.list())
# Outputs:
# 6*xbar^4 + 2*xbar^3 + 2*xbar^2 + 6*xbar + 3
# [3, 6, 2, 2, 6]
因此,對在多項式商環內的多項式 a(x) 取平方,這個動作可以視為一個在 n 維向量上的操作。同理,對 a(x) 取任何次方,這的動作也可以視為一個在 n 維向量上的操作!
考慮 Z_q 這個整數商環。
首先會找兩個數字,theta 與 h 使得
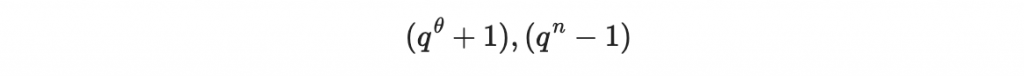
互質。並再找到 h 滿足:
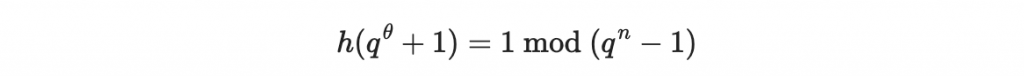
然後在多項式環內建構一個很好取反函數的
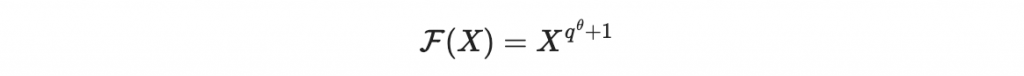
他的反函數其實就是
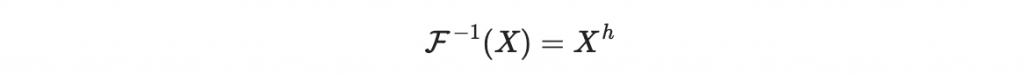
原因是
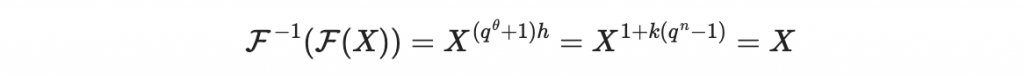
其中最後一個等號是來自費馬小定理,我們待會會用 SageMath 來做驗證。
於是,我們就建構好一個「很好取反函數的」F 了。
我們首先取 q = 2 的整數商環作為係數:
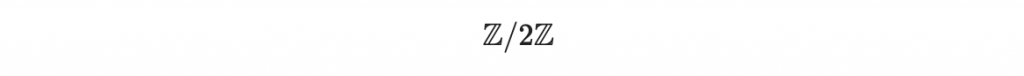
然後取 g(x) 為一個 n 次多項式,這裡取 n = 5
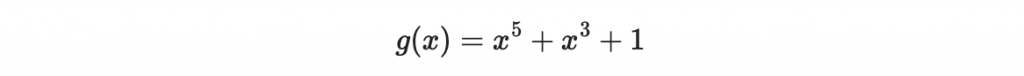
形成
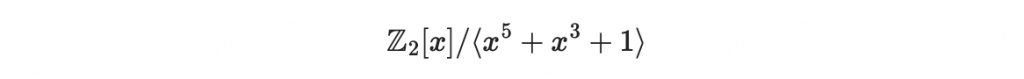
q = 2
R = quotient(ZZ,q*ZZ);
R_poly = PolynomialRing(R,x);
n = 5 #degree of g(x)
g = x^5 + x^3 + 1
R_poly_quotient = quotient(R_poly,g)
print(R_poly_quotient)
# Outputs:
# Univariate Quotient Polynomial Ring in xbar over Ring of integers modulo 2 with modulus x^5 + x^3 + 1
接著要選一個 theta 參數滿足:
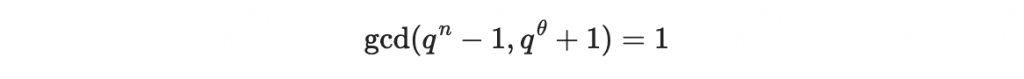
並要找到 h 滿足
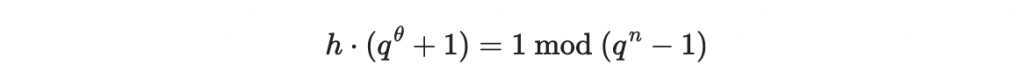
theta = 2
print(gcd((q^n)-1,(q^theta)+1))
# Outputs:
# 1
為了找到 h ,先使用 xgcd 函數
print(xgcd((q^n)-1,(q^theta)+1))
# Ouptuts:
# (1, 1, -6)
這個函數會有三個輸出:
其中第一個是最大公因數,第二個與第三個數字分別是以下的 h' 與 h
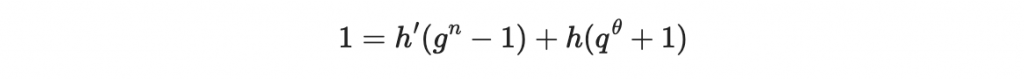
你可以看到這裡的 h 是負數,但因為我們等等要計算多項式商環中的 h 次方,我們需要取正號的 h
h = h + (q^n-1)
print(h)
# Outputs:
# 25
而我們仍然有
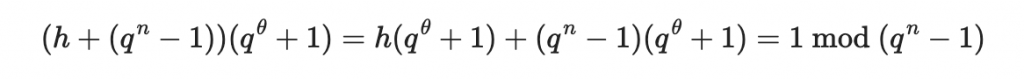
到此為止,我們就有雙極構造法(Bipolar Construction)裡的中間映射(Central Mapping),也就是很好算反函數的 F
# 我們定義函數的輸入輸出都是 list 型態,這樣會增加可用性
def Central_Map_poly(X):
X = R_poly_quotient(X)
return (X^(q^theta+1)).list()
def Central_Map_poly_inv(X):
X = R_poly_quotient(X)
return (X^h).list()
# 生成一個隨機的 n 維向量 a
a = [R(randint(0,1)) for i in range(5)]
print(a)
# 先經過中間映射得到 b
b = Central_Map_poly(a)
print(b)
# 再進行反中間映射看看是否與一開始的 a 相同
print(Central_Map_poly_inv(b))
print(a == Central_Map_poly_inv(b))
# Outputs:
# [1, 1, 1, 0, 1]
# [0, 1, 1, 1, 1]
# [1, 1, 1, 0, 1]
# True
有了很好算反函數的 F 之後,我們就可以把完整的雙極構造法給做出來。具體來講其實就是要寫一個函數來生成隨機的可逆仿射變換。仿射變換:Affine Map
def RandomAffineMapGenerator(n, R):
while True:
# Generate a random n x n matrix for the linear part of the affine map
A = random_matrix(R, n, n)
# Check if A is invertible
if A.is_invertible():
break
# Generate a random n-dimensional vector for the translation part
b = random_vector(R, n)
# Define the nested affine map function
def AffineMap(v):
v = vector(v)
v = A * v + b
return v.list()
# Define the inverse affine map function
def InverseMap(v):
v = vector(v)
v = A.inverse() * (v - b)
return v.list()
# Return the affine map function, the inverse map function, and the components
return AffineMap, InverseMap, A, b
接著就可以生成 T 與 S
S,S_inv,A,b = RandomAffineMapGenerator(n,R)
T,T_inv,A,b = RandomAffineMapGenerator(n,R)
在雙極構造法中,公鑰就是 S(F(T(x)))
def Public_key(x):
x = T(x)
x = R_poly_quotient(x)
x = Central_Map_poly(x)
x = S(x)
return x
我們可以開始示範加密與解密過程:
message = [0,0,0,1,1]
def Encrypt(plaintext):
return Public_key(plaintext)
cipher = Encrypt(message)
print(cipher)
# Outputs:
# [0, 0, 1, 1, 0]
def Decrypt(cipher):
result = cipher
result = S_inv(result)
result = Central_Map_poly_inv(result)
result = T_inv(result)
return result
print(Decrypt(cipher))
print(Decrypt(cipher) == message)
# Outputs:
# [0, 0, 0, 1, 1]
# True
細心的讀者可能會發現一件怪事,就是我們使用多項式的次方來定義的 F ,雖說他確實是輸入 n 維度向量、輸出 n 維度向量
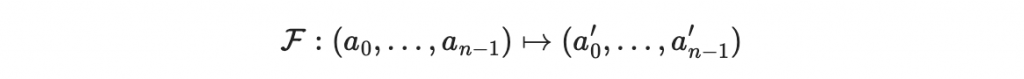
但那不代表說,這個函數的映射關係就滿足「多元二次多項式系統」的數學形式啊?
明天我們就來解釋這件事情,並給出另一個HFE密碼系統。
