在上一篇文章中,我們已經完成資料集的清理工作。接下來,我們將進行初步的資料探勘,透過視覺化方式分析目前評論的分布狀況,從中獲得初步洞察。
首先,我們從雲端儲存空間讀取之前清理好的資料檔案:
import pandas as pd
# 從指定路徑讀取已清理的資料
df = pd.read_excel('/content/drive/MyDrive/20250823_pchome.xlsx', sheet_name='cleaned_data')
df
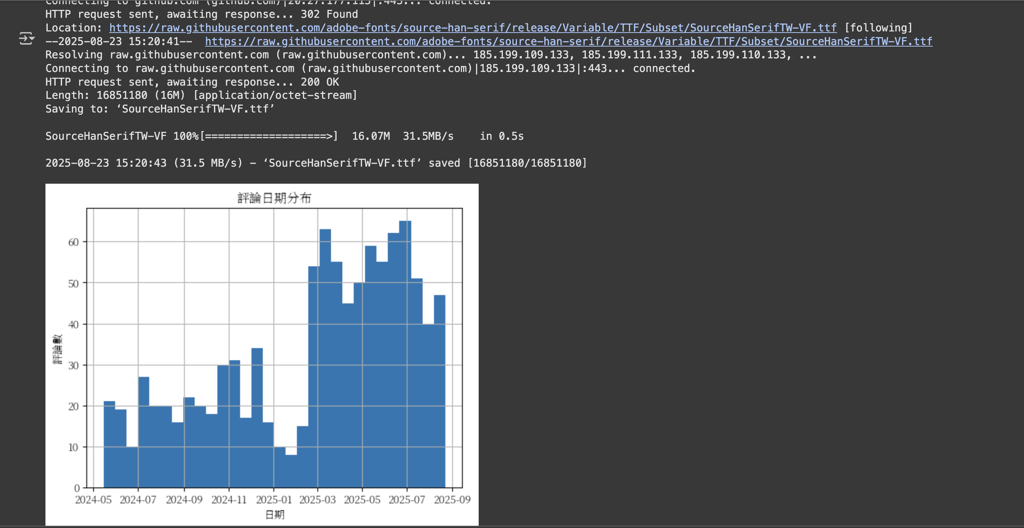
了解評論的時間分布有助於我們辨識評論數的趨勢。首先安裝必要的套件並設定中文字型:
!pip install wordcloud matplotlib -qqq
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 下載並設定繁體中文字型
!wget -O SourceHanSerifTW-VF.ttf https://github.com/adobe-fonts/source-han-serif/raw/release/Variable/TTF/Subset/SourceHanSerifTW-VF.ttf
fm.fontManager.addfont('SourceHanSerifTW-VF.ttf')
mpl.rc('font', family='Source Han Serif TW VF')
# 將日期欄位轉換為日期格式並繪製直方圖
df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'], errors='coerce')
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
df['date'].hist(bins=30)
plt.title('評論日期分布')
plt.xlabel('日期')
plt.ylabel('評論數')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
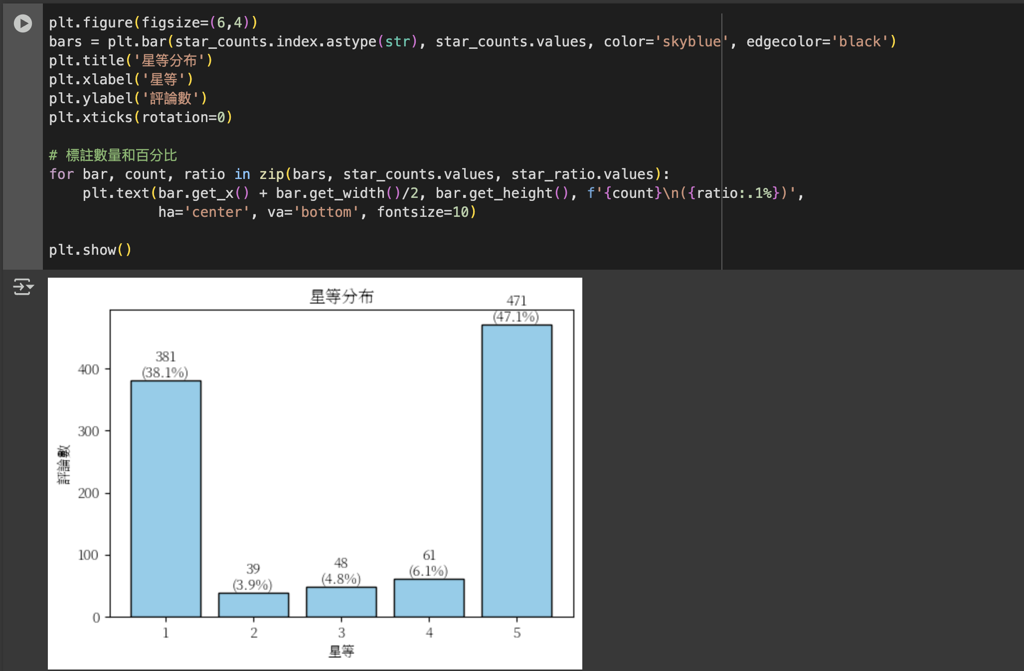
星等分布可以反映用戶對產品或服務的整體滿意度
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
star_counts = df['star'].value_counts().sort_index()
star_ratio = star_counts / star_counts.sum()
bars = plt.bar(star_counts.index.astype(str), star_counts.values, color='skyblue', edgecolor='black')
plt.title('評論星等分布')
plt.xlabel('星等')
plt.ylabel('評論數')
plt.xticks(rotation=0)
# 在每個柱狀圖上標註數量和百分比
for bar, count, ratio in zip(bars, star_counts.values, star_ratio.values):
plt.text(bar.get_x() + bar.get_width()/2, bar.get_height(),
f'{count}\n({ratio:.1%})',
ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
接下來,我們使用 TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) 技術來辨識評論中的關鍵詞彙。
import jieba
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
# 定義停用詞列表
stopwords = ["一直", "無法", "沒有", "app", "App", "APP",
"就是", "但是", "而且", "所以", "因為", "這個", "這樣", "到底",
"非常", "使用", "還有", "只有", "收到", "顯示", "通知",
"直接", "什麼", "處理", "good", "真的", "結果"]
# 定義分詞與過濾停用詞的函式
def tokenize_review(review, stopwords):
"""
分詞並過濾停用詞
:param review: 單一文本
:param stopwords: 停用詞集合
:return: 過濾停用詞後的分詞結果,格式為空格分隔的字串
"""
if pd.isna(review): # 若欄位為 NaN,回傳空字串
return ""
words = jieba.lcut(review, cut_all=False) # 精確模式分詞
return " ".join([word for word in words if word not in stopwords]) # 過濾停用詞
def tokenize_reviews(df, review_col, stopwords):
result_df = df.copy()
result_df['review_tokenized'] = result_df[review_col].apply(lambda x: tokenize_review(x, stopwords))
return result_df
def calculate_tfidf(reviews, stopwords):
# 使用 TF-IDF 向量化文本
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()
tfidf_matrix = vectorizer.fit_transform(reviews)
vocab = vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
idf_values = vectorizer.idf_
# 計算詞彙出現次數(TF)和 TF-IDF
word_count = (tfidf_matrix > 0).sum(axis=0).A1 # 詞出現次數
tf_values = word_count / len(reviews) # 平均 TF 值
tfidf_values = tfidf_matrix.toarray().sum(axis=0)
# 建立結果 DataFrame
tfidf_summary_df = pd.DataFrame({
"word": vocab,
"frequency": word_count,
"TF": tf_values,
"IDF": idf_values,
"TFIDF": tfidf_values
})
return tfidf_summary_df.sort_values(by="TFIDF", ascending=False)
# 處理評論文本
tokenize_df = tokenize_reviews(df, 'review', stopwords)
# 計算 TF-IDF 並顯示結果
tfidf_summary_df = calculate_tfidf(tokenize_df['review_tokenized'], stopwords)
tfidf_summary_df.head(20) # 顯示前20個關鍵詞
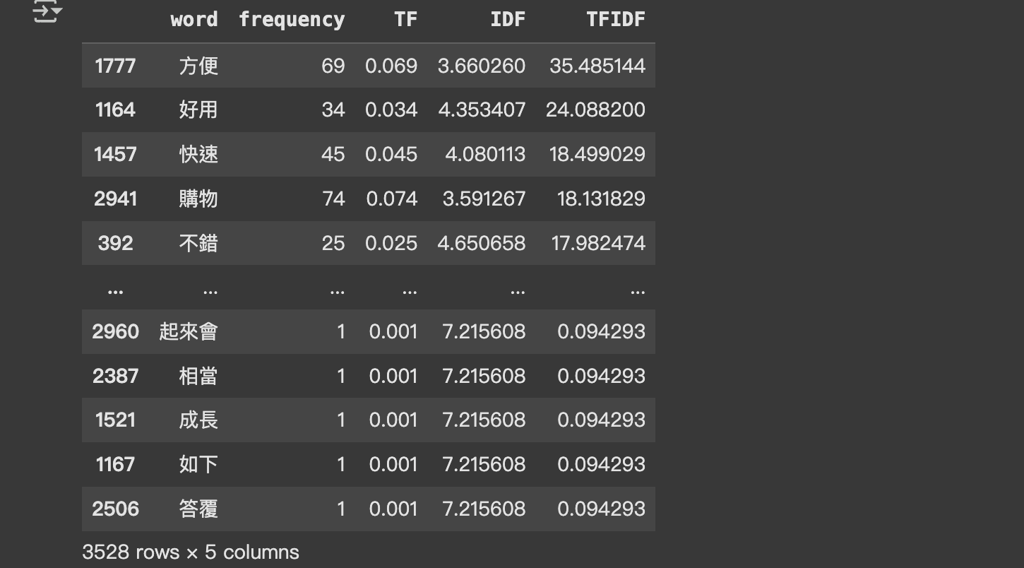
最後,我們將 TF-IDF 分析的結果轉換為文字雲,抓出用戶所提及的熱度關鍵字有哪些,例如「好用」、「快速」、「便宜」等等。
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import urllib.request
import os
def create_wordcloud(word_df):
"""
從詞頻DataFrame生成文字雲
Parameters:
word_df: 包含詞頻的DataFrame,需要有 'word' 和 'frequency' 列
"""
# 檢查字體文件是否存在
font_path = 'TaipeiSansTCBeta-Regular.ttf'
if not os.path.exists(font_path):
print("下載字體文件...")
url = "https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1eGAsTN1HBpJAkeVM57_C7ccp7hbgSz3_&export=download"
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, font_path)
# 添加字體
fm.fontManager.addfont(font_path)
plt.rc('font', family='Taipei Sans TC Beta')
# 將DataFrame轉換為字典格式
word_freq_dict = dict(zip(word_df['word'], word_df['frequency']))
# 生成文字雲
wordcloud = WordCloud(
font_path=font_path,
width=800,
height=400,
background_color='white',
max_words=100, # 最多顯示100個詞
min_font_size=10,
max_font_size=100
).generate_from_frequencies(word_freq_dict)
# 顯示文字雲
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.imshow(wordcloud, interpolation='bilinear')
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("評論關鍵詞文字雲", fontsize=16)
plt.tight_layout(pad=0)
plt.show()
return wordcloud
# 生成文字雲
try:
wordcloud = create_wordcloud(tfidf_summary_df)
except Exception as e:
print(f"生成文字雲時發生錯誤: {str(e)}")

透過這些初步的資料探勘與視覺化分析,我們可以清楚了解評論的時間分布、星等評分情況,以及用戶評論中最常提及的關鍵詞彙。
在接下來的文章中,我們將深入了解情感分析的模型,以及如何進行訓練,挖掘用戶評論上的情緒反應。
