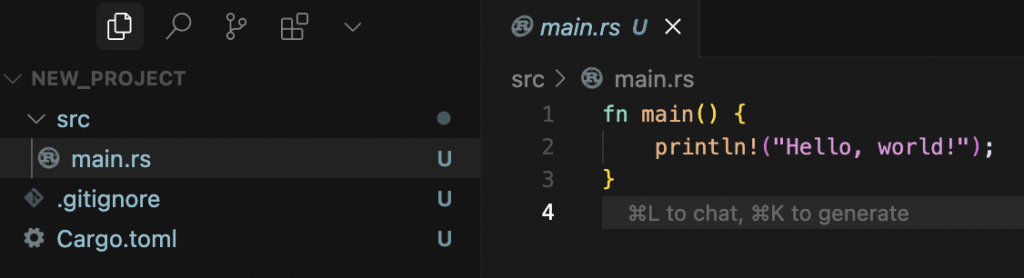
Rust中最基本的 編譯單位(compilation unit),簡單來說crate就是你寫的一個 Rust 專案或函式庫,可以是
cargo new --bin new_project
cargo new --lib new_lib
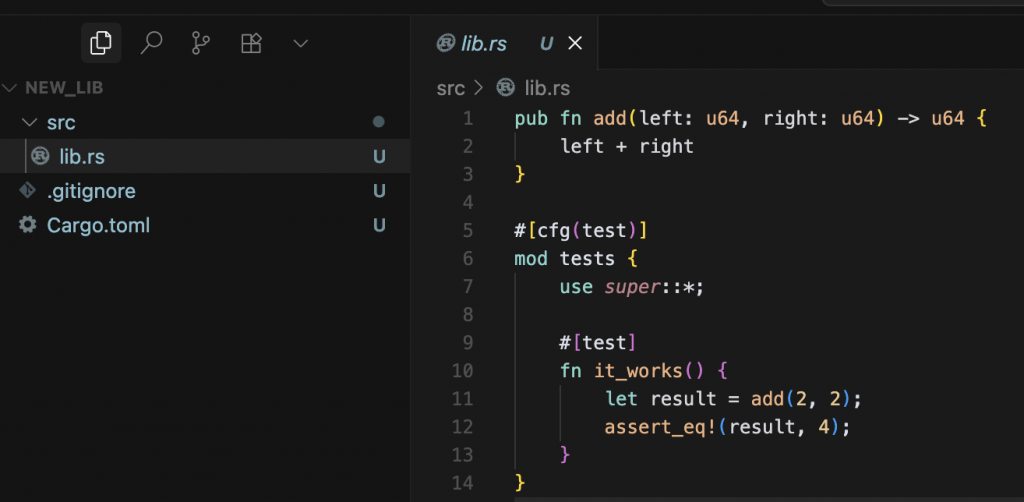
cargo 是 Rust 的 官方套件管理工具和建構工具,就像:
JavaScript 的 npm / yarn
Python 的 pip
Go 的 go
Java 的 maven / gradle
每次呼叫函式都要寫出路徑的話會很冗長、重複且不方便的,我們可以用 use 關鍵字建立路徑的捷徑,然後在作用域內透過更短的名稱來使用,參考連結。
使用use前
mod front_of_house {
pub mod hosting {
pub fn add_to_waitlist() {}
}
}
pub fn eat_at_restaurant() {
crate::front_of_house::hosting::add_to_waitlist();
}
使用use後
mod front_of_house {
pub mod hosting {
pub fn add_to_waitlist() {}
}
}
use crate::front_of_house::hosting;
pub fn eat_at_restaurant() {
hosting::add_to_waitlist();
}
//引用HashMap模組
use std::collections::HashMap;
impl Solution {
pub fn max_operations(nums: Vec<i32>, k: i32) -> i32 {
//create HashMap keys are number and values are count of the num
let mut hashmap = HashMap::new();
let mut pairs = 0;
for num in nums {
if let Some(count) = hashmap.get_mut(&(k-num)){
if(*count>0){
*count -=1;
pairs+=1;
}
if(*count==0){
hashmap.remove(&(k-num));
}
} else {
hashmap.entry(num).and_modify(|count| *count+=1).or_insert(1);
}
}
return pairs
}
}
解法中std::collections是標準函式庫中用來處理資料結構collections的模組,它提供了各種常用的容器類型,例如:
Vec和VecDeque
HashMap和BTreeMap
HashSet和BTreeSet
LinkedList
BinaryHeap
我們可從api doc看到HashMap結構和方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| HashMap::new() | 建立空的 HashMap |
| insert(key, value) | 插入一組鍵值對,若已存在該鍵會覆蓋並回傳舊值 |
| get(&key) → Option<&V> | 取得 key 對應的值(不可變借用) |
| get_mut(&key) → Option<&mut V> | 可變借用值 |
| contains_key(&key) → bool | 檢查是否存在該 key |
| entry(key).or_insert(value) | 若 key 不存在則插入 value,回傳可變引用 |
| entry(key).and_modify(f) | 若 key 存在則修改值 |
| remove(&key) → Option | 移除該 key 的資料,並回傳值(若有) |
| clear() | 清空整個 map |
使用方式
use std::collections::HashMap;
let mut map = HashMap::new();
map.insert("apple", 3);
map.insert("banana", 5);
if let Some(count) = map.get("apple") {
println!("Apple count: {}", count);
}
//Apple count: 3
if map.contains_key("banana") {
println!("We have bananas!");
}
//We have bananas!
map.entry("apple").or_insert(0); //如果map中沒有"apple",insert {"apple",0}
map.entry("apple").and_modify(|v| *v += 1); //如果map中有"apple",幫原本的value+1
map.remove("banana"); //移除key="banana"
map.clear(); //移除整個map
寫法1是先確定hashmap 中apple是否有值,再去修改參考值
寫法2是.entry()回傳一個Entry<K, V> enum,如果 key 已存在,就對 value 套用 closure function(|v| *v += 1)
use std::collections::HashMap;
let mut map = HashMap::new();
map.insert("apple", 1);
//寫法1
if let Some(v) = map.get_mut("apple") {
*v += 1;
}
//寫法2
map.entry("apple").and_modify(|v| *v += 1);
時間複雜度上O(n)<O(nlogn)但實際submit後時間竟然是向量陣列排列比較快,下篇介紹原因為何
| 方法 | 向量陣列排列 | hashmap |
|---|---|---|
| 時間複雜度 | O(nlogn) | O(n) |
| 實際時間 | 10ms | 23ms |

 iThome鐵人賽
iThome鐵人賽
 看影片追技術
看更多
看影片追技術
看更多