在HashMap HashSet中有提到當hashmap當發生碰撞時,使用linked list或動態陣列來解決,Rust doc提到使用 Vec 或 VecDeque 更好。
linked list結構如下
pub struct ListNode {
pub val: i32,
pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
}
資料來源:https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/collections/struct.LinkedList.html
需要固定address時可以用,Vec擴容需要搬動中間元素,linked list位置固定
把兩個列表串起來,當元素很大或不可輕易搬動時Linked List較有利。
我們來刷個幾題
題目:給一個linked list倒轉他的順序
輸入:[1,2,3,4,5]
輸出:[5,4,3,2,1]
限制:
[0, 5000].-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
解法:如何自訂義Priority Queue Top K比較方式中有提到可以自定義結構和方法來實現heap,在這題leetcode也有用到,定義ListNode,val為node的值,next記錄下一個指標位置,反轉的話
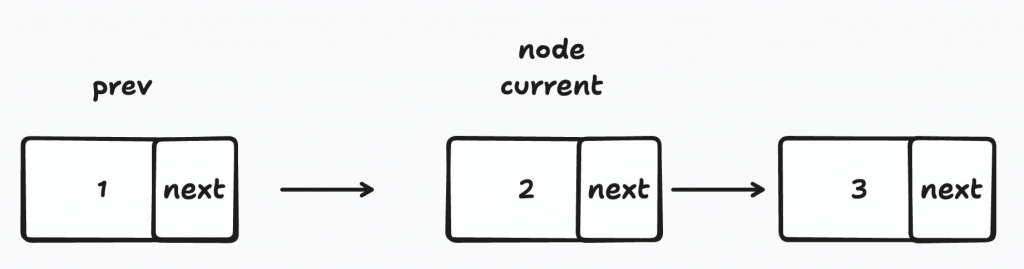
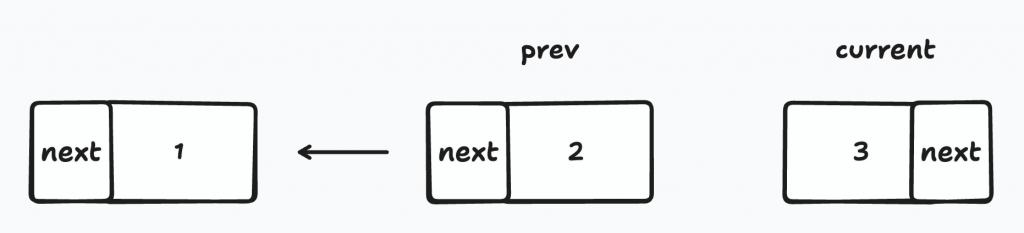
2-1. 先把current移到節點3
2-2. 目前node的next換成pre節點1
2-3. pre變成節點2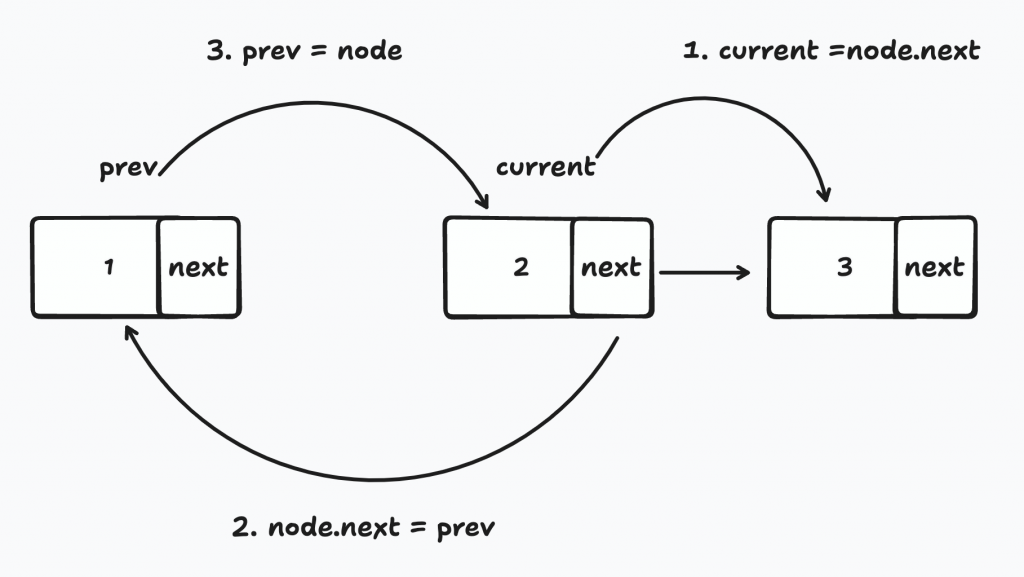
// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn reverse_list(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
if(head.is_none()){
return head
}
let (mut prev, mut current) = (None,head);
while let Some(mut node) = current {
current = node.next;
node.next = prev;
prev = Some(node);
}
prev
}
}
題目:給你一串linked list和左右邊界,將這左右邊界中的node倒轉,並返回倒轉後的結果。
輸入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
輸出:[1,4,3,5,2]
限制:
The number of nodes in the list is n.
1 <= n <= 500
-500 <= Node.val <= 500
1 <= left <= right <= n
解法:左右邊界把linked list分成 A→B→C 三部分,A、C照著原順序,B部分照著Leetcode 206. Reverse Linked List的想法做翻轉,翻轉後再把A→Reverse B→C接起。
impl Solution {
pub fn reverse_between(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, left: i32, right: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
if(left==right||head.is_none()){
return head
}
let mut origin = head;
let mut head_tail = &mut origin;
for i in 1..left {
head_tail=&mut head_tail.as_mut().unwrap().next;
}
let mut cur = head_tail.take();
let mut prev = None;
for i in left..right+1 {
let Some(mut node) = cur else{break};
cur=node.next;
node.next=prev;
prev=Some(node);
}
*head_tail=prev;
while (head_tail.as_mut().is_some()){
head_tail=&mut head_tail.as_mut().unwrap().next;
}
*head_tail= cur.take();
origin
}
}
解法優化:在A→Reverse B→C串聯過程中,會再重跑一遍B找到他最後一個node再接C,當B部分很大時會花不少時間,可以使用頭插法(head insertion)
impl Solution {
pub fn reverse_between(
head: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
left: i32,
right: i32,
) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
if left == right || head.is_none() {
return head;
}
let mut dummy = Some(Box::new(ListNode { val: 0, next: head }));
let mut pre = &mut dummy;
for _ in 1..left {
pre = &mut pre.as_mut().unwrap().next;
}
// curr = B 段原頭
let mut curr: *mut ListNode = pre.as_mut().unwrap().next.as_mut().unwrap().as_mut();
for _ in 0..(right - left) {
unsafe {
// 拿出 curr.next
let mut node = (*curr).next.take().unwrap();
// tail 跳過 node
(*curr).next = node.next.take();
// node 插到 pre 後面
node.next = pre.as_mut().unwrap().next.take();
pre.as_mut().unwrap().next = Some(node);
}
}
dummy.unwrap().next
}
}
這題頭插法是問chat gpt的卡在智慧指標和借用檢查原則很久,讓我們在後面幾天來介紹Rust智慧指標
let mut curr: *mut ListNode = pre.as_mut().unwrap().next.as_mut().unwrap().as_mut();
