在Day23介紹了後序遍歷(Postorder Traversal),接這介紹剩下兩個遍歷,三種差別只在於 root 出現的時間點。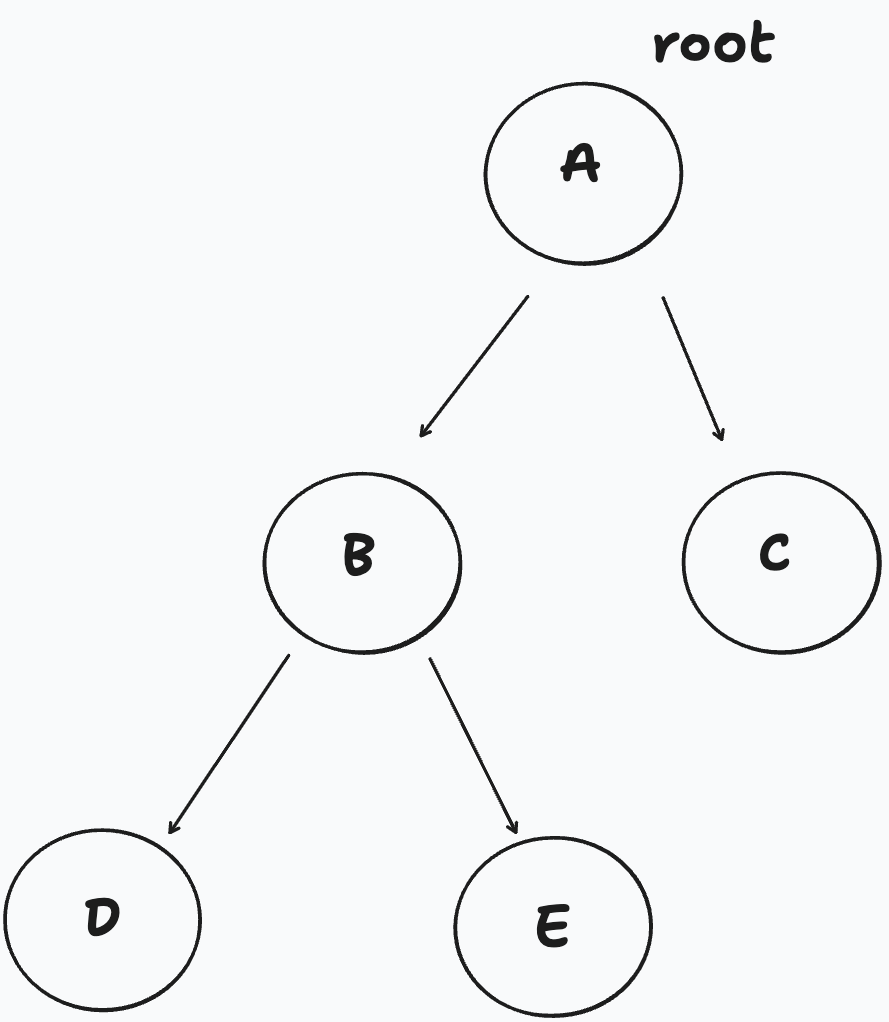
先訪問 root,再訪問左子樹,最後訪問右子樹,如圖走的順序A→B→D→E→C
主要用途:
序列化樹
題目:給一顆樹依照preorder順序將節點的值插入陣列回傳
輸入:root = [1,null,2,3]
輸出 : [1,2,3]
解法:依照preorder走法將節點的值存到陣列回傳
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn preorder_traversal(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut ans:Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
Self::get_vec(root,&mut ans);
ans
}
pub fn get_vec(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,v:&mut Vec<i32>){
let Some(node)=root else {return};
v.push(node.borrow().val);
Self::get_vec(node.borrow().left.clone(),v);
Self::get_vec(node.borrow().right.clone(),v);
}
}
提前判斷條件
題目:給兩顆樹判斷他是否相同
輸入:p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
輸出:true
解法:用preorder判斷每個節點值是否相同,如果不同回傳false提前結束,如果相同繼續往下比較子樹直到葉節點。
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn is_same_tree(p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
match((p,q)) {
(Some(node_p),Some(node_q))=>{
if(node_p.borrow().val==node_q.borrow().val) {
let left = Self::is_same_tree(node_p.borrow().left.clone(),node_q.borrow().left.clone());
let right = Self::is_same_tree(node_p.borrow().right.clone(),node_q.borrow().right.clone());
return left & right
} else {
return false
}
},
(Some(node_p),None)=>{
return false
},
(None,Some(node_q))=>{
return false
},
(None,None)=>{
return true
}
}
}
}
題目:判斷這棵樹是不是鏡像對稱
輸入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
輸出:true
解法:鏡像對稱,左子樹的左子樹=右子樹的右子樹,左子樹的右子樹=右子樹的左子樹,知道這個相等式就可以用leetcode 100 Same tree來解
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn is_symmetric(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
let Some(node)=root else { return true};
let left = node.borrow().left.clone();
let right = node.borrow().right.clone();
Self::is_same(left,right)
}
pub fn is_same(p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
match(p,q) {
(Some(p),Some(q))=>{
if(p.borrow().val==q.borrow().val){
let outter_sub_tree=Self::is_same(p.borrow().left.clone(),q.borrow().right.clone());
let inner_sub_tree=Self::is_same(p.borrow().right.clone(),q.borrow().left.clone());
return outter_sub_tree & inner_sub_tree
} else {
return false
}
},
(Some(n),None)|(None,Some(n))=>{
return false
},
(None,None)=>{
return true
}
}
}
}
先訪問左子樹,再訪問 root,最後訪問右子樹,走的順序D→B→E→A→C。
主要用途:
驗證一棵樹是不是 BST,並輸出有序資料
題目:給你一顆樹判斷是不是Binary Search Tree
輸入:root = [2,1,3]
輸出:true
解法:BST特徵 左節點比父節點小,右子樹比父節點大,依照這特性我們可以用inorder來判斷節點的值是否遞增,遞增極為BST
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn is_valid_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
let mut prev:i64=i32::MIN as i64 -1;
Self::inorder(root,&mut prev)
}
pub fn inorder(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,prev:&mut i64)->bool {
let Some(node) = root else { return true};
let b_n=node.borrow();
// push left
let l=Self::inorder(b_n.left.clone(),prev);
// push parent
let v = b_n.val as i64;
if(*prev>=v){
return false
} else {
*prev=v;
}
// push right
let r=Self::inorder(b_n.right.clone(),prev);
return l&r
}
}
找最小 / 最大 / 第 K 小元素
最小值:Inorder 的第一個節點
最大值:Inorder 的最後一個節點
第 K 小:Inorder 走到第 k 次訪問時
題目:找第k小的節點
輸入:root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
輸出:1
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn kth_smallest(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, k: i32) -> i32 {
let mut idx=0;
let mut ans=0;
Self::inorder(root,&mut idx,k,&mut ans);
ans
}
pub fn inorder(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,idx:&mut i32,k:i32,ans:&mut i32){
let Some(node)=root else { return };
let borrow_node= node.borrow();
//left
Self::inorder(borrow_node.left.clone(),idx,k,ans);
//parent
*idx+=1;
if(*idx==k){
*ans=borrow_node.val;
return
}
//right
Self::inorder(borrow_node.right.clone(),idx,k,ans);
}
}
我們在看樹的題目時都會看到這樣的輸入[3,9,20,null,null,15,7],所以能知道整個樹結構,那如果我們只有節點出現順序呢,能否知道整顆樹的結構?
如果我們有preorder或是postorder順序配合inorder順序就能重建樹
題目:給一顆樹節點的preorder和inorder順序,重建回樹狀結構
輸入:preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
輸出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
解法:
先找到root,preorder第一個值
知道root值後能在inorder切成[左子樹,跟節點,右子樹 ex 左子樹=[9] 右子樹=[15,20,7]
知道左子樹和右子樹數量後能在preorder切成[跟節點,左子樹,右子樹]
接著再對左子樹和右子數做步驟1~3直到全部排完
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn build_tree(preorder: Vec<i32>, inorder: Vec<i32>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if(preorder.len()==0){
return None
}
Self::build(&preorder[0..preorder.len()],&inorder[0..inorder.len()])
}
pub fn build(preorder:&[i32],inorder: &[i32])-> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if(preorder.len()==0){
return None
}
let root_val = preorder[0];
let mut idx = 0;
for i in 0..inorder.len(){
if(inorder[idx]==root_val){
break
}
idx+=1;
}
let node = Rc::new(RefCell::new(
TreeNode{
val:root_val,
left: Self::build(&preorder[1..idx+1],&inorder[0..idx]),
right: Self::build(&preorder[idx+1..],&inorder[idx+1..]),
}
));
return Some(node)
}
}
