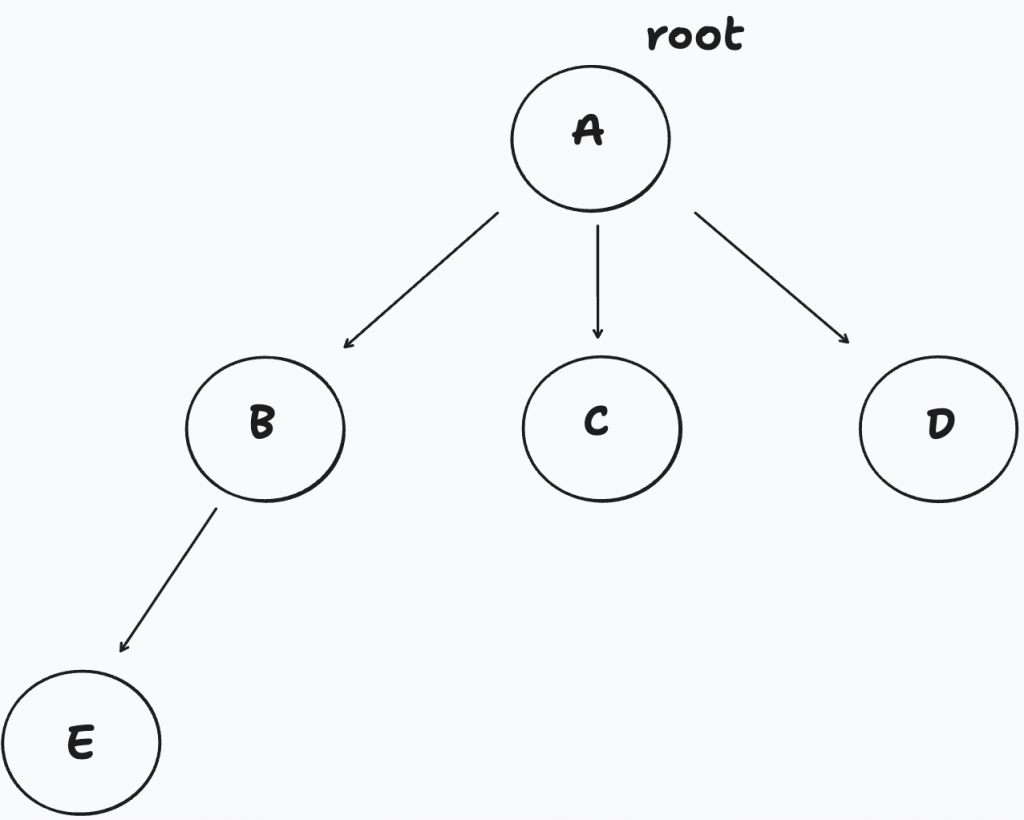
如圖來快速介紹下數的結構
A節點為這棵樹的根節點(root)
A是B、C、D的父節點(parent)
C、D、E沒有子節點 (children) 可以叫做葉節點**(leaf)**
有N個節點的樹有N-1個邊
不存在迴圈,所以到每個節點的方法只有一種
最多只有兩個子節點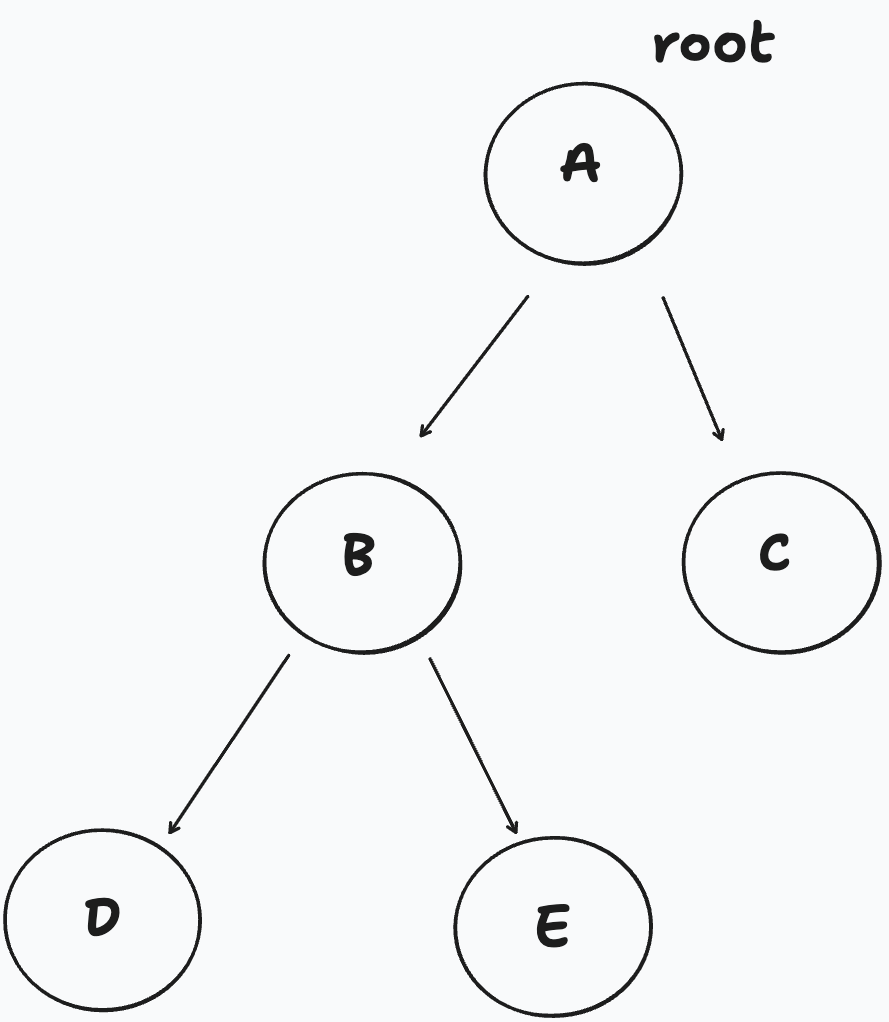
查詢與插入
Array → 查詢快 O(1),插入刪除慢 O(n)
LinkedList → 插入刪除快 O(1),查詢慢 O(n)
Tree (特別是平衡 BST) → 查詢、插入、刪除都 O(log n)
有序操作
HashMap 雖然查詢快 O(1),但沒有排序也不能範圍查詢需要找完全部HashMap O(n)
Tree(特別是 BST) inorder可得到排序結果,也能範圍查詢
可以表示層級關係
之前提到的Max Heap就是樹的延伸,再拿大最大值時O(1)
以上圖為例,我們先往下找子節點,沒有子節點或是找完了在往同輩去找。
A→B
B→D
沒有子節點回到B節點
B→E
沒有子節點回到B節點
子節點找完了回到A節點
A→C
沒有子節點回到A節點
我們解一題練習先
題目:給一顆樹返回的最大深度
輸入:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
輸出:3
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
解法1:
使用遞迴一直往下找到底,碰到None時回傳0
從底往上回傳時,判斷左、右子樹深度回傳最深的+1大表以這棵節點為跟節點的最大深度
跑完整顆樹回傳最大深度
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn max_depth(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
match root {
None => 0,
Some(node) => {
let l_depth = Self::max_depth(node.borrow().left.clone());
let r_depth = Self::max_depth(node.borrow().right.clone());
return l_depth.max(r_depth)+1;
}
}
}
}
時間複雜度 O(n),走完全部節點
解法2:
如stack中我們有看到遞迴能用stack來做
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn max_depth(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
if let None = root {
return 0
}
let mut stack:Vec<(Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>,i32)> = Vec::new();
let mut depth = 0;
stack.push((root.unwrap(),1));
while let Some((node,current_depth)) = stack.pop() {
if let Some(right) = node.borrow().right.clone() {
stack.push((right,current_depth+1));
}
if let Some(left) = node.borrow().left.clone() {
stack.push((left,current_depth+1));
}
depth = depth.max(current_depth);
}
depth
}
}
時間複雜度 O(n),走完全部節點
像這種先訪問左子樹,再訪問右子樹,最後訪問 root,以上面二元樹的圖為例走的順序D→E→B→C→A,叫做Postorder Traversal
主要用途:
計算樹的高度、節點數如 leetcode 104
更新全域最佳解
題目:找到兩個最遠的節點路徑長
解法:從底開始找左右子樹節點最長距離,並實時更新全域最長
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
// current left path len + right path len if greater then prev max update
// after recursion return max length
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn diameter_of_binary_tree(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut max_len=0;
Self::postorder(root,&mut max_len);
max_len
}
pub fn postorder(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,max_len:&mut i32)->i32{
let Some(node)=root else { return -1};
let b_n = node.borrow();
let left_path=Self::postorder(b_n.left.clone(),max_len);
let right_path=Self::postorder(b_n.right.clone(),max_len);
if(*max_len<left_path+right_path+2){
*max_len=left_path+right_path+2
}
return left_path.max(right_path)+1
}
}
刪除整棵樹時,先刪子樹再刪 root
題目:給一個目標值,刪掉等於這個值的葉節點
輸入:root = [1,2,3,2,null,2,4], target = 2
輸出:[1,null,3,null,4]
解法:從最底部開始刪,避免上層節點判斷到要刪但未刪得子節點而沒刪到。
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn remove_leaf_nodes(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target: i32) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
Self::post_order_delete(root,target)
}
pub fn post_order_delete(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target: i32) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let Some(node)=root else {return None};
let n_b = node.borrow();
let left = Self::post_order_delete(n_b.left.clone(),target);
let right = Self::post_order_delete(n_b.right.clone(),target);
if(n_b.val==target&&left.is_none()&&right.is_none()){
return None
}
return Some(Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode{
val:n_b.val,
left:left,
right:right
})))
}
}
