題目說明:給一棵二元樹以及一個目標數值,如果從根節點到葉節點有條路徑是可以將根節點的數值加總到葉節點等於給定的目標數值就回傳true,反之回傳false
Case 1: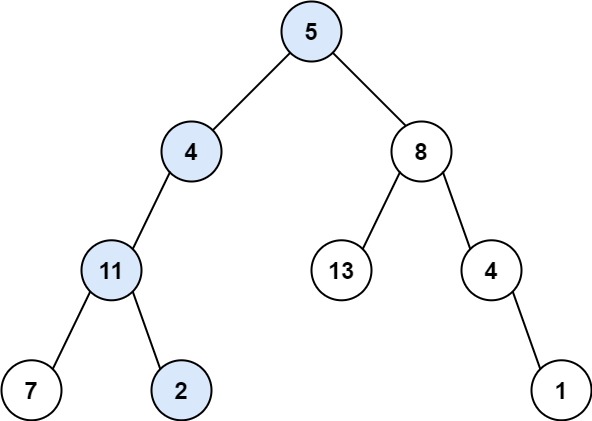
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
Output: true
Explanation: The root-to-leaf path with the target sum is shown.
Caser 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
Output: false
Explanation: There two root-to-leaf paths in the tree:
(1 --> 2): The sum is 3.
(1 --> 3): The sum is 4.
There is no root-to-leaf path with sum = 5.
Case 3:
Input: root = [], targetSum = 0
Output: false
Explanation: Since the tree is empty, there are no root-to-leaf paths.
解題思路:我們要考慮以下兩種的情況
因此用虛擬碼(pseudo code)可以這麼表示
haspath(root,target){
if(root==null){
return false //根節點為空必定是false
}
if (root.val==target){
return true//如果此樹只有根節點且根節點的值剛好等於target就回傳true
}
return haspath(root.left,target-root.val) || haspath(root.left,target-root.val)
//若根節點有左子樹或右子樹的話就持續追蹤根節點的左子樹或右子樹其中之一是否有路徑可以相加等於target
}
附上程式碼
Java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root == null) {
return false;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if(root.val == sum){
return true;
}
return false;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left,sum -root.val)||hasPathSum(root.right,sum - root.val);
}
}
Python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
if root==None:
return False
if root.val==targetSum:
return True
return self.hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum-root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum-root.val)
二元樹或是樹的問題大部分都是用遞迴(recursive)的方式去進行解題,在動手寫程式之前可以先思考一下邏輯或是拜訪方式(inorder, preorder, postorder),只要列出來解題基本上透過遞迴式子重複呼叫就可以得到答案了!
