終於來到第29天了!今天要介紹的也是這個系列中的最後一個模式,State 模式,我們就直接看範例吧,假設今天有個會員制度,當你存入銀行的錢有超過指定的標準,就會去提升你的會員階級,相反的如果裡面的存款是低於指定標準,就會去做降級。因此這個會員的階級狀態實際上是會一直變的,並且這個狀態裡面不只是紀錄一種屬性,同時可能會記錄一個以上的屬性以及一些判斷的方法。
會員的階級狀態就不僅僅用個字串去表示目前的階級,而是用一個狀態類別去做描述,並且狀態類別裡面會有自訂的方訪去判斷說目前的存款是否需要去做升級或者降級的動作,我們直接看範例吧!
將允許對象在內部狀態發生改變時改變它的行為,對象看起來好像修改了它的類。
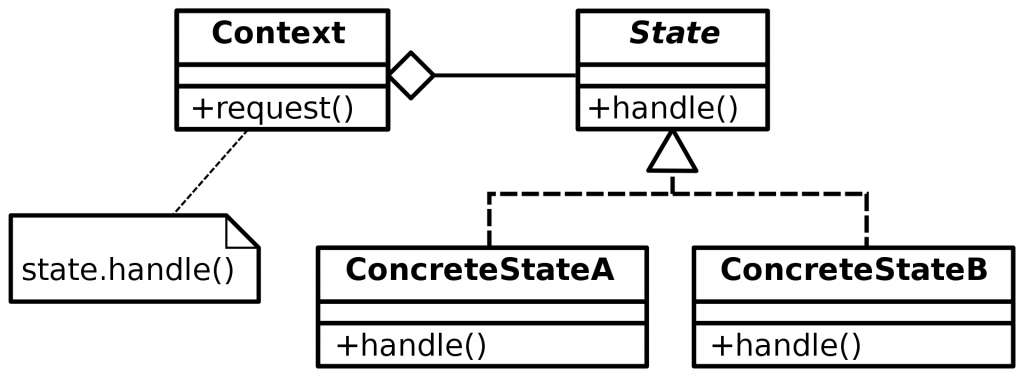
(圖片來源:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/State_pattern#/media/File:State_Design_Pattern_UML_Class_Diagram.svg)
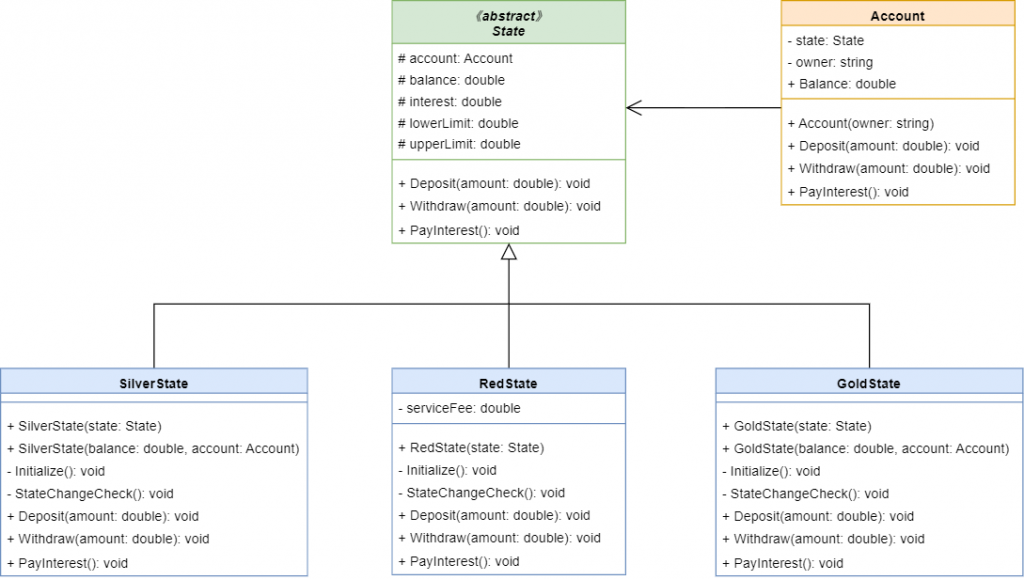
State是一個抽象類別,裡面最重要的是有共用的屬性Account以及Balance去記錄每個階級的狀態,屆時當狀態要做改變時就能直接共用目前的Account以及Balance。State的類別中,都會去覆寫方法,並且在Deposit、Withdraw以及PayInterest裡都會在後面去呼叫StateChangeCheck(),意即當做完存款的變化後,會去判斷目前的存款是否可以去升級或者降級,可以的話就將抽象類別裡的Account的State屬性賦予一個新狀態類別。using System;
namespace DAY29_State
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Account account = new Account("Howard");
account.Deposit(500.0);
account.Deposit(300.0);
account.Deposit(550.0);
account.PayInterest();
account.Withdraw(2000.00);
account.Withdraw(1100.00);
}
}
public abstract class State
{
// State中各個共通欄位
protected Account account;
protected double balance;
protected double interest;
protected double lowerLimit;
protected double upperLimit;
public Account Account
{
get { return account; }
set { account = value; }
}
public double Balance
{
get { return balance; }
set { balance = value; }
}
public abstract void Deposit(double amount);
public abstract void Withdraw(double amount);
public abstract void PayInterest();
}
public class RedState : State
{
private double serviceFee;
public RedState(State state)
{
// 將上個狀態的欄位值初始化給目前的State
this.balance = state.Balance;
this.account = state.Account;
Initialize();
}
// 數值初始化
private void Initialize()
{
interest = 0.0;
lowerLimit = -100.0;
upperLimit = 0.0;
serviceFee = 15.00;
}
public override void Deposit(double amount)
{
balance += amount;
StateChangeCheck();
}
public override void Withdraw(double amount)
{
amount = amount - serviceFee;
Console.WriteLine("沒有足夠的存款能提領!");
}
public override void PayInterest()
{
// No interest is paid
}
private void StateChangeCheck()
{
if (balance > upperLimit)
{
account.State = new SilverState(this);
}
}
}
public class SilverState : State
{
public SilverState(State state) : this(state.Balance, state.Account)
{
}
public SilverState(double balance, Account account)
{
this.balance = balance;
this.account = account;
Initialize();
}
private void Initialize()
{
interest = 0.0;
lowerLimit = 0.0;
upperLimit = 1000.0;
}
public override void Deposit(double amount)
{
balance += amount;
StateChangeCheck();
}
public override void Withdraw(double amount)
{
balance -= amount;
StateChangeCheck();
}
public override void PayInterest()
{
balance += interest * balance;
StateChangeCheck();
}
// 設定狀態轉換的條件
private void StateChangeCheck()
{
if (balance < lowerLimit)
{
account.State = new RedState(this);
}
else if (balance > upperLimit)
{
account.State = new GoldState(this);
}
}
}
public class GoldState : State
{
public GoldState(State state) : this(state.Balance, state.Account)
{
}
public GoldState(double balance, Account account)
{
this.balance = balance;
this.account = account;
Initialize();
}
private void Initialize()
{
interest = 0.05;
lowerLimit = 1000.0;
upperLimit = 10000000.0;
}
public override void Deposit(double amount)
{
balance += amount;
StateChangeCheck();
}
public override void Withdraw(double amount)
{
balance -= amount;
StateChangeCheck();
}
public override void PayInterest()
{
balance += interest * balance;
StateChangeCheck();
}
// 設定狀態轉換的條件
private void StateChangeCheck()
{
if (balance < 0.0)
{
account.State = new RedState(this);
}
else if (balance < lowerLimit)
{
account.State = new SilverState(this);
}
}
}
public class Account
{
private State state;
private string owner;
public Account(string owner)
{
this.owner = owner;
// 初始為 SilverState
this.state = new SilverState(0.0, this);
}
public double Balance
{
get { return state.Balance; }
}
public State State
{
get { return state; }
set { state = value; }
}
public void Deposit(double amount)
{
state.Deposit(amount);
Console.WriteLine($"{owner}存入 NT:{amount} ---");
Console.WriteLine($" 存款 = NT:{Balance}");
Console.WriteLine($" 階級 = {State.GetType().Name}\n");
}
public void Withdraw(double amount)
{
state.Withdraw(amount);
Console.WriteLine($"{owner}提款 NT:{amount} ---");
Console.WriteLine($" 存款 = NT:{Balance}");
Console.WriteLine($" 階級 = {State.GetType().Name}\n");
}
public void PayInterest()
{
state.PayInterest();
Console.WriteLine($"利息給{owner} --- ");
Console.WriteLine($" 存款 = NT:{Balance}");
Console.WriteLine($" 階級 = {State.GetType().Name}\n");
}
}
}
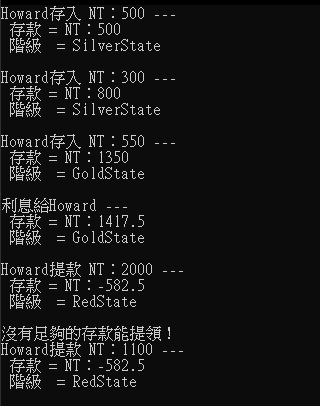
藉由 State 模式,我們可以將狀態抽出來,而並非綁定在物件上,也因此可以減少掉很多的if else,邏輯判斷寫在不同的State實體類別,也提高了内聚性。從UML來看,State 模式其實跟第9天介紹的 Strategy 模式很類似,差別在於每個實體類別實際上是不知道其他實體類別的存在,也沒有相互引用,但 State 模式的各個實體類別彼此互相知道,且都能去互相引用,達到狀態的轉變。
