今天回歸到大綱中,關於音樂的部分。我標題通常喜歡生動一點詞彙來表達,以專業的口吻就是資料前處理、資料視覺化、資料探勘。
首先要有辦法處理音訊檔案,我們可以使用pydub。
但比較麻煩的是如果在自己的電腦,需要有ffmpeg 才能匯入mp3等格式,不然就只能用wav檔,
但如果在Colab上就直接有ffmpeg 能使用。範例如下,匯入後,用list的運算就能切片、串接、重覆等,效果上用加減值就能直接調大調小音量,也能淡入淡出和轉場,此外還能倒著放!
from pydub import AudioSegment
song = AudioSegment.from_wav("Maple_Leaf.wav")
#Slice
first_10_seconds = song[:10 * 1000]
last_5_seconds = song[-5 * 1000:]
# boost volume by 6dB
beginning = first_10_seconds + 6
# reduce volume by 3dB
end = last_5_seconds - 3
#Concatenate audio (add one file to the end of another)
without_the_middle = beginning + end
# 1.5 second crossfade
with_style = beginning.append(end, crossfade=1500)
# repeat the clip twice
do_it_over = with_style * 2
# 2 sec fade in, 3 sec fade out
awesome = do_it_over.fade_in(2000).fade_out(3000)
awesome.export("awesome.wav", format="wav")
backwards = song.reverse()
backwards.export("backwards.wav", format="wav")
波紋的部分,在stackoverflow裡就有解答,但要用第二個,第一個在下面討論串中也有人提出我遇到的error的問題,第二個已經包好成function直接可以拿來用:
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import scipy.io.wavfile as wav
from numpy.lib import stride_tricks
""" short time fourier transform of audio signal """
def stft(sig, frameSize, overlapFac=0.5, window=np.hanning):
win = window(frameSize)
hopSize = int(frameSize - np.floor(overlapFac * frameSize))
# zeros at beginning (thus center of 1st window should be for sample nr. 0)
samples = np.append(np.zeros(int(np.floor(frameSize/2.0))), sig)
# cols for windowing
cols = np.ceil( (len(samples) - frameSize) / float(hopSize)) + 1
# zeros at end (thus samples can be fully covered by frames)
samples = np.append(samples, np.zeros(frameSize))
frames = stride_tricks.as_strided(samples, shape=(int(cols), frameSize), strides=(samples.strides[0]*hopSize, samples.strides[0])).copy()
frames *= win
return np.fft.rfft(frames)
""" scale frequency axis logarithmically """
def logscale_spec(spec, sr=44100, factor=20.):
timebins, freqbins = np.shape(spec)
scale = np.linspace(0, 1, freqbins) ** factor
scale *= (freqbins-1)/max(scale)
scale = np.unique(np.round(scale))
# create spectrogram with new freq bins
newspec = np.complex128(np.zeros([timebins, len(scale)]))
for i in range(0, len(scale)):
if i == len(scale)-1:
newspec[:,i] = np.sum(spec[:,int(scale[i]):], axis=1)
else:
newspec[:,i] = np.sum(spec[:,int(scale[i]):int(scale[i+1])], axis=1)
# list center freq of bins
allfreqs = np.abs(np.fft.fftfreq(freqbins*2, 1./sr)[:freqbins+1])
freqs = []
for i in range(0, len(scale)):
if i == len(scale)-1:
freqs += [np.mean(allfreqs[int(scale[i]):])]
else:
freqs += [np.mean(allfreqs[int(scale[i]):int(scale[i+1])])]
return newspec, freqs
""" plot spectrogram"""
def plotstft(audiopath, binsize=2**10, plotpath=None, colormap="jet"):
samplerate, samples = wav.read(audiopath)
s = stft(samples, binsize)
sshow, freq = logscale_spec(s, factor=1.0, sr=samplerate)
ims = 20.*np.log10(np.abs(sshow)/10e-6) # amplitude to decibel
timebins, freqbins = np.shape(ims)
print("timebins: ", timebins)
print("freqbins: ", freqbins)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 7.5))
plt.imshow(np.transpose(ims), origin="lower", aspect="auto", cmap=colormap, interpolation="none")
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel("time (s)")
plt.ylabel("frequency (hz)")
plt.xlim([0, timebins-1])
plt.ylim([0, freqbins])
xlocs = np.float32(np.linspace(0, timebins-1, 5))
plt.xticks(xlocs, ["%.02f" % l for l in ((xlocs*len(samples)/timebins)+(0.5*binsize))/samplerate])
ylocs = np.int16(np.round(np.linspace(0, freqbins-1, 10)))
plt.yticks(ylocs, ["%.02f" % freq[i] for i in ylocs])
if plotpath:
plt.savefig(plotpath, bbox_inches="tight")
else:
plt.show()
plt.clf()
return ims
ims = plotstft('Maple_Leaf.wav')
這是周杰倫的歌曲-楓的結果: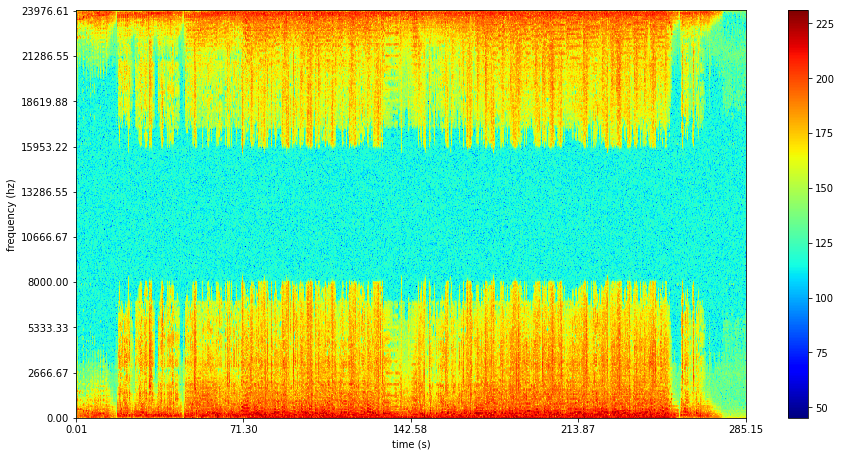
omnizart是個可以採譜的library,雖然我不是音樂家,但這聽起來很酷吧。所謂採譜就是它可以將輸入分離出鋼琴、鼓聲、人聲、和弦和節拍等。這是一個有發表paper的作品,雖然它有Colab環境,但我跑的結果是有error的,可以直接看說明文件中的範例。
