In Factory pattern, we create object without exposing the creation logic to the client and refer to newly created object using a common interface
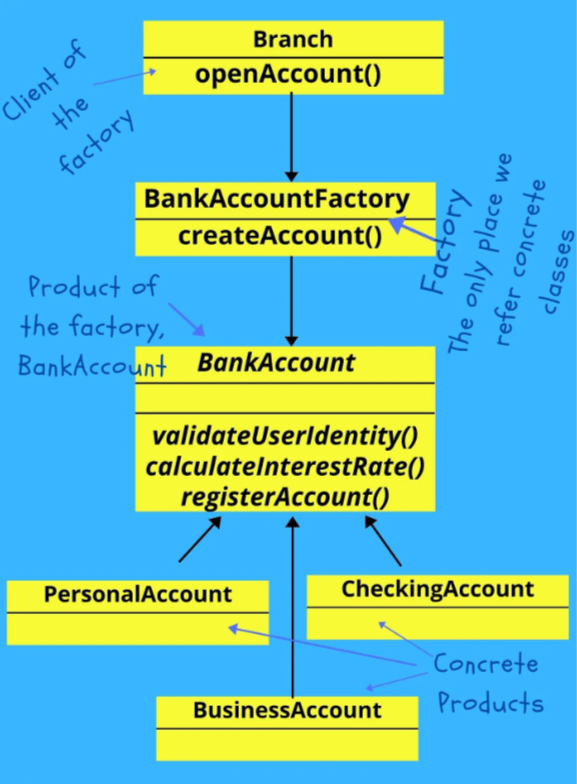
// 定義一個銀行帳戶的基礎接口
class BankAccount {
public:
virtual ~BankAccount() {}
virtual void validateUserIdentity() = 0;
virtual void calculateInterestRate() = 0;
virtual void registerAccount() = 0;
};
// 三種具體的銀行帳戶類型
class PersonalAccount : public BankAccount {
// 具體方法的實現可以根據需要填寫
void validateUserIdentity() override {}
void calculateInterestRate() override {}
void registerAccount() override {}
};
class BusinessAccount : public BankAccount {
void validateUserIdentity() override {}
void calculateInterestRate() override {}
void registerAccount() override {}
};
class CheckingAccount : public BankAccount {
void validateUserIdentity() override {}
void calculateInterestRate() override {}
void registerAccount() override {}
};
// 銀行帳戶工廠類
class BankAccountFactory {
public:
// 根據帳戶類型創建相應的帳戶對象
BankAccount* createAccount(const std::string& type) {
BankAccount* bankAccount = nullptr;
if (type == "P") {
bankAccount = new PersonalAccount();
} else if (type == "B") {
bankAccount = new BusinessAccount();
} else if (type == "C") {
bankAccount = new CheckingAccount();
} else {
std::cout << "Invalid type" << std::endl;
}
return bankAccount;
}
};
// 銀行分行類
class Branch {
private:
BankAccountFactory* bankAccountFactory;
public:
Branch(BankAccountFactory* factory) : bankAccountFactory(factory) {}
// 根據賬戶類型開設新賬戶
BankAccount* openAccount(const std::string& type) {
BankAccount* bankAccount = bankAccountFactory->createAccount(type);
bankAccount->validateUserIdentity();
bankAccount->calculateInterestRate();
bankAccount->registerAccount();
return bankAccount;
}
};
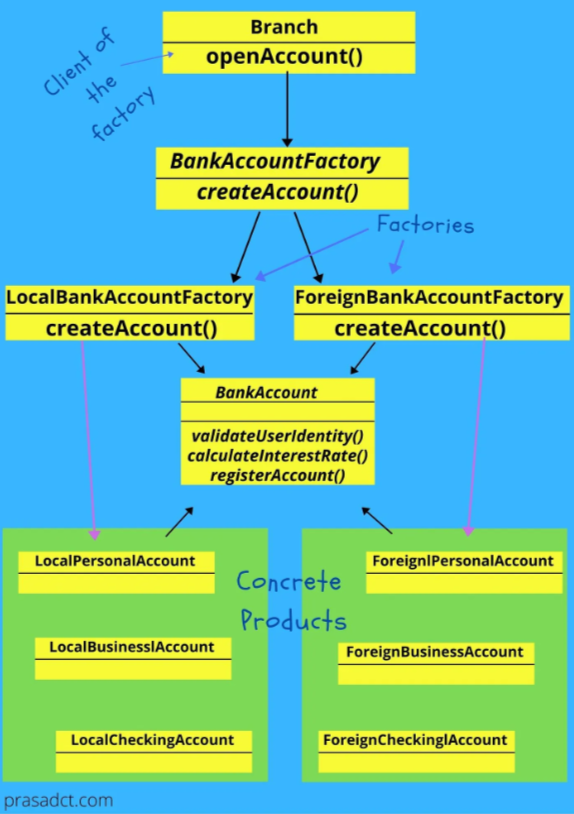
class Branch {
private:
std::unique_ptr<BankAccountFactory> bankAccountFactory;
public:
Branch(std::unique_ptr<BankAccountFactory> factory) : bankAccountFactory(std::move(factory)) {}
BankAccount* createBankAccount(const std::string& type) {
return bankAccountFactory->createAccount(type);
}
};
int main() {
std::unique_ptr<BankAccount> bankAccount;
std::cout << "Please enter" << std::endl
<< " P for Personal account" << std::endl
<< " B for Business account" << std::endl
<< " C for Checking account" << std::endl
<< "----------------------------" << std::endl;
std::string type;
std::getline(std::cin, type);
std::cout << "Please enter" << std::endl
<< " 1 for Local" << std::endl
<< " 2 for Foreign" << std::endl
<< "----------------------------" << std::endl;
int branch;
std::cin >> branch;
// 這邊再度改進了前一個範例的工廠模式,現在可以針對不同分行做出更彈性的 createBankAccount
if (branch == 1) {
Branch localBranch(std::make_unique<LocalBankAccountFactory>());
bankAccount.reset(localBranch.createBankAccount(type));
} else if (branch == 2) {
Branch foreignBranch(std::make_unique<ForeignBankAccountFactory>());
bankAccount.reset(foreignBranch.createBankAccount(type));
}
return 0;
}
[1]. https://www.tutorialspoint.com/design_pattern/factory_pattern.htm
[2]. https://prasadct.medium.com/factory-method-design-patternfactory-method-design-pattern-with-real-world-example-4ee909a24ab6
