昨天給大家介紹了二元樹,今天帶大家來看程式碼:
首先demo用linked list做binary tree,圖應該看起來像這樣: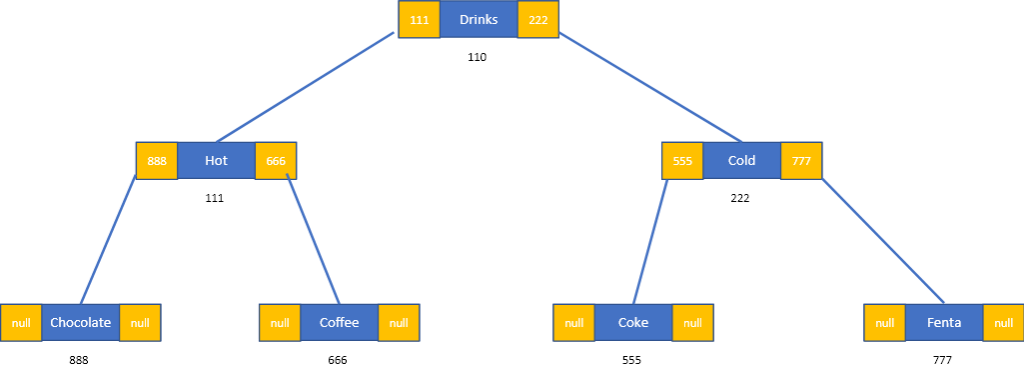
圖1 下面example對應到的樹畫出來應該長這樣。
# 我們先做TreeNode物件,這個物件裡有自己的值(data)、左邊分支(leftchild)、右邊分支(rightchild)
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.leftchild = None
self.rightchild = None
# 我們先做一個以BT為root的小tree來看看 (畫出來如圖1)
BT = TreeNode('Drinks')
BT.leftchild = TreeNode('Hot')
BT.rightchild = TreeNode('Cold')
BT.leftchild.leftchild = TreeNode('Chocolate')
BT.leftchild.rightchild = TreeNode('Coffee')
BT.rightchild.rightchild = TreeNode('Fenta')
BT.rightchild.leftchild = TreeNode('Coke')
我們先從depth first traversal開始看,猶如我們昨天介紹:
pre-order traversal: root -> left subtree -> right subtree
in-order traversal: left subtree -> root -> right subtree
post-order traversal: left subtree -> right subtree -> root
# pre-order traversal:
# root -> left subtree -> right subtree
# 時間複雜度: O(n), 空間複雜度: O(n)
def preordertraversal(node):
if not node:
return
print(node.data)
preordertraversal(node.leftchild)
preordertraversal(node.rightchild)
preordertraversal(BT)
>> Drinks
Hot
Chocolate
Coffee
Cold
Coke
Fenta
# Inorder traversal:
# left subtree -> root node -> right subtree
# 時間複雜度: O(n), 空間複雜度: O(n)
def inordertraversal(node):
if not node:
return
inordertraversal(node.leftchild)
print(node.data)
inordertraversal(node.rightchild)
inordertraversal(BT)
>> Chocolate
Hot
Coffee
Drinks
Coke
Cold
Fenta
# Postorder traversal:
# left subtree -> right subtree -> root node
def postordertraversal(node):
if not node:
return
postordertraversal(node.leftchild)
postordertraversal(node.rightchild)
print(node.data)
postordertraversal(BT)
>> Chocolate
Coffee
Hot
Coke
Fenta
Cold
Drinks
Level-order traversal (Breadth first search廣度優先搜尋)
搭配我們之前做的Queue.py檔
# 載入我們先前做的Queue.py檔 (這個在vscode裡做會方便些),但用jupyter notebook的可以直接看下面的deque方法
# 時間複雜度: O(n), 空間複雜度: O(n)
import Queue as queue
def levelordertraversal(node):
if not node:
return
customqueue = queue.Queue()
customqueue.enqueue(node)
while not (customqueue.isEmpty()):
root = customqueue.dequeue()
print(root.value.data)
if root.value.leftchild is not None:
customqueue.enqueue(root.value.leftchild)
if root.value.rightchild is not None:
customqueue.enqueue(root.value.rightchild)
levelordertraversal(BT)
>> Drinks
Hot
Cold
Chocolate
Coffee
Coke
Fenta
當然我們也可以搭配python module collections裡deque,出來的結果也一樣,兩種方法都可以!如果是在jupyter notebook玩的話,import deque可能就會方便許多。
from collections import deque
def levelordertraversal2(node):
if not node:
return
customqueue = deque()
customqueue.append(node)
while len(customqueue) != 0:
root = customqueue.popleft()
print(root.data)
if root.leftchild is not None:
customqueue.append(root.leftchild)
if root.rightchild is not None:
customqueue.append(root.rightchild)
levelordertraversal2(BT)
>> Drinks
Hot
Cold
Chocolate
Coffee
Coke
Fenta
接著我們來試著做搜尋功能,看想找的值是否在binary中存在,其實可以從任一個traversal改,下面就用上面的level-order traversal改,時間複雜度: O(n),空間複雜度: O(n):
def searchBT(node, target):
customqueue = deque()
customqueue.append(node)
while len(customqueue) != 0:
root = customqueue.popleft()
if root.data == target:
return 'Found!'
if root.leftchild is not None:
customqueue.append(root.leftchild)
if root.rightchild is not None:
customqueue.append(root.rightchild)
return 'Not Found!'
print(searchBT(BT, 'Chocolate'))
>> Found!
print(searchBT(BT, 'Apple'))
>> Not Found!
在tree裡插入新的值,這裡我們還是用Queue做
# 時間複雜度: O(n),空間複雜度: O(n)。
def insertNode(node, new_node):
customqueue = deque()
customqueue.append(node)
while len(customqueue) != 0:
root = customqueue.popleft()
if root.leftchild is not None:
customqueue.append(root.leftchild)
else:
root.leftchild = new_node
return 'The value is inserted'
if root.rightchild is not None:
customqueue.append(root.rightchild)
else:
root.rightchild = new_node
return 'The value is inserted'
tea = TreeNode('Tea')
print(insertNode(BT, tea))
levelordertraversal(BT)
>> The value is inserted
>> Drinks
Hot
Cold
Chocolate
Coffee
Coke
Fenta
Tea
刪除最後/最深的值(deepest node),這一步是為了之後要寫刪除特定node功能的時候,deepest node要取代被刪除的node的位子,所以這個在寫的時候,除了刪除deepest node外,要回傳deepest node的值。
# 取得deepest node
# 時間複雜度: O(n),空間複雜度: O(n)。
def getDeepestNode(node):
customqueue = deque()
customqueue.append(node)
while len(customqueue)!=0:
root = customqueue.popleft()
if root.leftchild is not None:
customqueue.append(root.leftchild)
if root.rightchild is not None:
customqueue.append(root.rightchild)
deepestnode = root
return deepestnode
print(getDeepestNode(BT).data)
>> Tea
# 刪除deepest node
# 時間複雜度: O(n),空間複雜度: O(n)。
def deletedeepestNode(node):
dnode = getDeepestNode(node)
customqueue = deque()
customqueue.append(node)
while len(customqueue)!=0:
root = customqueue.popleft()
if root == dnode:
root = None
if root.leftchild is not None:
if root.leftchild == dnode:
root.leftchild = None
else:
customqueue.append(root.leftchild)
if root.rightchild is not None:
if root.rightchild == dnode:
root.rightchild = None
else:
customqueue.append(root.rightchild)
return dnode
print(deletedeepestNode(BT).data)
>> Tea
# Traversal check
levelordertraversal(BT)
>> Drinks
Hot
Cold
Chocolate
Coffee
Coke
Fenta
# 刪除樹裡的特定值
# 時間複雜度: O(n),空間複雜度: O(n)。
def deleteNode(node, target):
customqueue = deque()
customqueue.append(node)
dnode = deletedeepestNode(BT)
while len(customqueue) != 0:
root = customqueue.popleft()
if root.data == target:
root.data = dnode.data
if root.leftchild is not None:
if root.leftchild.data == target:
root.leftchild.data = dnode.data
customqueue.append(root.leftchild)
if root.rightchild is not None:
if root.rightchild.data == target:
root.rightchild.data = dnode.data
customqueue.append(root.rightchild)
return f'The node is deleted!{target} is deleted. {dnode.data} replace the position'
print(deleteNode(BT, 'Coffee'))
>> The node is deleted!Coffee is deleted. Fenta replace the position
# traversal check
levelordertraversal(BT)
>> Drinks
Hot
Cold
Chocolate
Fenta
Coke
刪除整個二元樹,時間複雜度: O(1),空間複雜度: O(1)。
def deleteBT(rootnode):
rootnode.data = None
rootnode.leftchild = None
rootnode.rightchild = None
return 'The BT is successfully deleted!'
print(deleteBT(BT))
>> The BT is successfully deleted!
levelordertraversal(BT)
>> None
到這裡,相信大家都相當熟悉用linked list做Binary Tree了。那明天我們要用python list做Binary Tree,可能會比用linked list更容易理解,然後我們在統整一下用兩種不同方法的時間與空間複雜度。
參考資料:
本文主要為udemy課程: The Complete Data Structures and Algorithms Course in Python的學習筆記,有興趣的人可以自己上去看看。
