昨天剛學習 Coroutine 就想直接配合 OKHttp 實作,然後就失敗了,今天筆者就從簡單的開始學習吧!
今天來實作 Google Codelab,一起來從頭走一遍。
為什麼一直在提 Thread 或是 Coroutine? 因為在 Android 上,我們需要避免主線程阻塞的情況發生,如果主線程花費過多的時間來執行任務,就會有 ANR ( Application Not Responding ) 的狀況,想深入了解可以參考這邊。
所以我們在處理耗時任務時,大多需要其他的工作執行緒以避免上述的 ANR 發生。最直觀的像是建立新的執行緒、使用 Handler 處理,以及本篇的主角,也是 Kotlin 的親兒子 - Coroutine。
Coroutine 可看作是一種輕量化的執行緒,主要用來協同處理多個程序。在管理和操作執行上非常輕鬆,可以輕鬆切換執行緒、讓非同步的程式碼用同步的程式碼來撰寫以及輕鬆取消 Coroutine 的執行,還有脫離 Callback Hell 等等。
這是使用 Callback 的程式碼 :
// Async callbacks
networkRequest { result ->
// Successful network request
databaseSave(result) { rows ->
// Result saved
}
}
改用 Coroutine:
// The same code with coroutines
val result = networkRequest()
// Successful network request
databaseSave(result)
// Result saved
看出差異了嗎? 非同步執行和一般同步程式碼的寫法一樣,閱讀起來十分輕鬆、直觀。
打開 coroutines-codelab
加入 Coroutine library
dependencies {
...
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:x.x.x"
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:x.x.x"
}
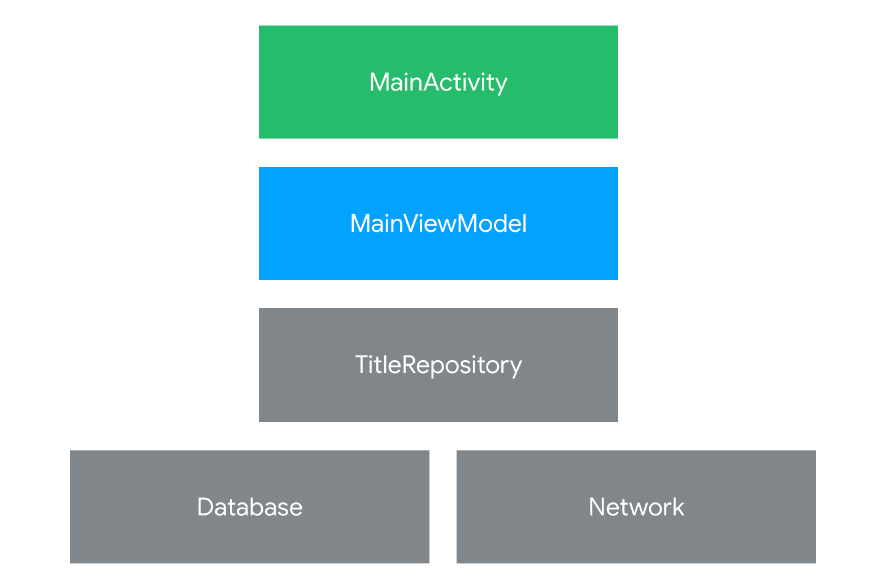
這是專案的架構圖
在 Android 上,主線程是一個負責處理畫面更新的線程,一個沒處理好就很容易造成使用者體驗不佳。主線程的更新每秒約 60 幀,但像是解析 JSON 數據、寫入資料庫或是向 Server 請求資料等等,其所花費的時間都比主線程更新的時間還長,以至於畫面卡頓,甚至會造成 crash。
先來看一段使用 callback 取得網路請求資料的程式碼 :
// Slow request with callbacks
@UiThread
fun makeNetworkRequest() {
// The slow network request runs on another thread
slowFetch { result ->
// When the result is ready, this callback will get the result
show(result)
}
// makeNetworkRequest() exits after calling slowFetch without waiting for the result
}
suspend關鍵字 : 標記函式為可供協程使用的函式,makeNetworkRequest() 和 slowFetch() 都是 suspend 函式。
suspend 不會指定執行程式碼的協程,掛上後可直接在工作執行緒或是主線程上執行。
// Slow request with coroutines
@UiThread
suspend fun makeNetworkRequest() {
// slowFetch is another suspend function so instead of
// blocking the main thread makeNetworkRequest will `suspend` until the result is
// ready
val result = slowFetch()
// continue to execute after the result is ready
show(result)
}
// slowFetch is main-safe using coroutines
suspend fun slowFetch(): SlowResult { ... }
以下範例為使用 Coroutine 向網路取得資料後,儲存於本地端的的任務 :
// Request data from network and save it to database with coroutines
// Because of the @WorkerThread, this function cannot be called on the
// main thread without causing an error.
@WorkerThread
suspend fun makeNetworkRequest() {
// slowFetch and anotherFetch are suspend functions
val slow = slowFetch()
val another = anotherFetch()
// save is a regular function and will block this thread
database.save(slow, another)
}
// slowFetch is main-safe using coroutines
suspend fun slowFetch(): SlowResult { ... }
// anotherFetch is main-safe using coroutines
suspend fun anotherFetch(): AnotherResult { ... }
在 Kotlin 中,所有的 coroutine 都會在 CoroutineScope 中執行,主要是用來控制 coroutine 的生命週期,我們可以用來啟動和取消被啟動的 coroutine。
又稱為調度器,用來啟動或是切換線程。通常會使用 Dispatcher.Main 啟動協程,因為最後 UI 的更新都會回到主線程上,而且 coroutine 在被掛起後除了不會阻塞主線程外,還能隨時透過 Dispatcher 切換到其他的線程。
呼~今天先對 coroutine 的家庭成員有基本的認識,之後在實作時才不會一頭霧水!
晚上很開心的去拿 i15,對我就是那個花大錢買 USB 2.0 的盤子,現在 andoid 和 iphone 都有拉可以實際比較 UI 上的設計和操作拉
