Balvis記錄每個選擇的基底和測量結果,並測量過所有光子後,他與 Asja 通過公共的古典通道聯繫,Asja 公布創造每個光子時所選擇的基底。
此時,Asja 與 Balvis 可比對選擇相同的基底並且捨棄不同基底的量測結果 (根據量子力學,隨機量測時,錯誤大約佔有一半) ,最後利用剩下的位元還原為他們共有的金鑰。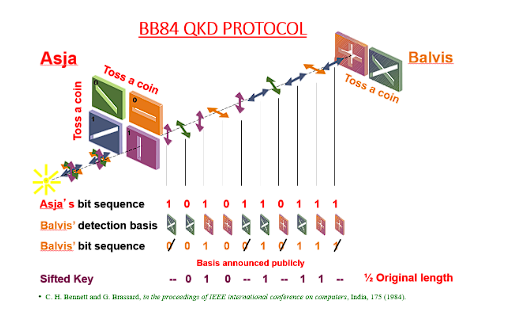
# import all necessary objects and methods for quantum circuits
from qiskit import QuantumRegister, ClassicalRegister, QuantumCircuit, execute, Aer
from random import randrange
def print_outcomes_in_reserve(counts): # takes a dictionary variable
for outcome in counts: # for each key-value in dictionary
reverse_outcome = ''
for i in outcome: # each string can be considered as a list of characters
reverse_outcome = i + reverse_outcome # each new symbol comes before the old symbol(s)
return reverse_outcome
#Source: awards/teach_me_qiskit_2018/cryptography/Cryptography.ipynb
def SendState(qc1, qc2, qc1_name):
''' This function takes the output of a circuit qc1 (made up only of x and
h gates and initializes another circuit qc2 with the same state
'''
# Quantum state is retrieved from qasm code of qc1
qs = qc1.qasm().split(sep=';')[4:-1]
# Process the code to get the instructions
for index, instruction in enumerate(qs):
qs[index] = instruction.lstrip()
# Parse the instructions and apply to new circuit
for instruction in qs:
if instruction[0] == 'x':
if instruction[5] == '[':
old_qr = int(instruction[6:-1])
else:
old_qr = int(instruction[5:-1])
qc2.x(qreg[old_qr])
elif instruction[0] == 'h':
if instruction[5] == '[':
old_qr = int(instruction[6:-1])
else:
old_qr = int(instruction[5:-1])
qc2.h(qreg[old_qr])
elif instruction[0] == 'm': # exclude measuring:
pass
else:
raise Exception('Unable to parse instruction')
qreg = QuantumRegister(16) # quantum register with 16 qubits
creg = ClassicalRegister(16) # classical register with 16 bits
# Quantum circuit for Asja state
asja = QuantumCircuit(qreg, creg, name='Asja')
send=[] #Initial bit string to send
asja_basis=[] #Register to save information about encoding basis
balvis_basis=[] #Register to save information about decoding basis
#Creating random bit string
for i in range(16):
bit = randrange(2)
send.append(bit)
#Preparing qubits, apply X gate if bit is equal 1
for i, n in enumerate(send):
if n==1:
asja.x(qreg[i]) # apply x-gate
#send_str = ''.join(str(e) for e in send)
#Encoding
for i in range(16):
r=randrange(2) #Asja randomly pick a basis
if r==0: #if bit is 0, then she encodes in Z basis
asja_basis.append('Z')
else: #if bit is 1, then she encodes in X basis
asja.h(qreg[i])
asja_basis.append('X')
balvis = QuantumCircuit(qreg, creg, name='Balvis') #Defining Balvis circuit
SendState(asja, balvis, 'Asja') #Asja sends states to Balvis
#Balvis measures qubits
for i in range(16):
r=randrange(2) #Balvis randomly pick a basis
if r==0: #if bit is 0, then measures in Z basis
balvis.measure(qreg[i],creg[i])
balvis_basis.append('Z')
else: #if bit is 1, then measures in X basis
balvis.h(qreg[i])
balvis.measure(qreg[i],creg[i])
balvis_basis.append('X')
job = execute(balvis,Aer.get_backend('qasm_simulator'),shots=1) #Note that Balvis only has one shot to measure qubits
counts = job.result().get_counts(balvis) # counts is a dictionary object in python
counts = print_outcomes_in_reserve(counts)
#Saving Balvis received string as a list
received = list(map(int, counts))
print("Asja sent:", send)
print("Asja encoding basis:", asja_basis)
print("Balvis received:", received)
print("Balvis decoding basis:", balvis_basis)
#Sifting
asja_key=[] #Asjas register for matching rounds
balvis_key=[] #Balvis register for matching rounds
for j in range(0,len(asja_basis)): #Going through list of bases
if asja_basis[j] == balvis_basis[j]: #Comparing
asja_key.append(send[j])
balvis_key.append(received[j]) #Keeping key bit if bases matched
else:
pass #Discard round if bases mismatched
print("Asjas key =", asja_key)
print("Balvis key =", balvis_key)
透過這套程序,他們之間就完成了Sifting。
完成Sifting後,此時雙方透過計算位元,會得知有多少錯誤發生,透過互相比較錯誤的發生,便可以知道他們的通訊有沒有被竊聽,這叫做QBER。根據QBER,Asja 和 Balvis 可以估計竊聽者在量子傳輸階段獲得的資訊。
對於無噪音版本的BB84
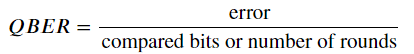
#QBER
rounds = len(asja_key)//3 #To divide without remainer, use //
errors=0
for i in range(rounds):
bit_index = randrange(len(asja_key))
tested_bit = asja_key[bit_index]
print ("Asja randomly selected bit index =", bit_index, ", and its value is = ", tested_bit)
if asja_key[bit_index]!=balvis_key[bit_index]: #comparing tested rounds
errors=errors+1 #calculating errors
#removing tested bits from key strings
del asja_key[bit_index] #Use del to specify the index of the element you want to delete
del balvis_key[bit_index]
QBER=errors/rounds #calculating QBER
print("QBER value =", QBER)
print("Asja's secret key =", asja_key)
print("Balvis' secret key =", balvis_key)
大家有空可以嘗試把Sifting 和 QBER 合在一起寫個24位元的版本。
參考資料:womanium教材和QKD極簡介
