油:Oil
醋:vinegar
首先生成 v 與 o ,分別叫做醋變量數量、油變量數量,
我們會使用 n 個未知數,n = o + v
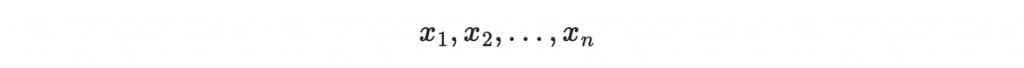
其中前 v 個我們叫做「醋變量」、後 o 個叫做「油變量」
我們把以下的多項式叫做「油醋多項式」
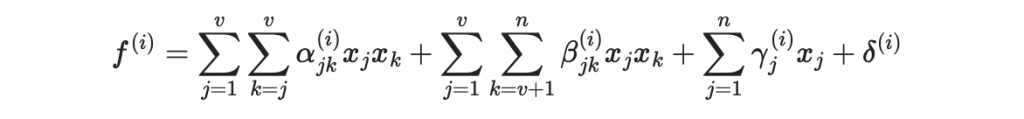
其中的係數通常是隨機生成。注意到第一大項只有醋變量參與,第二大項醋變量油變量都有參與,第三大項是一次項,最後是常數。
關鍵點在於:如果已知 alpha, beta, gamma, delta 、也已知 f^{(i)} 、也已知醋變量的真實數字,則剩餘的方程式是油變量的線性方程式。
我們仍然使用雙極構造法,其中的中間映射就是由 o 個形如上述的油醋多項式組成。
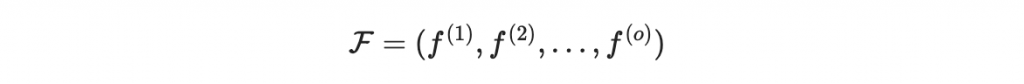
接著注意到,在 F 後面接上一個仿射變換 S 後,出來的 o 個多項式仍然是油醋多項式。那因為我們的 F 本來就是隨機生成,所以接不接 S 無所謂。
根據雙極構造法,我們會再生成一個仿射變換 T。
公鑰為 P(x) = F(T(x))
私鑰為 F(x), T(x)
首先生成公私鑰:就是隨機生成 o 個油醋多項式
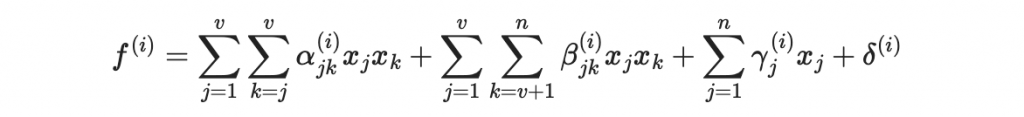
係數都是隨機生成。
接著,把欲簽章的文件 hash 到長度為 o 的數字序列。(如果你不知道什麼是 hash ,你就當作我們要簽章的文件可以壓縮為長度 o 的數字序列,這個壓縮是不可逆的,但每次壓縮結果都一樣)
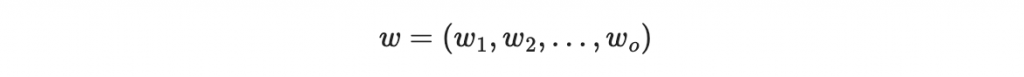
接著,簽章者會計算一個「簽章」sigma 滿足
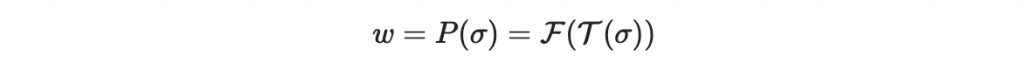
換句話說
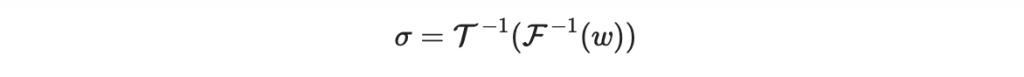
注意到 sigma 是一個長度為 n = v + o 的數字序列。
為了計算這個 sigma,第一步要先計算 F^-1(w):
隨機生成 v 個數字,代入醋變量。
於是上面的油醋多項式
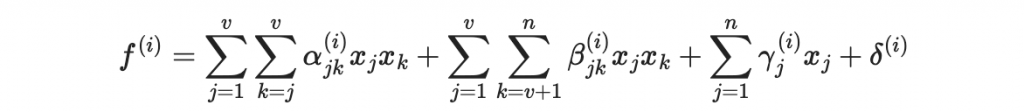
就變成油變量的線性方程式:(紅色是油變量)
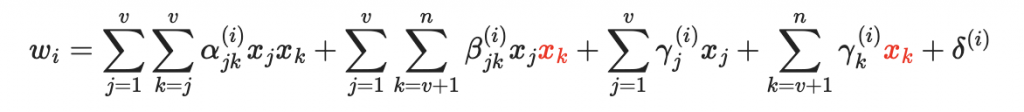
此時,我們有 i = 1, 2, ..., o 共 o 個油變量的線性方程組,這可以用高斯消去法來求解。
此時,如果油變量無解的話,重新生成 v 個醋變量,重新嘗試求解油變量。
如果油變量有解的話,那我們把醋變量跟油變量接在一起
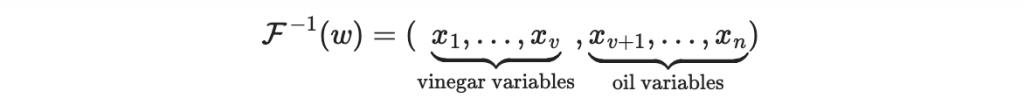
下一步,計算
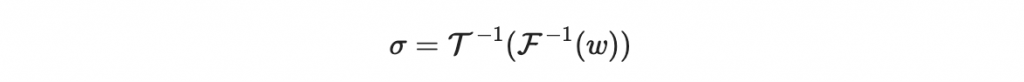
於是你就有了簽章 sigma
把 sigma 代入公鑰 P ,看看有沒有等於 w 。Done
我們就按照剛剛的順序來用 SageMath 實作,因為過程中沒有涉及什麼高難度的多項式商環,我們把參數用的大一些些😀
首先我們設定所有數字所在的整數環:Z / 79 Z
q = 79
R = quotient(ZZ, q*ZZ)
print(R)
# Outputs:
# Ring of integers modulo 79
使用 19 個醋變數、21 個油變數
v = 19
o = 21
n = o + v
仿射變換
# Function to generate a random affine map
def RandomAffineMapGenerator(n, R):
while True:
# Generate a random n x n matrix for the linear part of the affine map
A = random_matrix(R, n, n)
# Check if A is invertible
if A.is_invertible():
break
# Generate a random n-dimensional vector for the translation part
b = random_vector(R, n)
# Define the nested affine map function
def AffineMap(v):
v = vector(v)
v = A * v + b
return v.list()
# Define the inverse affine map function
def InverseMap(v):
v = vector(v)
v = A.inverse() * (v - b)
return v.list()
# Return the affine map function, the inverse map function, and the components
return AffineMap, InverseMap, A, b
T,T_inv,A,b = RandomAffineMapGenerator(n,R)
生成 o 個油醋多項式:
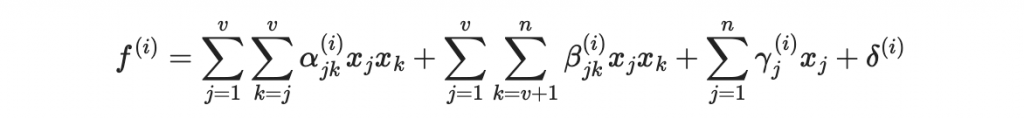
其中我們把 alpha 係數存在 VV 矩陣內,beta 係數在 VO,gamma 係數在 L
VVs = []
VOs = []
Ls = []
Ds = []
for _ in range(o):
# Generate a random v x v upper triangular matrix
VV = random_matrix(R, v, v)
for i in range(v):
for j in range(i):
VV[i, j] = 0
# Generate a random v x o matrix
VO = random_matrix(R, v, o)
# Generate a random 1 x n matrix
L = random_matrix(R, 1, n)
# Generate a random constant term
D = R.random_element()
VVs.append(VV)
VOs.append(VO)
Ls.append(L)
Ds.append(D)
print(VVs[0],"\n")
print(VOs[0],"\n")
print(Ls[0] ,"\n")
print(Ds[0] ,"\n")
# Output:
# (two matrices and a row matrix and a constant term)
現在開始進行簽章
# Sign a message
# 我們就假裝要簽章的文件就是隨機的
w = [randint(0, q-1) for _ in range(o)]
print(w)
# Outputs:
# [50, 14, 32, ..., 34, 74, 26, 5]
先計算
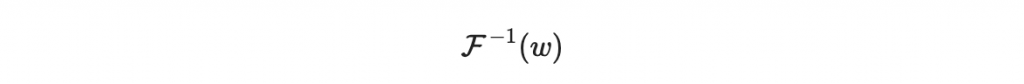
生成隨機的醋變量值
vinegar_variables = [randint(0, q-1) for _ in range(v)]
print("Vinegar variables: ", vinegar_variables)
# Outputs:
# Vinegar variables: [3, 31, ..., 25, 41, 77, 57]
將醋變量值代入油醋多項式後,會剩下油變量的線性方程組
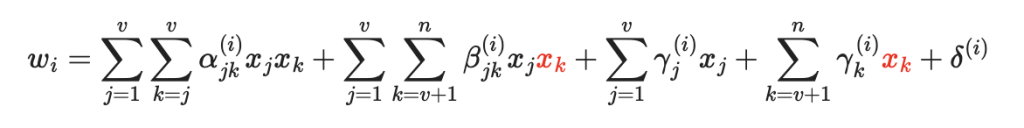
改寫一下:
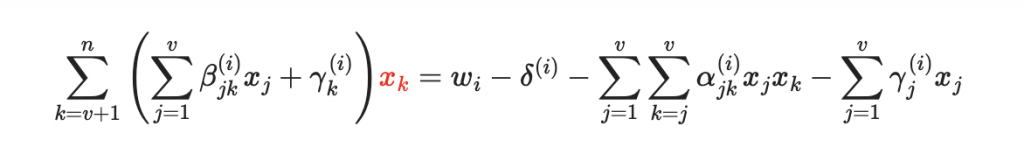
現在我們生成這部分的係數矩陣
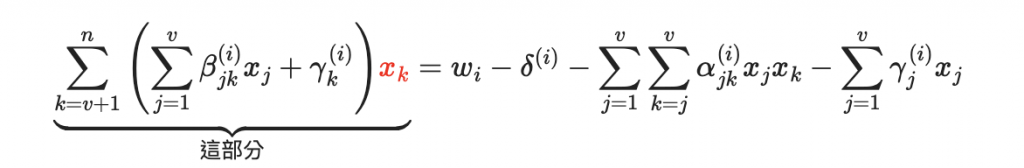
Linear_System = [[0 for i in range(o)] for k in range(o)]
for i in range(o):
for k in range(v,n):
coeff = 0
for j in range(v):
coeff += VOs[i][j, k-v] * vinegar_variables[j]
coeff += Ls[i][0, k]
Linear_System[i][k-v] = coeff
印出矩陣
Linear_System = Matrix(Linear_System)
print("Linear System:\n\n"+str(Linear_System))
# Outputs:
# (A big matrix)
接著計算右側的常數向量
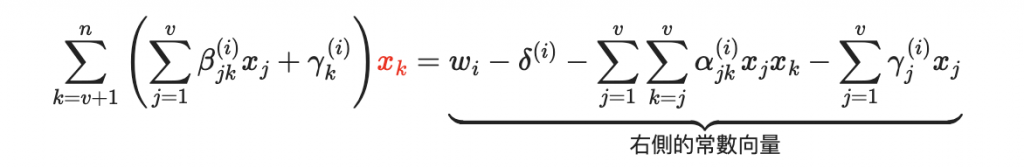
# Calculate the constant terms
constant_terms = [0 for _ in range(o)]
for i in range(o):
constant_terms[i] = w[i] - Ds[i]
vinegar_variables_vector = Matrix([[vinegar_variables[j]] for j in range(v)]) # column vector
num = vinegar_variables_vector.T * VVs[i] * vinegar_variables_vector
constant_terms[i] -= num[0,0]
for j in range(v):
constant_terms[i] -= Ls[i][0, j] * vinegar_variables[j]
constant_terms = vector(constant_terms)
print("Constant terms: ", constant_terms)
# Outputs:
# Constant terms: Constant terms: (25, 69, 47, ..., 31, 22, 68, 21)
現在嘗試解線性方程
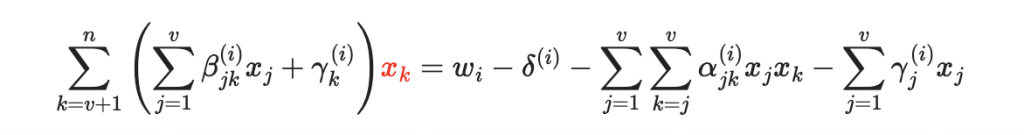
try:
solution = Linear_System.solve_right(constant_terms)
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Please re-select the vinegar variables: {e}")
print(solution)
# Outputs:
# (71, 48, 46, 18, ... 3, 15, 76, 72)
最後,計算
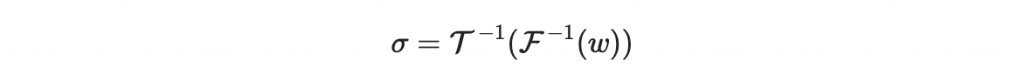
all_variables = vinegar_variables + solution.list()
signature =T_inv(all_variables)
print("Signature: ", signature)
# Outputs:
# Signature: [57, 74, 48, 18, ..., 67, 6, 69, 25]
好!來驗章!
我們把中間映射定義好
def Central_map(all_variables):
result = []
for i in range(o):
result.append(Ds[i])
for j in range(v):
for k in range(j, v):
result[i] += VVs[i][j, k] * all_variables[j] * all_variables[k]
for j in range(v):
for k in range(v, n):
result[i] += VOs[i][j, k-v] * all_variables[j] * all_variables[k]
for j in range(0, n):
result[i] += Ls[i][0, j] * all_variables[j]
return result
然後計算 P(x) ,看看有沒有等於 w
signature = T(signature)
print(Central_map(signature))
print(Central_map(signature) == w)
# Outputs:
# [1, 2, 7, 59, ... , 37, 34, 49, 73]
# True
(你可以看到,與之前 MI 的介紹一樣,這裡的公鑰係數需要被計算出來,但是那已經偏離此文重點,故省略之)
好!明天我們來看彩虹簽章!
ref
DING, Jintai; GOWER, Jason E.; SCHMIDT, Dieter S. Multivariate public key cryptosystems. Springer Science & Business Media, 2006.
