
在資料庫中使用 Index 能夠加快查詢的速度,但前面有提到 Index 加速的做法其實是用「空間換取時間」的方式,因此在設計 table schema 的時候,需要思考和取捨是否真的有必要將資料設為 Index。
今天這篇要介紹的「Partial Index」,是為了應對部分資料被查詢頻率較高的情境。Partial Index 允許我們只針對特定條件的資料建立 Index,來避免不必要的資源消耗。
什麼時候該使用 Partial Index?
Partial Index 的使用情境主要是針對不常見的值進行 Index,因為如果某個值在資料表裡出現得太頻繁(佔了幾 % 甚至更多的資料列),查詢時 PostgreSQL 可能根本不會用 Index,直接全表掃描(Seq Scan)反而更快。與其讓這些常見值佔用空間,不如直接把它們排除在外,專注加速那些少見、但查詢時更需要優化的資料。
Since a query searching for a common value (one that accounts for more than a few percent of all the table rows) will not use the index anyway, there is no point in keeping those rows in the index at all.
他的概念有點想是設立「快速通道」,快速通道是設計給少數特殊情況的人使用。如果某種類別的人(資料值)太常出現,那排隊系統幫他開特別通道(Index)其實沒什麼用,因為大部分人都會走那條路,反而會塞車。與其這樣,不如只幫那些少見但需要優先處理的對象建立通道,這樣資源才花得值得。
使用Partial Index的好處,第一個是可以縮小 Index 大小,第二個是提升寫入效能:因為 Index 更新範圍較小,insert 和 update 操作不會因此而花費過多的時間。
This reduces the size of the index, which will speed up those queries that do use the index. It will also speed up many table update operations because the index does not need to be updated in all cases.
測試:查詢未付款的訂單
假設我們的情況是有一個 orders 的 table,裡面的資料僅有少部分為未付款 billed = false 的訂單,而這些訂單卻是常常需要取出來看的資料,就可以使用到 Partial Index。
orders tableCREATE TABLE orders (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
order_nr INT NOT NULL,
customer_id INT NOT NULL,
total_amount INT NOT NULL,
billed BOOLEAN NOT NULL DEFAULT FALSE
);
billed = false
INSERT INTO orders (order_nr, customer_id, total_amount, billed)
SELECT
gs AS order_nr,
(RANDOM() * 1000)::INT + 1 AS customer_id,
(RANDOM() * 5000)::INT + 100 AS total_amount,
CASE WHEN gs <= 200 THEN FALSE ELSE TRUE END AS billed
FROM (
SELECT gs
FROM generate_series(1, 10000) gs
ORDER BY RANDOM()
) shuffled;
billed = false 的資料設為 Index:CREATE INDEX orders_unbilled_index ON orders (order_nr)
WHERE billed IS NOT TRUE;
EXPLAIN ANALYZE 查詢未付訂單,會看到 SQL 有正確的使用到 Index:EXPLAIN ANALYZE
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE billed IS NOT TRUE AND order_nr = 76;
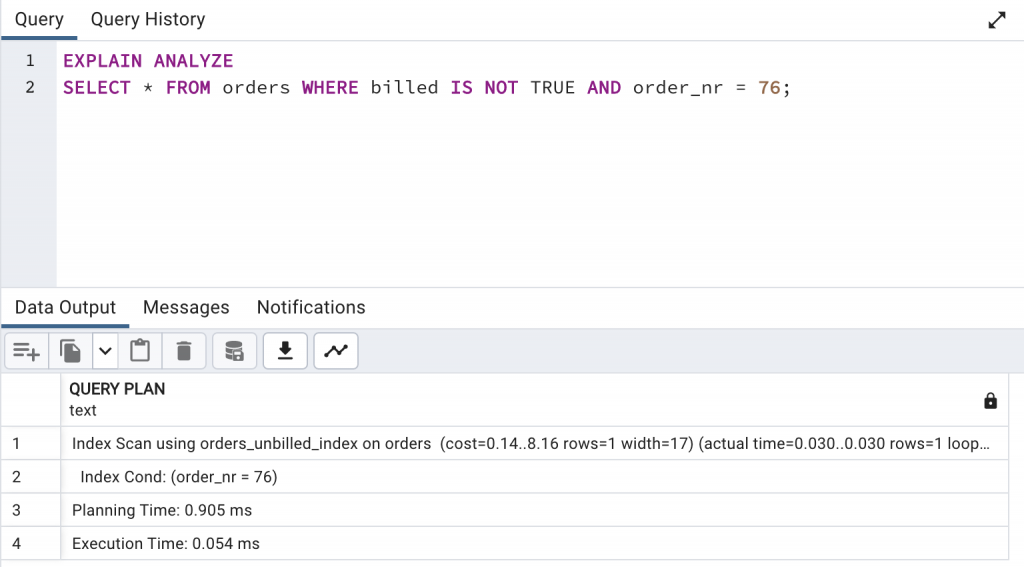
這時候先看一下只將 billed = false 設成 Index 的大小:
SELECT pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size('orders_unbilled_index'));
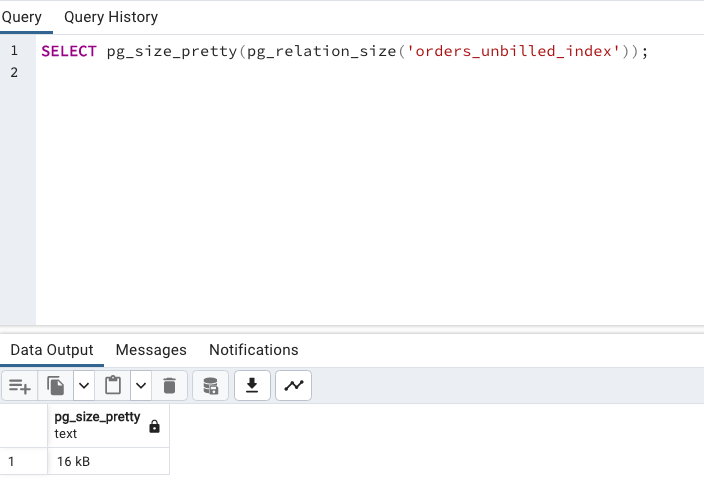
總共 16 KB,那如果沒有特別篩選 billed = false,將全部資料的 order_nr 都設定成 Index 呢?
比較:Index vs. Partial Index
DROP INDEX orders_unbilled_index
CREATE INDEX orders_nr_index ON orders (order_nr);
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE billed IS NOT TRUE AND order_nr = 76;
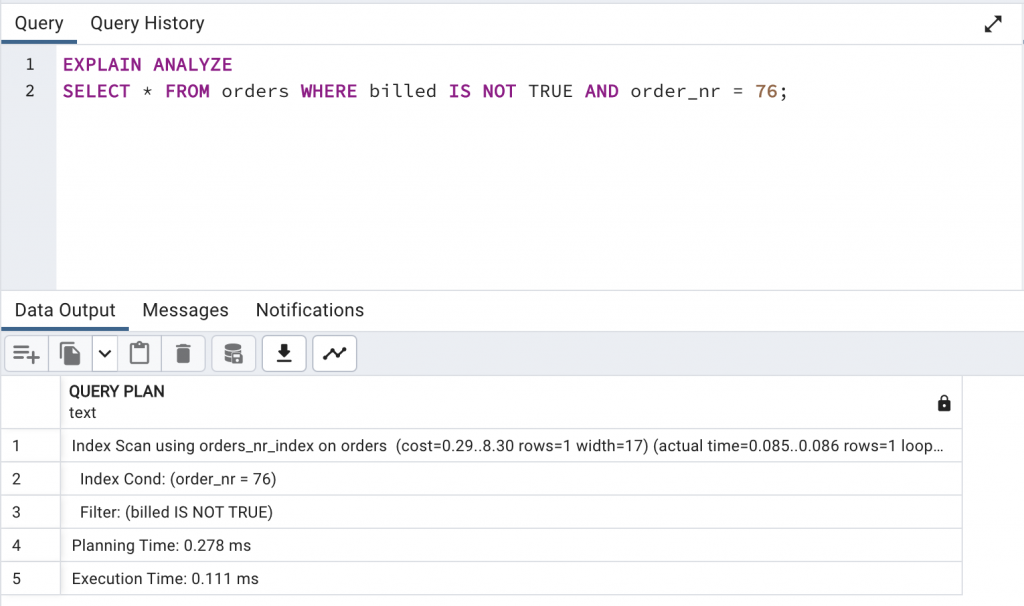
這裡還是有使用到 Index,查詢速度慢一點點(0.054 ms -> 0.111 ms)。不過如果看完整 Index 的大小,就會發現差比較多了,從 16KB 變成 240KB。
SELECT pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size('orders_nr_index'));
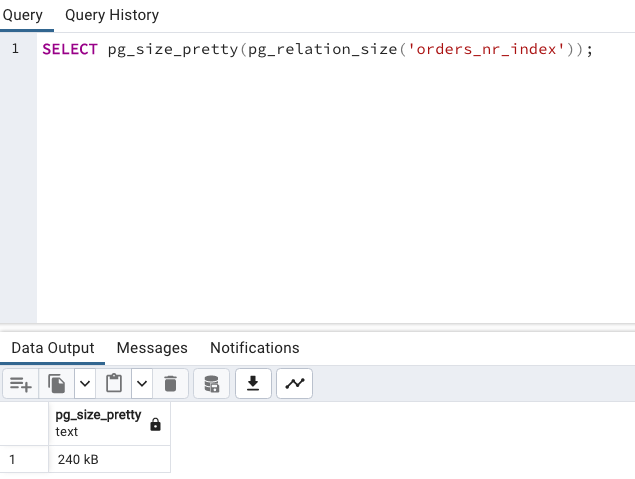
因此在需要查詢特定條件的資料,並且這些資料在佔全部資料比例較少的情況,就可以使用 Partial Index。它能夠縮小 Index 的空間,也可以減少寫入時的負擔。
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/indexes-partial.html
