有了 B+Tree 查詢單筆資料只要 O(LogN),但除了單筆查詢還有範圍查詢 id between 1 AND 100 以及多條件查詢 user_id = ? AND status = ? 等,MySQL 是如何高效地處理複雜的查詢情境?
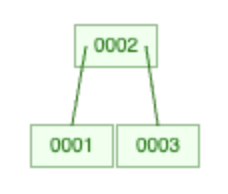
B+Tree 是 B-Tree 的衍生版,傳統 B-Tree 在分裂的時候,會把分裂點留在 parent node,其餘資料放到 child node,例如 [1,2,3] page 分裂後會變成, 1<-2->3,parent node 為 2,左 child node 為 1 右 child node 為 3:
(作者產圖)
單筆查詢很快,但範圍查詢 id > 10 需要從 root 往左 sub tree 掃描,然後再回到 root 從右 sub tree 掃描,在 tree 結構來回穿梭效率差。
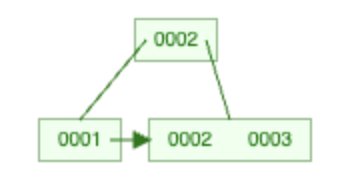
而 B+Tree 在分裂時,會把分裂點放在 parent node & child node,例如 [1,2,3] page 會分裂成 1<-2->[2,3],parent node 為 2,左 child node 為 1 右 child node 為 [2,3]:
(作者產圖)
雖然資料多儲存一份,但可以保證 leaf node 包含所有資料,此時將 leaf node 左右關聯建立 double linked list,範圍查詢 id > 10 就只要先找到 id = 10 的 leaf node 然後往右找出其他資料,線性掃描不用來回穿梭,效率比 B-Tree 快多了。
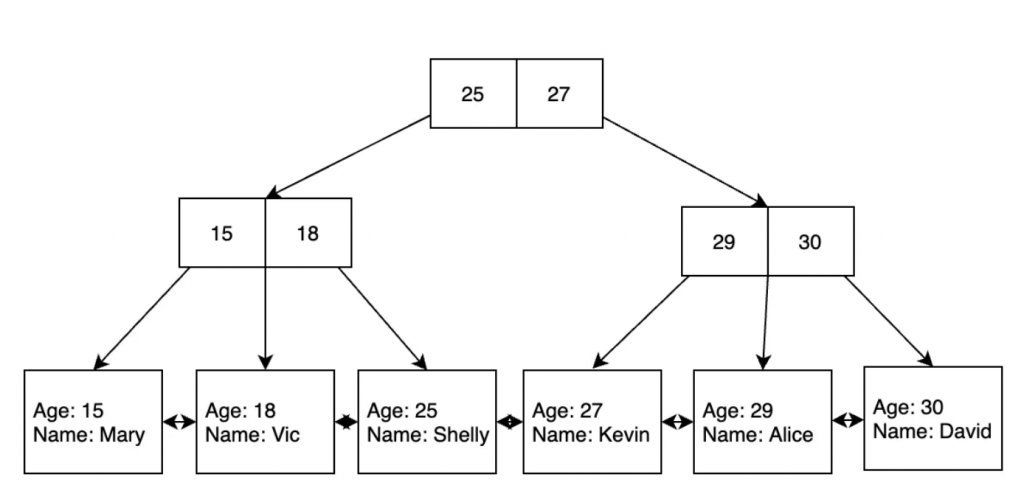
然而實際資料不會只有 1, 2 or 3,而是一筆多欄位紀錄,如果每次分裂都複製一份完整記錄到 parent & child node B+Tree 容量會變很大,因此 B+Tree 分裂時只複製排序 key 到 parent node,並把完整資料移到 child node 上,最終 B+Tree 結構中 Non-Leaf Node 只儲存排序 key,Leaft Node 儲存完整資料。
(作者產圖)
當建立 Table 時,B+Tree 會用 primary key 作為排序 key 建立第一個 B+Tree 並在 Leaf Node 儲存完整資料,但查詢光靠 primary key 不夠,還會用到其他欄位 e.g user_id = ?,此時建立 user_id 的 index,MySQL 會建立額外的 B+Tree 並用 user_id 作為排序 key,但 Leaf Node 不會儲存完整資料,而是儲存 primary key。
因此在 MySQL 中有兩種類型 B+Tree:
該設計好處是建立非 primary key 的 index 不會佔用太多空間,且更新非排序欄位時,只要更新 Clustered Index Tree 就好,缺點是用非 primary key 的 index 查詢完整資料時,要先從 Secondary Index Tree 中找到 primary key,再去 Clustered Index Tree 找完整資料,會有兩次 O(LogN)。
例如 user_id = ? AND status = ? 查詢,直觀做法是分別從 user_id 的 Index Tree 和 status 的 Index Tree 取兩批資料後取交集,但這個做法 I/O 次數太多,且 status 可能很多筆資料,取交集效率會很差。
更好地做法是建立 Composite Index 用多個欄位組成排序 Key,例如 (user_id, status) 作為排序 Key,先排序 user_id,相同 user_id 的資料再排序 status。
使用 Composite Index 後,user_id = 1 AND status = 2 查詢只需要從 (user_id, status) 的 Index Tree 中先依照 user_id 進行 binary search 找到第一筆 user_id = 1 的 Node,此時該 Node 的 status 會為最小值且 sub tree 包含 user_id = 1 且 status 是有序的節點,再用 status 進行 binary search 從 sub tree 中找到 status = 2 的資料,I/O 次數少也不用取交集,效率更好。
Composite Index 會依照 index 宣告的欄位順序決定誰先排序,(user_id, status) vs (status, user_id) 前者先排序 user_id 後再排序 status,後者相反,此外誰先排序對於查詢性能是有很大影響的。
例如查詢 user_id = 1 AND status BETWEEN 1 AND 3 時,(user_id, status) 的性能會比 (status, user_id) 好很多,假設用 (status, user_id) Index Tree,status 先排序,相同 status 的資料在用 user_id 排序,依照上面查詢要先找出 status BETWEEN 1 AND 3 的資料,但這個 sub tree 中的資料 user_id 已經不是有序的:
| status | user_id |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 |
因此無法再用 user_id 進行 binary search,反觀 (user_id, status) 的 Index Tree 是先找出 user_id = 1 的 sub tree 且該 sub tree status 是有序的,因此可用 binary search 在 sub tree 中在找出 status between 1 AND 3 的資料。
| user_id | status |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 |
也就是說,當查詢是 a = ? AND b = ? AND c >= ? 時,Composite Index 的宣告順序要把 c 放在最後面,因為一旦經過範圍查詢,後面欄位已不在有序無法用 binary search 過濾資料,此外如果 composite index 是 (a, b, c) 是無法 cover 到 b AND = ? AND c >= ? 的查詢條件,因為要先用 a 欄位過濾資料, b 欄位才是有序的,而反過來 (a, b, c) 可以 cover a = ? 的條件,因此 index (a) 跟 index (a, b, c) 是有同樣效果的。
