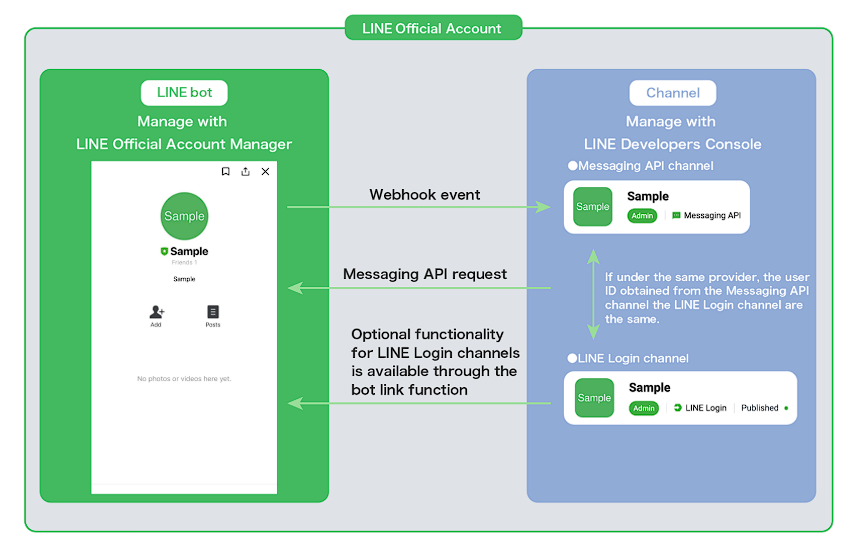
A webhook is a lightweight, event-driven communication that automatically sends data between applications via HTTP. Triggered by specific events, webhooks automate communication between application programming interfaces (APIs) and can be used to activate workflows, such as in GitOps environments. -RedHat
https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/automation/what-is-a-webhook
簡單來說,webhook 是一種 push-based 的事件驅動 (event-driven) 通訊。
你只要在 server 端註冊一個 URL,server 發生事件時就會「主動推送」資料到這個端口。
對於 Webhook的 definition 以下是簡單的說文解字:
因為 webhook 只有在事件發生時才 push data,client 不需要 continuous polling。
只有事件發生時,server 才會通知 client
→ 就像把電話號碼給朋友,叫他「有事再打給你」,不需要你一直去問。
它自動發 HTTP request (通常是 POST) 帶 event data
Webhook 就像是一個 API-based notification,可以 decouple 兩個系統,並且直接傳遞 event data。
LINE Java SDK 有提供 custom annotations。
import com.linecorp.bot.spring.boot.handler.annotation.EventMapping;
import com.linecorp.bot.spring.boot.handler.annotation.LineMessageHandler;
它們在做什麼?
@LineMessageHandler
ApplicationContext
@EventMapping
@EventMapping,分別處理不同的事件型別(text、image、follow、join…)。官方文件也有提到,這些 annotation 是 Spring Boot Starter 封裝後提供的語法糖,省下我們去手動解析 webhook JSON payload
一些 java 範例 :
先定義你的 annotation
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) // 可以標在 method 上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyEventMapping {
String value() default ""; // 可以帶一個事件名稱 @MyEventMapping("事件名稱")
// default 是為了 讓它是可選的 不寫也不會錯
}
將你的 annotation 標在需要的 method 上,注意至樣還只是補充 class 和 method 的訊息而已
public class MyWebhookHandler {
@MyEventMapping("text")
public void handleText(String message) {
System.out.println("Handle TEXT event: " + message);
}
@MyEventMapping("image")
public void handleImage(String message) {
System.out.println("Handle IMAGE event: " + message);
}
}
物件 MyDispatcher 依據這個 annotation 的訊息做事
public class MyDispatcher {
private final Object handler;
public MyDispatcher(Object handler) {
this.handler = handler;
}
public void dispatch(String eventType, String payload) {
Method[] methods = handler.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
Arrays.stream(methods).forEach(method -> {
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyEventMapping.class)) {
MyEventMapping mapping = method.getAnnotation(MyEventMapping.class);
if (mapping.value().equals(eventType)) {
try {
method.invoke(handler, payload); // 呼叫對應的方法
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyWebhookHandler handler = new MyWebhookHandler();
MyDispatcher dispatcher = new MyDispatcher(handler);
dispatcher.dispatch("text", "Hello from user!");
dispatcher.dispatch("image", "Image uploaded.");
}
}
Handle TEXT event: Hello from user!
Handle IMAGE event: Image uploaded.
Annotation 就像「小貼紙」(metadata) 一樣,如果只是貼上去,程式本身不會自動「知道要做什麼」,要讓它動起來,就會需要有人去「看」這張小貼紙,並根據這個 metadata 做一些邏輯。
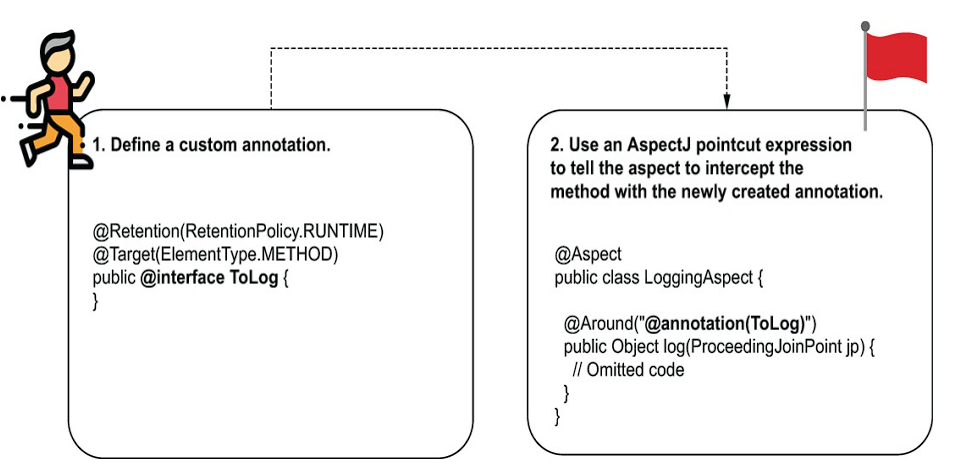
你可以實作 Annotation 當 Aspect 用。 (Spring Start Here)
上面的 code 中 RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME 表示註解的資料在 runtime 也會保留,這樣就可以透過 java reflection 讀取。javadoc 有提及 Retention Policy,來定義 Annotation 要保留多久。
(https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java/reflection-in-java/ 可簡單參閱 Reflection API)
有三種:
如果你只是寫文件註解用,SOURCE 就好。eg.
@Override
如果你想讓框架在 runtime 用 annotation 來 dispatch 事件(像@EventMapping),就必須用 RUNTIME。
可參見 https://www.baeldung.com/java-custom-annotation
當初我也在 Maven 找很久的 dependency :
<dependency>
<groupId>com.linecorp.bot</groupId>
<artifactId>line-bot-messaging-api-client</artifactId>
<version>9.11.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.linecorp.bot</groupId>
<artifactId>line-bot-webhook</artifactId>
<version>9.11.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.linecorp.bot</groupId>
<artifactId>line-bot-spring-boot-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>9.11.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.linecorp.bot</groupId>
<artifactId>line-bot-spring-boot-client</artifactId>
<version>9.11.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.linecorp.bot</groupId>
<artifactId>line-bot-spring-boot-handler</artifactId>
<version>9.11.0</version>
</dependency>
LineWebhookHandler.java
@LineMessageHandler
public class LineWebhookHandler {
private final MessagingApiClient messagingApiClient;
private final ArticleService articleService;
public LineWebhookHandler(
MessagingApiClient messagingApiClient,
ArticleService articleService) {
this.messagingApiClient = messagingApiClient;
this.articleService = articleService;
}
// When a user messages your bot, LINE sends a POST to your webhook URL.
@EventMapping
public void handleTextMessageEvent(MessageEvent event) {
System.out.println("event: " + event);
final String originalMessageText = ((TextMessageContent) event.message()).text();
messagingApiClient.replyMessage(
new ReplyMessageRequest.Builder(
event.replyToken(),
List.of(new TextMessage(originalMessageText))
).build()
);
}
// further method
@EventMapping
public void handleDefaultMessageEvent(Event event) {
System.out.println("event: " + event);
}
}
new TextMessage(originalMessageText)
這裡就是可以 回傳訊息 的地方。小心 LINE 的 Reply 和 Push API 都有一些限制,請參見官方文件。
我自己踩過的坑是:訊息可以「切開來分批傳送」(有字數上限),要小心每一個訊息也不能為空。一個比較好的做法是:你可以另外包一個 LineMessageRender,專門來 handle 這些細節。
還有這裡要注意訊息的型態 (若有寫錯請指正~)
TextMessage 不是 TextMessageContent。但 TextMessage 可以被當成 Message 傳給 ReplyMessageRequest,因為TextMessage implements Message interface
(回覆訊息必須是 List<Message>)。
當使用者傳文字訊息時,LINE 會 POST 到 /callbackapplication.yml
line.bot:
channel-token: ${LINE_CHANNEL_TOKEN}
channel-secret: ${LINE_CHANNEL_SECRET}
handler:
path: /callback
#The starter binds /callback for you; you don’t need a manual @PostMapping. This is exactly how the official sample is set up.
你需要 ngrok 來測試 line bot 及 webhook 有沒有接通~
Ngrok is a secure tunneling tool that exposes a local server (e.g., localhost:8080) to the internet via a public HTTPS URL. It's commonly used to test webhooks, third-party API callbacks, or mobile app integrations during development—without deploying to a public server.
它常用來 測試 webhooks、第三方 API callback,或是 mobile app integration,在開發階段就能模擬外部服務,完全不用先部署到雲端。有點像 proxy port 的概念:
https://www.browserstack.com/guide/proxy-port
當有人 access 公開的 ngrok URL(例如 LINE server 發訊息通知你,順便附上 token),ngrok 會把這個 HTTP traffic forward 回你本機的 server,就像是在你電腦和外部世界之間挖了一條安全的「隧道」。
ngrok config add-authtoken <token>
ngrok http 80
https://ngrok.com/downloads/windows?tab=download
https://a75422dd43a2.ngrok-free.app URL。application.yml 裡設定的 /callback。https://a75422dd43a2.ngrok-free.app/callback 登記,之後 LINE server 就會透過這個 webhook 把事件推送給 ngrok,而 ngrok 會再把 POST request forward 到你本地端正在跑的 Spring Boot core app。如果你不會創辦 Line Developer 帳號 :
請參考 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mw3cODdkaFM 他甚至有python實作
java sdk 相關請參閱 :
https://github.com/line/line-bot-sdk-java?tab=readme-ov-file
或是前人分享的文章 :
https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10311687
https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10196397
