以下提供幾個常用、具教學與實務價值的古典密碼與密碼學核心程式碼示範,涵蓋對稱加密(AES)、非對稱加密(RSA)、雜湊函數(SHA256)及數位簽章。
內容有 AES、RSA、SHA-256 雜湊與數位簽章的實用程式碼示範,以及它們在資安中的重要性:
AES 是現在資訊安全中最常用的對稱加密演算法,我們用它來把資料加密,再用同一把金鑰解密。程式碼示範中,我們首先生成安全的隨機金鑰和初始向量,把明文「This is a secret message.」填充後加密,最後解密回原文。
這裡最重要的是「對稱」:加密和解密用的是同一把密鑰,像是一把能開啟與關閉保險箱的鑰匙。所以交換密鑰的安全性很重要,若被人偷聽密鑰,整個加密就不安全了。
RSA 不同於 AES,是「非對稱加密」,使用一對公鑰和私鑰。公鑰會公開給別人用來加密資料,而私鑰只有自己持有用來解密。示範程式碼中,我們產生了一對長度 2048 位元的金鑰,就可以用公鑰加密「RSA secret message」,然後用私鑰解密回原文。
非對稱加密最大的好處是不用擔心密鑰被洩露,公鑰隨時公開使用,私鑰保密就好!
SHA-256 是一種單向加密演算法,它可以把任何資料轉化成固定長度的雜湊值。這個值是獨一無二的數字指紋,任何改變輸入的微小細節都會產生完全不同的雜湊。
我們用 Python 的 hashlib 套件做示範,對資料「Data to hash」計算出 SHA-256 雜湊,方便用在檔案完整性檢驗、密碼存儲加鹽等場景。
最後,我們用 RSA 的私鑰對一段訊息做簽章,任何人用對應的公鑰驗證這段簽章是否有效,確保了檔案的真實性與完整性。
示範中用 PSS 標準的簽章方式,能防止重播攻擊和偽造。驗證成功就是告訴我們這份資訊是私鑰持有者真的簽發的,沒被篡改過。
可以先閱讀下列文章
(https://cryptography.io/en/latest/hazmat/primitives/symmetric-encryption/)
(https://stackoverflow.com/questions/58049057/cryptography-hazmat-aes-cipher-output-length)
(https://www.cnblogs.com/testlearn/p/16177034.html)
(https://ssojet.com/encryption-decryption/aes-256-in-python/)
(https://gist.github.com/tcitry/df5ee377ad112d7637fe7b9211e6bc83)
今天一樣用昨天的虛擬機來跑程式碼(偶然發現這個虛擬機還不錯,雖然不能模擬桌面,但是可以拿來跑python、oracle等等)
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.ciphers import Cipher, algorithms, modes
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import padding
from cryptography.hazmat.backends import default_backend
import os
#金鑰與初始向量產生
key = os.urandom(32) # 256-bit AES key
iv = os.urandom(16) # 128-bit IV
#要加密的明文
plaintext = b"This is a secret message."
#填充使長度為128位元組倍數
padder = padding.PKCS7(128).padder()
padded_data = padder.update(plaintext) + padder.finalize()
#建立加密器,以CBC模式
cipher = Cipher(algorithms.AES(key), modes.CBC(iv), backend=default_backend())
encryptor = cipher.encryptor()
ciphertext = encryptor.update(padded_data) + encryptor.finalize()
print("Ciphertext:", ciphertext.hex())
#解密
decryptor = cipher.decryptor()
decrypted_padded = decryptor.update(ciphertext) + decryptor.finalize()
unpadder = padding.PKCS7(128).unpadder()
decrypted_data = unpadder.update(decrypted_padded) + unpadder.finalize()
print("Decrypted:", decrypted_data.decode())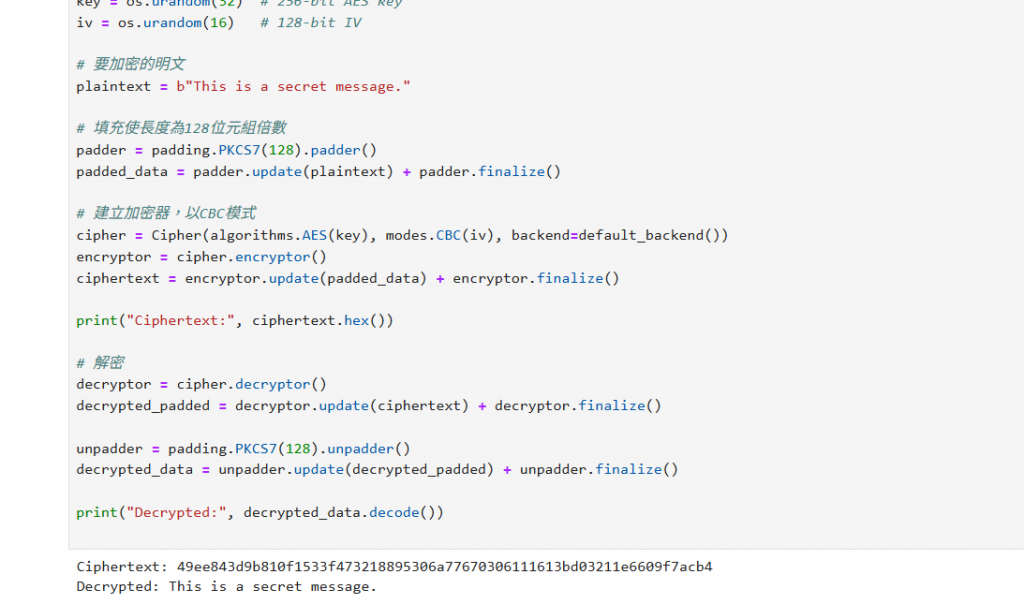
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import rsa, padding
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes, serialization
#產生 2048-bit RSA 金鑰對
private_key = rsa.generate_private_key(public_exponent=65537, key_size=2048)
public_key = private_key.public_key()
message = b"RSA secret message"(你的資訊)
#用公鑰加密
ciphertext = public_key.encrypt(
message,
padding.OAEP(mgf=padding.MGF1(algorithm=hashes.SHA256()), algorithm=hashes.SHA256(), label=None)
)
print("Ciphertext:", ciphertext.hex())
#用私鑰解密
plaintext = private_key.decrypt(
ciphertext,
padding.OAEP(mgf=padding.MGF1(algorithm=hashes.SHA256()), algorithm=hashes.SHA256(), label=None)
)
print("Decrypted:", plaintext.decode())

python
import hashlib
data = b"Data to hash"
hash_obj = hashlib.sha256()
hash_obj.update(data)
hashed = hash_obj.hexdigest()
print("SHA-256 hash:", hashed)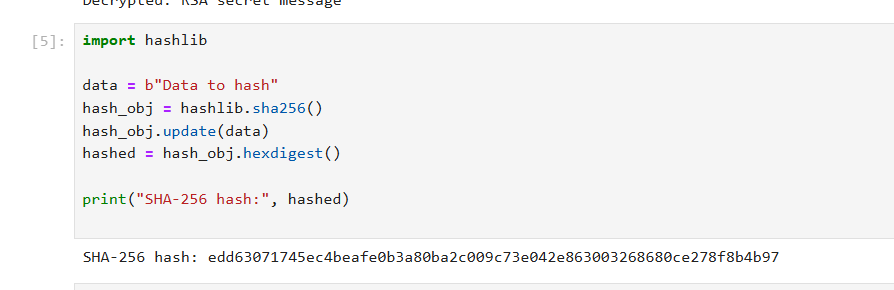
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import padding
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes
message = b"Message for signing"
signature = private_key.sign(
message,
padding.PSS(mgf=padding.MGF1(hashes.SHA256()), salt_length=padding.PSS.MAX_LENGTH),
hashes.SHA256()
)
print("Signature:", signature.hex())
#驗證簽章
try:
public_key.verify(
signature,
message,
padding.PSS(mgf=padding.MGF1(hashes.SHA256()), salt_length=padding.PSS.MAX_LENGTH),
hashes.SHA256(),
)
print("Signature valid!")
except:
print("Signature invalid!")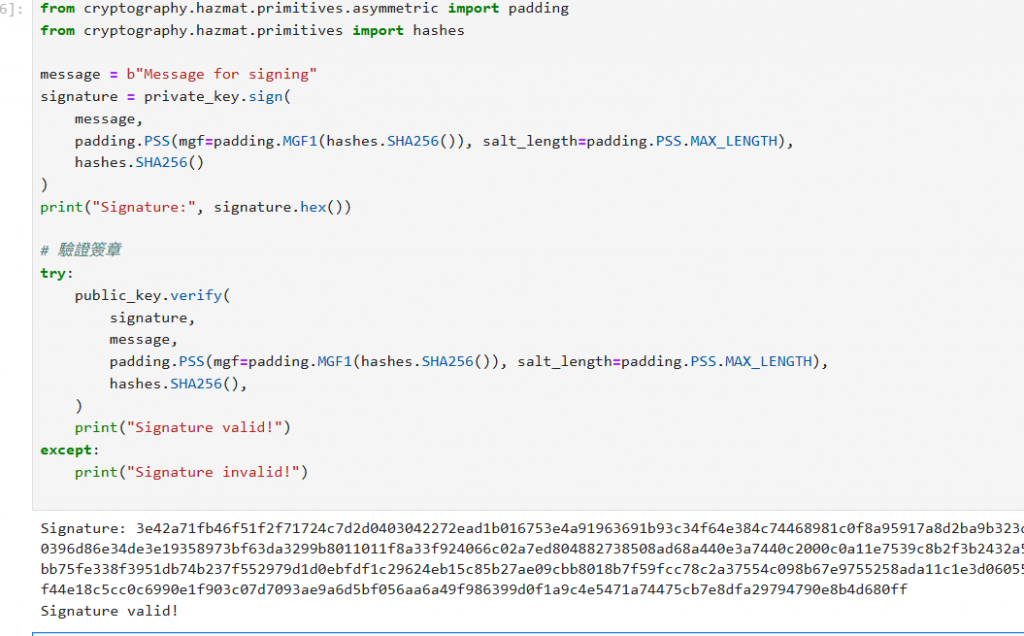
這次跑完真的很開心,因為很常聽到密碼學相關資訊,但自己也不是很懂,這次終於釐清了他們的差別!!!
未來有機會再學吧~~~感覺蠻難的
