前言
昨天我們完成了邏輯迴歸模型的建立與深入分析,包括特徵權重與混淆矩陣評估。
今天學習重點包括:
一、邏輯迴歸主要超參數介紹
為什麼要調參數?
二、使用交叉驗證評估模型
交叉驗證(Cross-Validation)
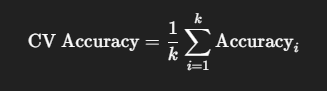
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# 建立模型
model = LogisticRegression(max_iter=500, C=1.0, penalty='l2', solver='lbfgs')
# 5-fold 交叉驗證
scores = cross_val_score(model, X_train, y_train, cv=5, scoring='accuracy')
print("每折準確率:", scores)
print("平均準確率:", scores.mean())
程式碼解釋
三、視覺化不同 C 值對準確率影響
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
C_values = [0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100] # 嘗試不同正則化強度
mean_scores = []
for C in C_values:
# 建立模型,僅改變 C
model = LogisticRegression(max_iter=500, C=C, penalty='l2', solver='lbfgs')
scores = cross_val_score(model, X_train, y_train, cv=5)
mean_scores.append(scores.mean())
plt.figure(figsize=(8,5))
plt.plot(C_values, mean_scores, marker='o')
plt.xscale('log') # 對數刻度,更直觀
plt.xlabel('C (正則化強度倒數)')
plt.ylabel('平均準確率')
plt.title('調整 C 值對模型準確率影響')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
解釋
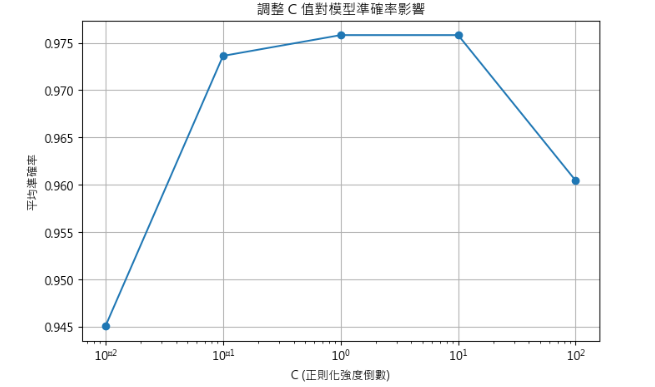
小結
今天我們學習了邏輯迴歸的主要超參數,包括 C 值、正則化類型、最大迭代次數以及求解器(solver),並透過交叉驗證了解模型在未見資料上的穩定性。此外,我們還視覺化了不同 C 值對平均準確率的影響,幫助找到最佳的正則化設定。透過這些操作,我們不僅能調整模型參數,也對模型的學習能力與泛化能力有初步認識。後續章節中,我們將進一步解釋這些專有名詞,包括正則化、梯度以及優化算法,並搭配簡單數學例子,讓今天學到的超參數調整背後原理更加清楚。
