code在這裡
昨天雖然已經交代過理論,也有一些些簡單的實作,不過為了讓大家更了解一般會如何打造出一個檢索引擎,因此這篇文章將帶領大家一步步打造出一個檢索引擎。我將從新竹市政府社會處爬下來的常見問答集,透過使用者的關鍵字檢索,檢索出他們比較可能希望的答覆。
import jieba
jieba.set_dictionary('dict.txt.big')
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
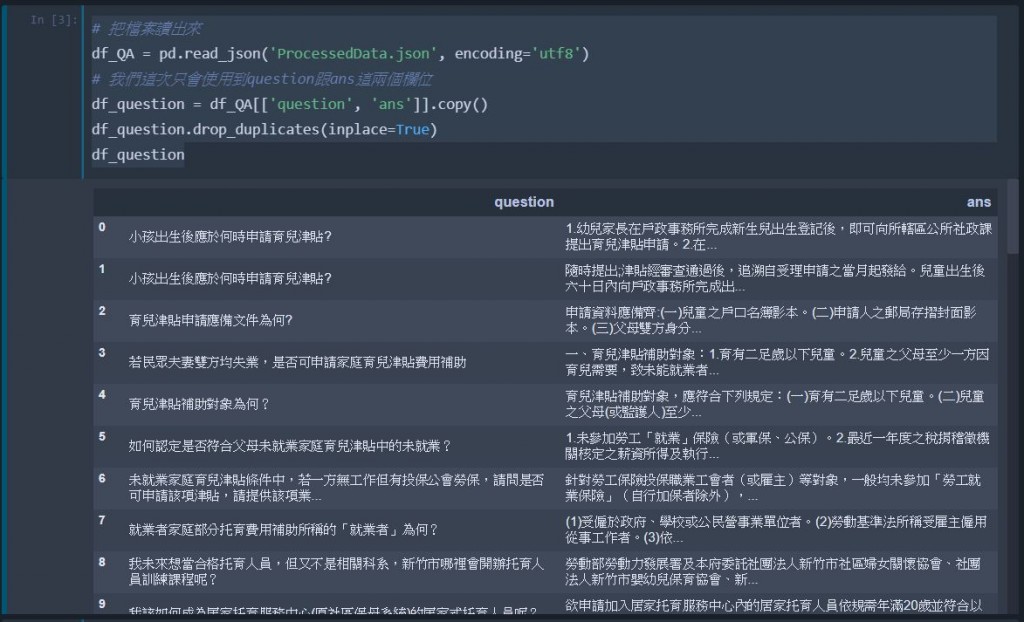
# 把檔案讀出來
df_QA = pd.read_json('ProcessedData.json', encoding='utf8')
# 我們這次只會使用到question跟ans這兩個欄位
df_question = df_QA[['question', 'ans']].copy() ## 不要更動到原始的DataFrame
df_question.drop_duplicates(inplace=True) ## 丟掉重複的資料
df_question ## show出來
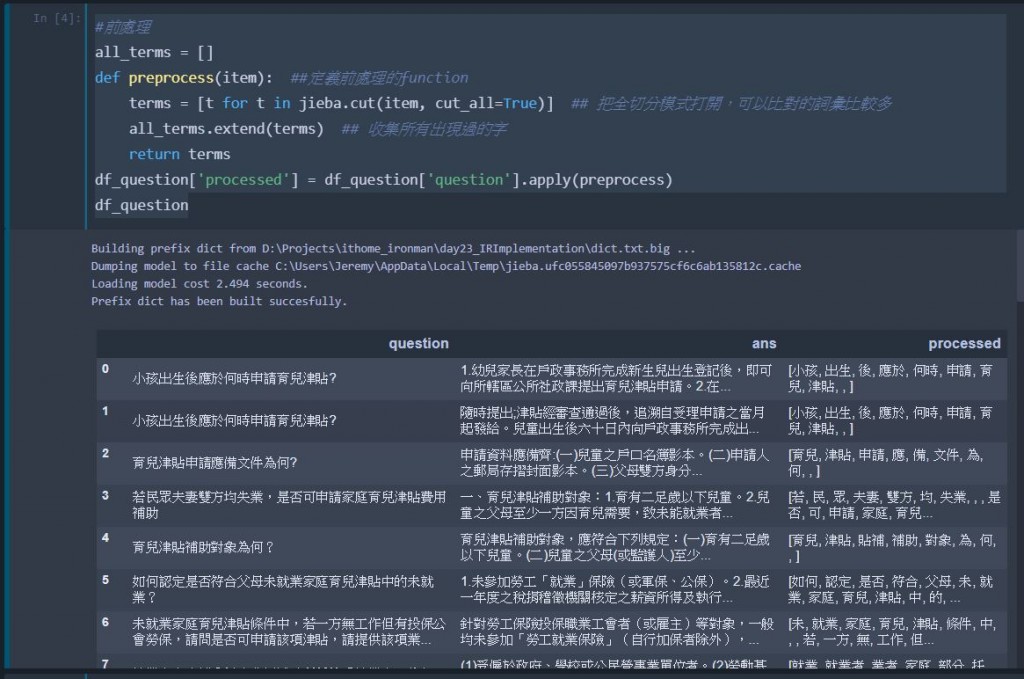
all_terms = []
def preprocess(item): ##定義前處理的function
terms = [t for t in jieba.cut(item, cut_all=True)] ## 把全切分模式打開,可以比對的詞彙比較多
all_terms.extend(terms) ## 收集所有出現過的字
return terms
df_question['processed'] = df_question['question'].apply(preprocess)
df_question
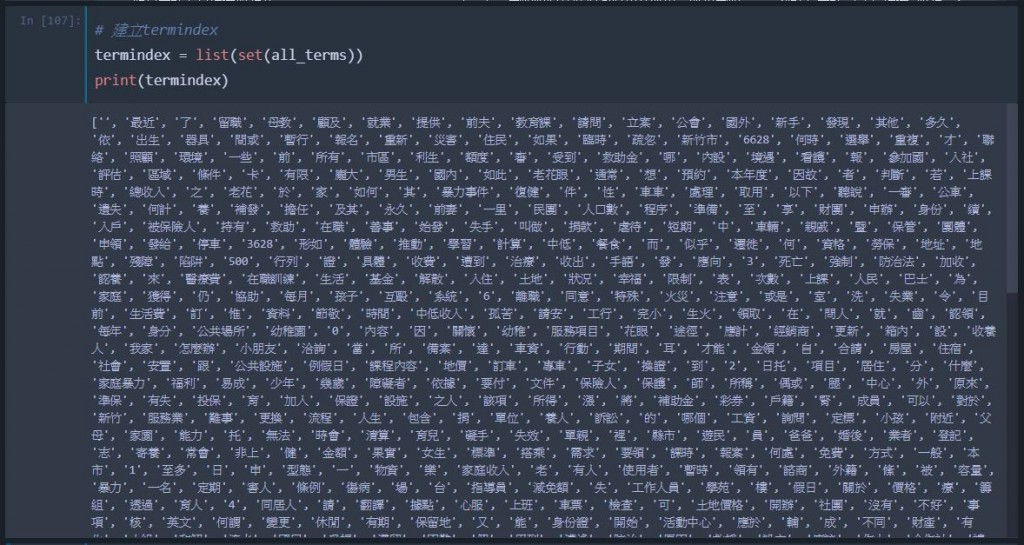
把上面收集所有字取出不重複的部分,並建立成一條termindex,如此一來便能統一每一個問句的向量中的每一個維度所代表的意義是一致的。
# 建立termindex
termindex = list(set(all_terms)) ## 用set轉型可以將list中重複的部分拿掉
print(termindex)
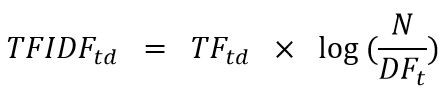
也就是昨天文章出現的這個公式後面log那一串東西,每一個詞彙會有一個IDF值,因此,這邊先計算好並根據termsindex的順序儲存成一條向量,以方便後面計算。
Doc_Length = len(df_question) ## 計算出共有幾篇文章
Idf_vector = [] ## 初始化IDF向量
for term in termindex: ## 對index中的詞彙跑回圈
num_of_doc_contains_term = 0 ## 計算有機篇文章出現過這個詞彙
for terms in df_question['processed']:
if term in terms:
num_of_doc_contains_term += 1
idf = np.log(Doc_Length/num_of_doc_contains_term) ## 計算該詞彙的IDF值
Idf_vector.append(idf)
def terms_to_vector(terms): ## 定義把terms轉換成向量的function
vector = np.zeros_like(termindex, dtype=np.float32) ## 建立一條與termsindex等長、但值全部為零的向量
for term in terms:
if term in termindex:
idx = termindex.index(term) ## 測試時如果有字沒有在索引中,需要保護
vector[idx] += 1 ## 計算term frequency
vector = vector * Idf_vector ## 如果兩個vector的型別都是np.array,把兩條vector相乘,就會自動把向量中的每一個元素成在一起,建立出一條新的向量
return vector
df_question['vector'] = df_question['processed'].apply(terms_to_vector) ## 將上面定義的function,套用在每一筆資料的terms欄位上
df_question
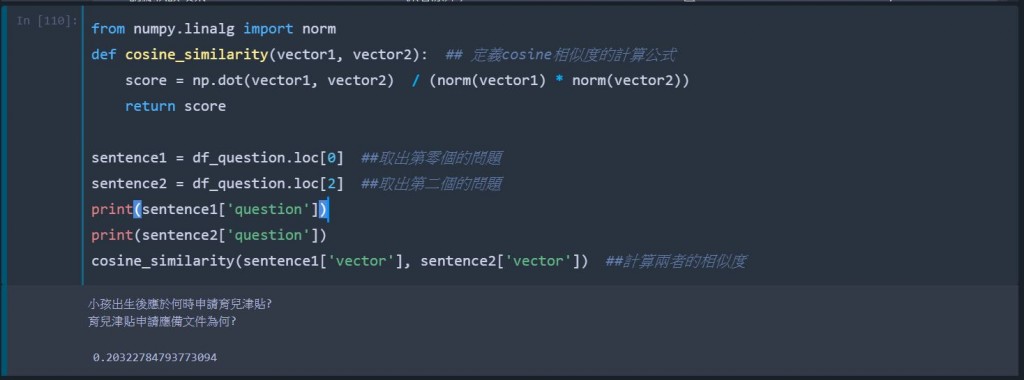
from numpy.linalg import norm
def cosine_similarity(vector1, vector2): ## 定義cosine相似度的計算公式
score = np.dot(vector1, vector2) / (norm(vector1) * norm(vector2))
return score
sentence1 = df_question.loc[0] ##取出第零個的問題
sentence2 = df_question.loc[2] ##取出第二個的問題
print(sentence1['question'])
print(sentence2['question'])
cosine_similarity(sentence1['vector'], sentence2['vector']) ##計算兩者的相似度
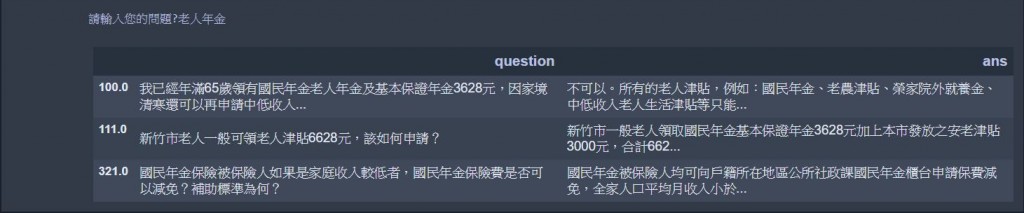
def retrieve(testing_sentence, return_num=3): ## 定義出檢索引擎
testing_vector = terms_to_vector(preprocess(testing_sentence)) ## 把剛剛的前處理、轉換成向量的function,應用在使用者輸入的問題上
score_dict = {} ## 準備把每一個問題對應到使用者問題的cosine分數記錄下來
for idx, vec in enumerate(df_question['vector']): ## 計算每一個問題與使用者問題的cosine分數
score = cosine_similarity(testing_vector, vec)
score_dict[idx] = score
idxs = np.array(sorted(score_dict.items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True))[:return_num, 0] ##排序出最相關的前N個問題的row index
return df_question.loc[idxs, ['question', 'ans']]
query = input('請輸入您的問題?')
retrieve(query)
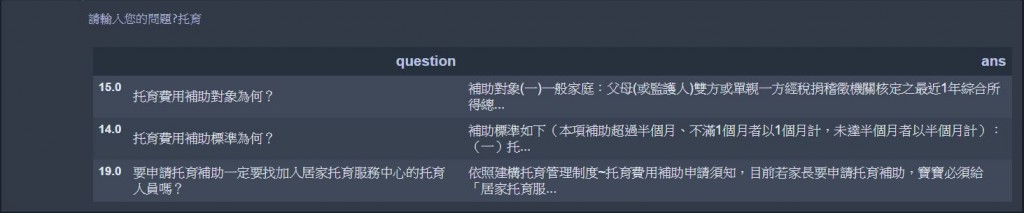
恭喜大家已經做出LineBot的檢索引擎拉~~~
