本系列目錄 《來做個網路瀏覽器吧!》文章列表
昨天討論了什麼是 box。算是對 layout 有初步認識了。
今天來看 robinson/src/layout.rs 裡面如何實作。
首先定義 box 的模型,包含 x、y 位置,寬度、高度、padding、margin、邊框。
#[derive(Clone, Copy, Default, Debug)]
pub struct Rect {
pub x: f32,
pub y: f32,
pub width: f32,
pub height: f32,
}
#[derive(Clone, Copy, Default, Debug)]
pub struct Dimensions {
/// Position of the content area relative to the document origin:
pub content: Rect,
// Surrounding edges:
pub padding: EdgeSizes,
pub border: EdgeSizes,
pub margin: EdgeSizes,
}
#[derive(Clone, Copy, Default, Debug)]
pub struct EdgeSizes {
pub left: f32,
pub right: f32,
pub top: f32,
pub bottom: f32,
}
layout tree 是由許多 box 所組成。這邊定義一個 box,包含他的模型、型別和他的 child。
struct LayoutBox<'a> {
dimensions: Dimensions,
box_type: BoxType<'a>,
children: Vec<LayoutBox<'a>>,
}
再來是定義 box 型別,也就是 CSS 的 deplay。
這邊只定義三種型別:block、inline、anonymous
這邊可以看一下 Mozilla 的說明。
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| block | The element generates a block element box. |
| inline | The element generates one or more inline element boxes. |
| 如下圖所示(來源) | |
 |
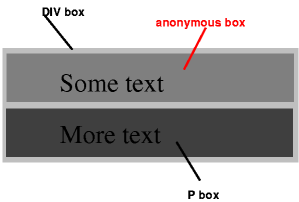
至於什麼是 Anonymous 可以看以下圖解(來源):
<DIV>
Some text
<P>More text
</DIV>
pub enum BoxType<'a> {
BlockNode(&'a StyledNode<'a>),
InlineNode(&'a StyledNode<'a>),
AnonymousBlock,
}
為了讓 layout tree 取得 DOM 的 display 是什麼,我們在 style 的模組中有以下的 code 來取得:
enum Display {
Inline,
Block,
None,
}
impl StyledNode {
// Return the specified value of a property if it exists, otherwise `None`.
fn value(&self, name: &str) -> Option<Value> {
self.specified_values.get(name).map(|v| v.clone())
}
// The value of the `display` property (defaults to inline).
fn display(&self) -> Display {
match self.value("display") {
Some(Keyword(s)) => match &*s {
"block" => Display::Block,
"none" => Display::None,
_ => Display::Inline
},
_ => Display::Inline
}
}
}
接著就可以來建立用 style tree 建立 layout tree。
順著 root 不斷遞迴把樹建構起來。
如果 display 是 none 的節點則不列入計算。
/// Transform a style tree into a layout tree.
pub fn layout_tree<'a>(node: &'a StyledNode<'a>, mut containing_block: Dimensions) -> LayoutBox<'a> {
// The layout algorithm expects the container height to start at 0.
containing_block.content.height = 0.0;
let mut root_box = build_layout_tree(node);
root_box.layout(containing_block);
root_box
}
/// Build the tree of LayoutBoxes, but don't perform any layout calculations yet.
fn build_layout_tree<'a>(style_node: &'a StyledNode<'a>) -> LayoutBox<'a> {
// Create the root box.
let mut root = LayoutBox::new(match style_node.display() {
Display::Block => BlockNode(style_node),
Display::Inline => InlineNode(style_node),
Display::None => panic!("Root node has display: none.")
});
// Create the descendant boxes.
for child in &style_node.children {
match child.display() {
Display::Block => root.children.push(build_layout_tree(child)),
Display::Inline => root.get_inline_container().children.push(build_layout_tree(child)),
Display::None => {} // Don't lay out nodes with `display: none;`
}
}
root
}
關於作者
劉安齊
軟體工程師,熱愛寫程式,更喜歡推廣程式讓更多人學會

請問 <'a> 是什麼意思呢?
Rust 語言特有的語法
代表自己定義生命週期
https://rustbyexample.com/scope/lifetime.html