昨天用ESLint,照顧程式碼風格,今天真的要來寫程式了
ES6 有些讓人欲罷不能的語法,它們超超超…常用,不能不會:
在 Day 3 - 一周目- 建立 第一個Node.js 專案 我們安裝了人生第一個套件 lodash,在我們的程式中要怎麼用呢?
不幸的,javascript 程式碼是否能正常執行是由執行環境境決定的,所以不同的環境語法可能有些微的不同。Node.js 和多數瀏覽器用的ES6 有不同的模組引入方法
總結如下:(截錄自exports、module.exports和export、export default到底是怎回事)
require: Node.js 和 ES6 都支援的引入export / import : 只有ES6 支援的導出引入module.exports / exports: 只有 Node.js 支援的導出從環境的角度:
require
const _ = require('lodash');
module.exports / exports
module.exports = {
myFun: ()=>{}
}
require / import
import _ from 'lodash'; // 或 const _ = rquire('lodash');
export
export default {
myFun: ()=>{}
};
Node.js雖然是CommonJS規範, 但不久的將來也可以用 import 了,見Node.js v10.11.0 - ECMAScript Modules
下面可以看到完整的範例:
node ./src/index.js,看到結果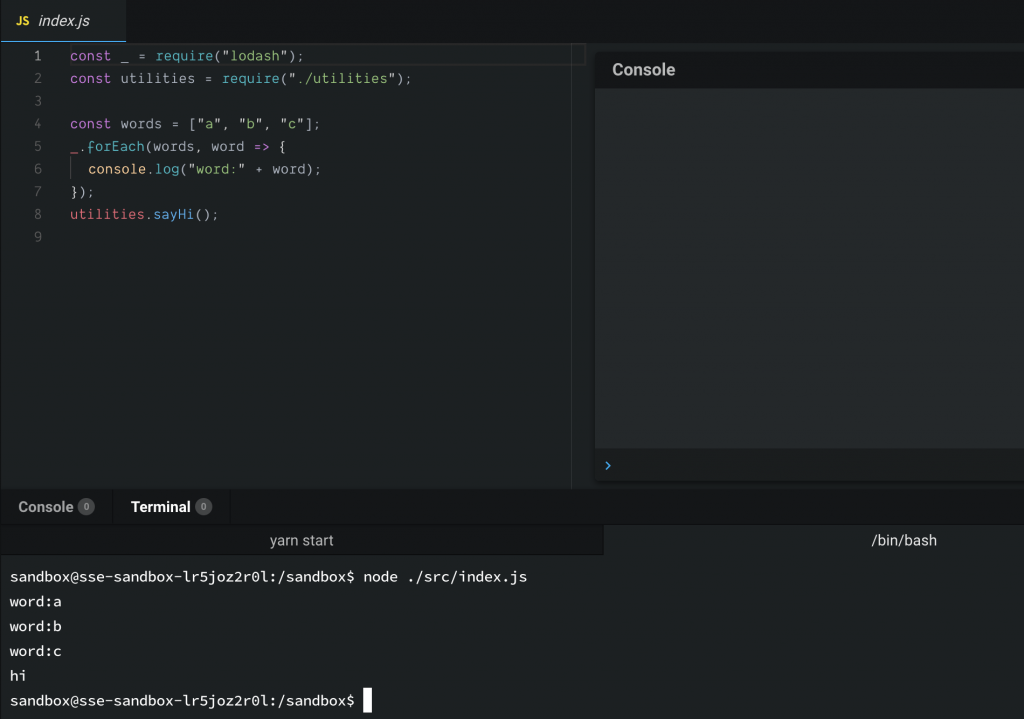
這曾在Day 5 - 一周目- 從VSCode debug 模式看作用域(Scope)、this、閉包(Closure)介紹過,他的外型如同他名字有箭頭 () => {}
不用命名的函數/暱名函數:有些時候命名函數是多此一舉的事
const names = ['billy', 'may'];
const persons = names.map(name => {
return {name: name};
});
這裡的箭頭函數表明了把字串(ex: 'billy') 轉成物件(ex: {name: 'billy'}),函數命名是多些一舉的
簡化表達式: 除了 function 字拿掉了,若回傳值可以用一行程式碼表達,連 {…} 和 return 也可以拿掉
const names = ['billy', 'may'];
const persons = names.map(name => ({name: name}));
是不是更簡化了阿~
注意,因為回傳是物件,但物件的 {…} 會和函數的{…}區塊弄混,所以要用 (…) 包起來
清楚的函數表達作用:常出現在 Functional programming 中,像是 Ramda文件中經常會出現用來表達作用。
我們舉線性函數例子,你覺得哪個清楚表達作用呢?
// Statements - 一般函數版本
function plus(b, x) {
return x + b;
}
function mult(a, x) {
return a * x;
}
function linear(a, b, x) {
return plus(b, mult(a, x));
}
console.log(linear(2, 1, 3));
// Declarative programming - 箭頭函數版本
const linearGen = a => b => x => a * x + b;
const linear21 = linearGen(2)(1);
console.log(linear21(3));
// linearGen 用一般函數就像下面
function _linearGen(a) {
return function (b) {
return function (x) {
return a * x + b;
};
};
}
console.log(_linearGen(2)(1)(3));
其實 一般的函數和箭頭函數還是有些微的不同,可以見 Arrow function vs function declaration / expressions: Are they equivalent / exchangeable?。通常是發生在
this被動態修改時就會出現差異(像是:call,apply…之類的)。
Destructuring Assignment 我覺得是 ES6 最酷的語法(我目前只在 ES6 看到,其它語言沒見過),一行程式碼做兩件事(以物件為例):
const person = {name: 'Billy'};
const name = person.name // 取出值
const person = {name: 'Billy'};
const id = person.id || 'No ID'
用 Destructuring Assignment 就是
const person = {name: 'Billy'};
const {name, id = 'No ID'} = person;
若 name 已被宣告過可以換變數名字,用 : 符號
const person = {name: 'Billy'};
const {name: nickname, id = 'No ID'} = person;
console.log(nickname, id); // Billy, No ID
Destructuring Assignment 可以對 Array 或 Object 使用,文件 Destructuring Assignment 舉了很多用法,我只列我常用的
const person = {name: 'Billy', gender: 'man'};
const {name: nickname, id = 'No ID'} = person;
const person = {name: 'Billy', gender: 'man'};
const {name, ...others} = person;
console.log(others); // { gender: 'man' }
const person = {name: 'Billy', gender: 'man'};
function welcomePerson({name = 'guest'} = {}) {
console.log(`Hi! ${name}`);
}
welcomePerson(person); // Hi! Billy
welcomePerson(); // Hi! guest
welcomePerson({name = 'guest'} = {}) 中的 = {},是函數參數若沒傳就是空物件 {}
f(a, b) 改成 f(obj)。經常被用在 options
const options = {type: 'type1'};
function welcomePrefix(options = {}) {
const {type} = options;
return type === 'type1' ? 'Hi! ' : 'Hello! ';
}
console.log(welcomePrefix(options) + 'Billy');
function getPerson() {
const person = {name: 'Billy'};
return person;
}
const {name} = getPerson();
console.log(name); // Billy
陣列解構依於 順序 ,我反而少用
function getPair() {
return ['a', 1];
}
const [word, number] = getPair();
console.log(word, number); // a 1
... Spread syntax 也是 ES6 必用的語法。可以用在 React component 中,把值「展開」送到 component中,例如:假設 props = {name: 'Name', price: 1},放到 <MyComonent/> 中 <MyComonent title='Title' {...props} />, 相當於 <MyComonent title="Title" name="Name" price=1 />。
以下是我常用的情況
保留剩餘:「物件解構-保留剩餘」中的 const {name, ...others} = person 就是用到 Spread syntax
用建立新陣列/物件
// object
const options = {type: 'type1', auto: true};
const newOptions1 = {enable: true, ...options};
const newOptions2 = {enable: true, ...options, auto: false};
console.log(newOptions1); // { enable: true, type: 'type1', auto: true }
console.log(newOptions2); // { enable: true, type: 'type1', auto: false },這裡後出現的 auto 會蓋住前面的
// array
const words = ['b', 'c'];
const allWords = ['a', ...words, 'd'];
console.log(allWords);
注意:Object 的同名屬性可能是被後面的覆蓋
不定長度參參數呼叫: 有沒有發現 console.log 可以輸入不同長度的參數?
console.log('a'); // a
console.log('a', 'b'); // a b
可以利用 Spread syntax,把陣列展開
const words = ['a', 'b'];
// 送入一整個陣列
console.log(words); // [ 'a', 'b' ]
// 展開元素,這等價於 console.log(words[0], words[1])
console.log(...words); // a b
所以,words的長度改變,console.log(...words) 也不用修改了
Bonus:製做非固定長度的函數 - arguments 是存在於一般函數(非箭頭函數)的區域變數(local variable),它是 array-like(可以用
arguments[0]取值,但沒有 Array 的所有函數),可以來定義非固定長度的函數,像是console.log
function mylog() {
// const badPrefixArgs = arguments.map(arg => '=>' + arg); // 這拿掉會丟出錯誤:TypeError: arguments.map is not a function
// 這裡呼叫空陣列[]的 map函數,把 this 換成 arguments
const prefixArgs = [].map.call(arguments, arg => '=>' + arg);
console.log(...prefixArgs);
// 或用 lodash
//const _ = require('lodash');
//const prefixArgs = _.map(arguments, arg => '=>' + arg);
}
mylog('a', 'b'); // =>a =>b
這是大家常用的物件編程語法,更多內容可以看 ECMAScript 6 入門
class MyError extends Error {
constructor() {
super(...arguments);
}
toJson() {
return {
message: this.message
}
}
}
const error = new MyError('my error');
console.log(error.toString());
console.log(error.toJson());
JSON 這內建物件,不用 new 就可以直接使用,在序列化(serialization)物件和還原物件很好用
JSON.stringify 和 JSON.parse 分別是序列化和還原,其中序列化的對像是 objects、arrays、numbers、strings、booleans, 和 null的值。
它們執行失敗時可能會丟例外(exception),一個穩健(robust)的程式應該要處理它們。
const person = {name: 'billy', orderIds: ['0A', '0B']}
let serializedPerson = '';
try {
serializedPerson = JSON.stringify(person);
console.log(serializedPerson); // {"name":"billy","orderIds":["0A","0B"]}
} catch(e) { // TypeError exception
console.error(e);
}
let newPerson = {};
try {
newPerson = JSON.parse(serializedPerson);
console.log(newPerson); // Object {name: "billy", orderIds: Array(2)}
} catch(e) { // SyntaxError exception
console.error(e);
}
今天提的所有語法,在未來一定會一直出現,尤其是 模組使用 、 箭頭函數、 解構賦值 會一直陪伴著你。

函數回傳解構
function getPerson() {
const person = {name: 'Billy'};
return type === 'type1' ? 'Hi! ' : 'Hello! ';
}
const {name} = getPerson();
console.log(name); // Billy
陣列解構 Array destructuring
請問,不瞭解 "const {name} = getPerson();" 中 name一直都是undefined。
不好意思,是我copy/past貼錯了,已修正。
謝謝您的提醒。