這篇簡單介紹mapping的定義以及如何自己設定他
_index, _id, _source, and etcmapping explosion
如果定義太多fields可能導致 mapping explosion ,像是 out of memory errors 或是 很難復原的情況
之前提過,es index預設是可以不用自己定義 mappings ,輸入document時,自動辨別資料類型產生出對應的field及data type,這種情況下,如果輸入的資料結構不是固定的,此時 mappings 就會一直增長
Dynamic Mapping
在第二重有說明過,所以這邊就不概述了
畢竟什麼資料會進到es自己最清楚,所以有些情境或use case是會需要明確指定mappings的
主要有兩個時機點是可以建立mappings
Create an index with an explicit mapping
新增index時,明確指定mapping,即上述第一個時機點
Request
PUT /my-index-000001
{
"mappings": { (1)
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "integer" (2)
},
"email": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
(1): 如沒有此 mappings ,則不定義 mappings,直接建立index而已
(2): 此 type 為 field data type,後續會詳細介紹有哪些 data type
Response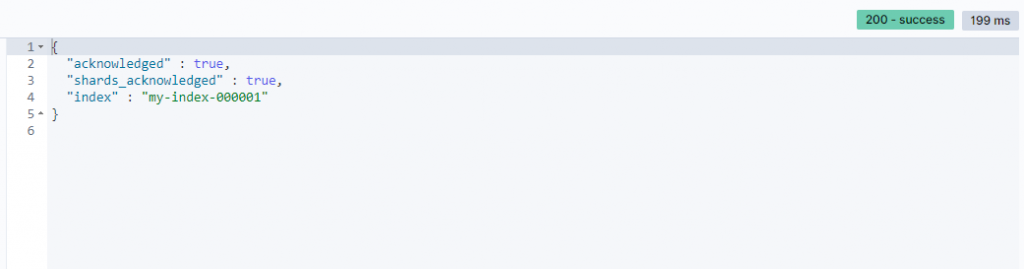
Add a field to an existing mapping
新增field到存在的mapping,即上述第二個時機點
Request
PUT /my-index-000001/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"employee-id": { (1)
"type": "keyword",
"index": false (2)
}
}
}
(1): 新增了一個field employee-id
(2): index 為 mapping parameter ,代表著是否會被搜尋得到,後續會更詳細介紹有哪些 mapping parameter
Response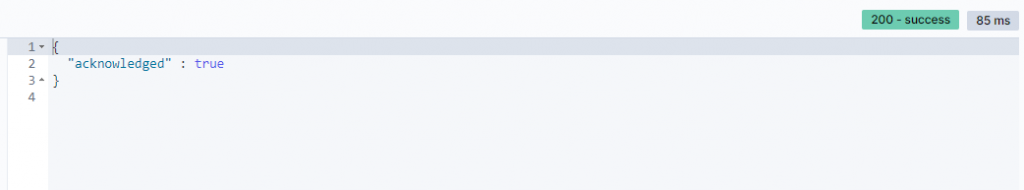
View the mapping of an index
查看index的mapping,可用來驗證上述兩種建立mapping是否正確
Request
GET /my-index-000001/_mapping
Response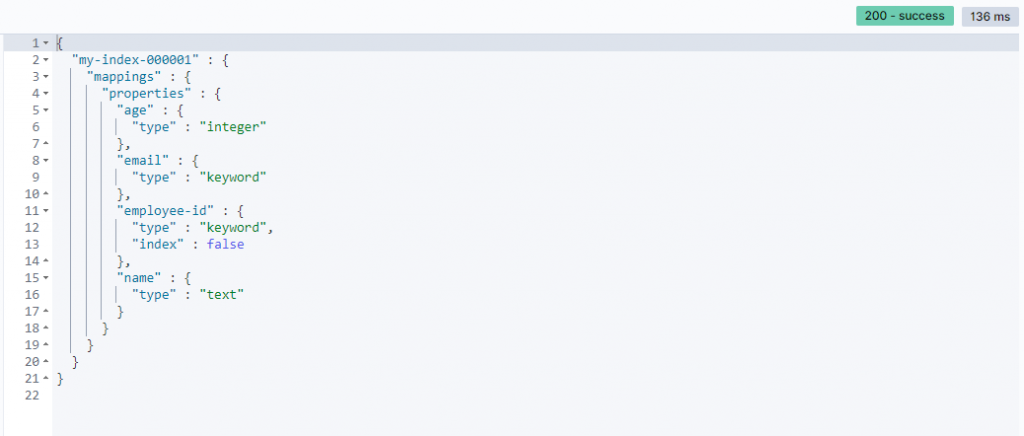
Update the mapping of a field
更新mapping內已存在的field
會發現上述其實都是建立新的field,而沒有更新現有的,
es是沒有辦法直接更新現有的field的data type,
想想也是,畢竟如果已經有資料已建立,更改field data type可能會讓已建立的data失效
當然,還是有方法可以做到,就是先建立一個新的index,裡面明確定義了正確的mapping後,再透過 reindex 資料到那個index
小小新手,如有理解錯誤或寫錯再請不吝提醒或糾正
