在 Angular 的 Component 中有一個生命週期,當 Angular 實例化這個 Component 並且把它或他的 sub-component 呈現在 UI 時便會開始,而 Lifecycle 會持續的檢測是否有綁定的數據被更改,因為這些綁定數據的更改可能會需要更新 UI 或 Component 的內容,而當 Angular 銷毀了這個 Component 實例並從 DOM 中移除這個 Component 的 Template 後 Lifecycle 就會結束。
簡單來說,當 Angular 在某一個地方的 HTML 發現了一個 Component 的 selector(身分證號碼)後,便會找到這個 Component 並將他實例化和將他的 Template 呈現在 UI 上(放進 DOM 中),這個時候這個 Component 就開始了他的一生,他會在他的一生中不斷的檢測是否有東西需要改變,最後當使用者離開了這個頁面,代表著這個 Component 不在被需要了,他就會被銷毀掉結束他的一生。

了解了什麼是 Lifecycle 後,我們要正式介紹 Lifecycle 了,首先你可以透過 import angular/core 引入一個或多個 lifecycle 使用。
import { Component, OnInit, OnChanges, ... } from '@angular/core';
每一個 Lifecycle method 前面都有 ng 當作前綴字,舉例來說如果要使用 OnInit 這個 Lifecycle method 則要在你的 TypeScript Class 中輸入 ngOnInit( ),而當你要使用某一個 Lifycycle method 時,記得要在你的 Class 使用 implements 繼承這個 Lifycycle。
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-first-component',
templateUrl: './first-component.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./first-component.component.css']
})
export class FirstComponentComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
}
每一個 Lifecycle method 都有對應的被調用時機,Angular 會自動在最適當的時間調用適當的 Lifecycle method,以下是 Angular 按照順序執行的 Lifecycle method。
Name | Purpose | Timing
------------- | -------------
ngOnChanges() | 當這制或重置綁定的數據時會被調用,比如你在這個 Component 中綁定了一個由父層傳下來的數據,當這個數據發生改變(父層丟新的東西下來)時就會觸發,要注意的是如果在這個 method 的邏輯沒有處理好,可能會發生無限迴圈的問題,所以需要特別注意。 | 他會在 Component 剛被創造出來就被調用一次,會比 OnInit() 還早,還有每當一個或多個數據綁定 @Input 屬性發生改變時會觸發。
ngOnInit() | 會在 Component 完成數據綁定(ngOnChanges)後初始化 Component。 | 在第一個 ngOnChange() 之後觸發,只會被調用一次。
ngDoCheck() | 當 Angular 無法獲不會自動檢測到變化並採取行動,在每次更改檢測運行期間被調用,會跟在 ngOnChanges() 和 ngOnInit() 後面,有點抽象我會在下面有詳細解釋。 | 在每次更改檢測運行時立即在 ngOnChanges() 之後調用,在第一次運行時立即在 ngOnInit() 之後調用。
ngAfterContentInit() | Angular 將 ng-content 的內容投影到 Component 的 view 後被調用 | 在第一個 ngDoCheck() 後被調用
ngAfterContentChecked() | 每次完成 ng-content 的變更檢測之後調用 | 在 ngAfterContentInit() 之後和每一個 ngDoCheck() 之後被調用
ngAfterViewInit() | 當 Angular 初始化自身 Component和子 Component 的 view 後被調用。 | 在第一個 ngAfterContentChecked() 之後調用一次
ngAfterViewChecked() | 每次做完自身 Component和子 Component 的變更檢測後呼叫 | 在 ngAfterViewInit() 和每個 ngAfterContentChecked() 之後調用
ngOnDestroy() | 在 Angular 銷毀 directive 或 Component 之前調用,主要用於 unsubscribe Observable 以防內存泄露 | 在 Angular 銷毀 directive 或 Component 之前立即調用
當我第一次在 Angular 官方文件中看到這個我看了十幾次我都看不懂,查了一些文章後才大概了解他是在什麼時候被呼叫到,我們就來詳細介紹一下吧。
在 Angular 官方文檔中這樣寫到:
Detect and act upon changes that Angular can’t or won’t detect on its own.
Called during every change detection run, immediately after ngOnChanges() and ngOnInit()
相當抽象對吧,,雖然知道他會是在 ngOnChanges( ) 和 ngOnInit( ) 之後觸發的,但是當他被觸發的時候 Component 是否有被檢查?而 Angular 無法自動檢查是指什麼?要解答這個問題我們需要先了解什麼是 Component check,在 Component 變更檢測有三個核心的操作:
除了這些之外 Angular 還會觸發 Lifecycle 作為變更檢測的一部分,所以當檢查父層時會觸發子層的 Lifycycle,假設我們有一個這樣的結構:
ComponentA
ComponentB
ComponentC
當 Angular 運行檢測時的順序如下:
Checking A component:
- update B input bindings
- call NgDoCheck on the B component
- update DOM interpolations for component A
Checking B component:
- update C input bindings
- call NgDoCheck on the C component
- update DOM interpolations for component B
Checking C component:
- update DOM interpolations for component C
上面的順序只是一個簡單的順序列表,可以看到 DoCheck 會在何時被觸發。
可以看到在檢查父層時子層就會調用 ngDoCheck ,假設我們在 ComponentB 使用了 onPush 會發生什麼事:
Checking A component:
- update B input bindings
- call NgDoCheck on the B component
- update DOM interpolations for component A
if (bindings changed) -> checking B component:
- update C input bindings
- call NgDoCheck on the C component
- update DOM interpolations for component B
Checking C component:
- update DOM interpolations for component C
可以看到我們在 ComponenB 檢測前加上了一個小判斷,如果這個判斷為 false 就會滿足官方文檔提到的當 Angular 無法獲不會自動檢測到變化並採取行動,所以即使不會檢查 ComponentB 但是仍然會觸發 ComponentB 上面的 ngDoCheck。
我們來透過程式碼直接操作看看,首先我們先定義一個 sub-component
@Component({
selector: 'app-first-component',
template: '<h2>The name is: {{o.name}}</h2>',
changeDetection: ChangeDetectionStrategy.OnPush // (1)
})
export class FirstComponentComponent implements OnChanges {
@Input() o: { id: number; name: string; } = { id: NaN, name: '' }; // (2)
id: number = NaN;
ngOnChanges() {
console.log('first-component OnChange() been call'); // (3)
this.id = this.o.id;
}
ngDoCheck() {
console.log('first-component DoCheck() been call'); // (4)
if (this.id !== this.o.id) {
this.cd.markForCheck();
}
}
}
接著我們在父層將 o 這個物件向下傳給 sub-component,在2秒內他通過更新 name 和 id 來改變這個物件
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<h1>Hello {{name}}</h1>
<a-comp [o]="o"></a-comp> // (1)
`
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit{
o = {id: 1, name: 'Fandix'};
ngOnInit() {
setTimeout(() => { // (2)
this.o.id = 2;
this.o.name = 'Jane';
}, 2000);
}
}
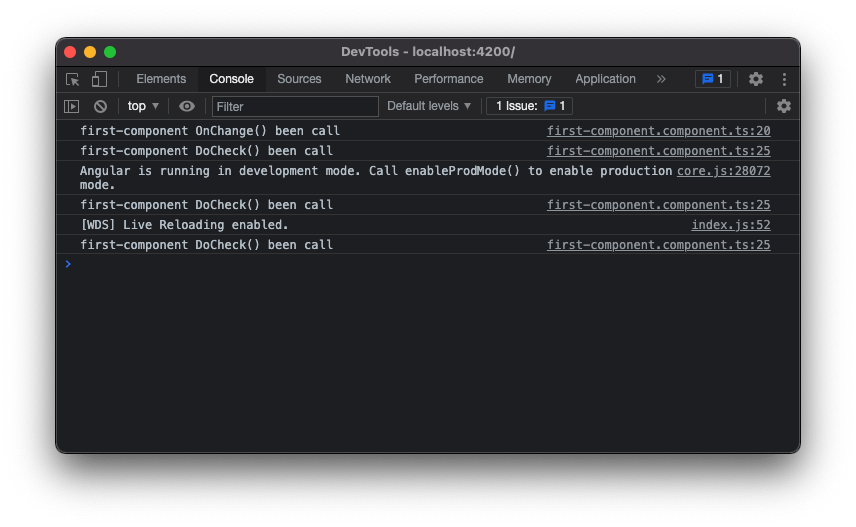
由於 Angular 追蹤的是 o 這個物件的 reference,所以當我們以不更改 reference 的情況下改變 o 的內容就不會被 Angular 檢測到,這就是為什麼 sub-component 的 ngOnChanges() 只有被呼叫一次(創建 Component 時第一次呼叫),但是經過上面的解說後可以知道,就算 sub-component 不會被 Angular 給自動檢測,但是由於父層發生了改變就會讓子層的 ngDoCheck 自動被呼叫到,所以在 AppComponent 發生改變時 sub-component 的 ngDoCheck 依然會被觸發,這就是當 Angular 無法或不會自動檢測到變化並採取行動的意思。
大概介紹完 Angular 的 Lifecycle,我們來看看 ngOnInit 的使用場景。
在開發 Angular component 時可以將清理的邏輯放在 ngOnDestroy( ) 中,這些邏輯必須在 Angular 銷毀這個 Component 之前執行,這裡是釋放不會自動釋放資源的地方,如果一直建立不會自動釋放資源的東西最後卻沒有將他清理掉,可能會造成內存洩漏或滿載的問題,這裡可以用來:
在本章中我們談到了 Angular 的 Lifecycle,了解有哪些 Lifecycle method 可以使用以及他們被調用的時機點,掌握好如何在對的時機點使用對的 Lifecycle method 是非常重要的,如果在錯的時間使用錯的 Lifecycle method 會造成非預期的錯誤,下一章將介紹在 Angular 中父子層 Component 之間是如何共享數據的,雖然在本章節有提到一點點( @Input( ) ),不過將會在下一張更詳細的說明,那我們下一章再見。
