特徵工程可以分為兩大部分,一是根據現有的資料特徵進行篩選,選出較有影響力的特徵進行訓練,另一個是根據現有的資料特徵,去衍生出資料集中沒有的特徵來讓模型學習。今天我們會將重點放在前者。
有時候一個數據集可能可以蒐集到海量的特徵資料,例如一個實驗往往有上百個感測器(Sensor)在記錄資料,但那麼多的特徵不見得對模型的訓練有幫助,甚至還會造成過度擬合(Over-fitting)問題,因此我們今天介紹特徵選取,來對資料進行化約,保留重要的特徵。
特徵選取是依據所訂定的特徵衡量條件,刪除不相關的特徵或屬性,以選取用於分析資料最佳特徵的過程,使用特徵選取的目的與時機有以下幾點:
其操作步驟依序為:
下面我們介紹幾種特徵選取的方法,並運用套件sklearn.feature_selection 裡的函數來實現。
過濾法是列入一些篩選特徵的標準,檢測與目標變數相關的特徵,挑選出具變化性以及中高度相關的特徵,方法包含:
什麼是低變異數的特徵呢?就是一些資料幾乎沒有變化的特徵,像是:
from sklearn.feature_selection import VarianceThreshold
constant = VarianceThreshold(threshold=0)
constant.fit(x_train) #fit我們的資料集
# 得到常數特徵的欄位
constant_columns = [column for column in x_train.columns
if column not in
x_train.columns[constant.get_support()]]
print(constant_columns)
# 設定門檻,要刪除幾%的資料
threshold = 0.95
quasi_constant_feature = [] #用來記錄的list
for i in x_train.columns: #每個特徵依序看
# 計算比率
predominant = (x_train[i].value_counts() /
np.float(len(x_train))).sort_values(ascending=False).values[0]
# 假如大於門檻 加入 list
if predominant >= threshold:
quasi_constant_feature.append(i)
print(quasi_constant_feature)
# 轉置特徵矩陣
train_features_T = x_train.T
#找出重複的欄位
duplicated_columns = train_features_T[train_features_T.duplicated()].index.values
print(duplicated_columns )
利用一些判斷指標來衡量變數與目標變數之間的關係
● SelectKBest:選取 K 個最好的特徵,k 為參數,代表選擇的特徵數。
● SelectPercentile:選取多少百分比的特徵,percentile 為參數,代表百分比,用 10 代表 10%。
以鐵達尼號資料集為例:
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest
from sklearn.feature_selection import chi2
#離散型資料要先轉成數值
x=_train_df[['Pclass', 'Sex', 'Age', 'Fare', 'Embarked', 'IsAlone','Cabin']]
y=data['Survived']
x_new = SelectKBest(chi2, k=2).fit_transform(x, y) #挑選2個最好的特徵
display(x_new)
假設預測股價
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest
from sklearn.feature_selection import f_regression
x=data[['前一天價格','前一季價格', '前一年價格','同性質股票價格']]
y=data['Price']
x_new = SelectPercentile(chi2, percentile=50).fit_transform(x, y) #取前50%的特徵
display(x_new)
是一種特徵選擇和演算法訓練同時進行的方法,根據某一種評量標準,每次選擇某些特徵或排除某些特徵,常用的方法為遞歸特徵消除(RFE)。
RFE是根據問題為離散或連續,利用機器學習的模型進行挑選,為一貪婪優化演算法,目的在找尋最佳的特徵子集。
#RFE
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE
rf = RandomForestClassifier()
rfe = RFE(rf, 6) #篩選6個特徵
rfe.fit(X_train, Y_train)
print(f"Number of selected features: {rfe.n_features_}\n\
Selected Features:", [feature for feature, rank in zip(X_train.columns.values, rfe.ranking_) if rank==1]) #列出挑選的6個變數
以鐵達尼號資料集為例,我們找到以下6個特徵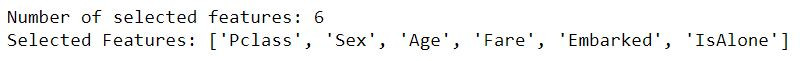
運作方式為:一開始模型有全部k個變數,一個接一個從k個變數中選取對 y (label)變異最沒顯著影響的變數刪除,直到剩餘的變數對解釋y (label)剩餘變異皆有顯著影響才停止。
import statsmodels.api as sm
import pandas as pd
#Stepwise
def stepwise_selection(data, target,SL_in=0.05,SL_out = 0.05):
initial_features = data.columns.tolist()
best_features = []
while (len(initial_features)>0):
remaining_features = list(set(initial_features)-set(best_features))
new_pval = pd.Series(index=remaining_features)
for new_column in remaining_features:
model = sm.OLS(target, sm.add_constant(data[best_features+[new_column]])).fit()
new_pval[new_column] = model.pvalues[new_column]
min_p_value = new_pval.min()
if(min_p_value<SL_in):
best_features.append(new_pval.idxmin())
while(len(best_features)>0):
best_features_with_constant = sm.add_constant(data[best_features])
p_values = sm.OLS(target, best_features_with_constant).fit().pvalues[1:]
max_p_value = p_values.max()
if(max_p_value >= SL_out):
excluded_feature = p_values.idxmax()
best_features.remove(excluded_feature)
else:
break
else:
break
return best_features
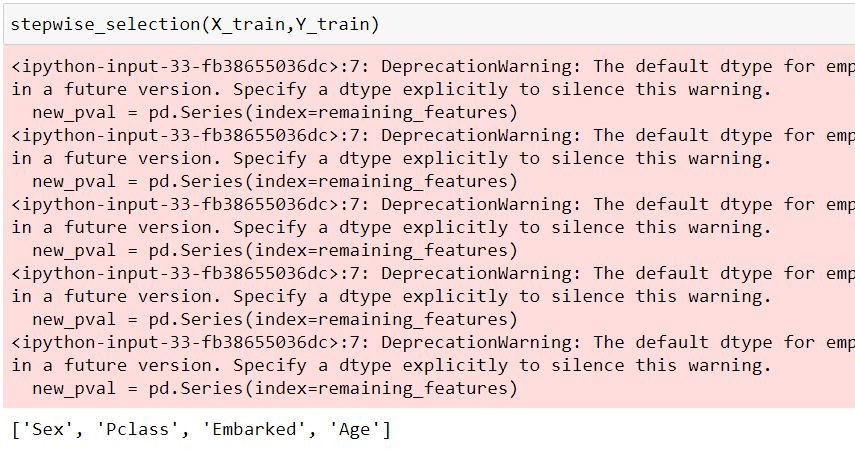
今天介紹了幾種方法用於特徵選取,有時候我們拿到的資料集的特徵很多,模型訓練起來狀況不佳的話,就可以考慮使用特徵選取來篩選好的特徵,但也要注意閥值、參數的控制,不要弄巧成拙的把好特徵刪除。
篩選出壞的特徵並不難,但當我們手邊的資料特徵沒有這麼多時,就要想辦法生出新的特徵,舉例來說:我們可以透過身高及體重資料生成出BMI的資料,這個"衍生"資料的步驟比特徵選取還難的多,卻也更重要,需要結合對於分析行業的知識量以及對數據的敏感度,當然,接觸過越多資料分析專案就能越上手!
