Seq2seq with attention 這個是從上一篇文章直接加入 attention 機制改出來的,attention 機制如果不懂的話可能要先去爬文。
那有加入attention 的話,encoder 跟 decoder 的部分都要做一些調整
translate function 因為加入了attention 的關係,因此在使用上要翻譯的時候要記得把 encoder 產出的 state 跟 content vector 帶入到 encoder裡面,剩下的後面再講
def translate_sentence(model, sentence, chinese, english, device, max_length=50):
# 先載入 tokensizer
spacy_zh = spacy.load("zh_core_web_sm")
# Create tokens using spacy and everything in lower case (which is what our vocab is)
if type(sentence) == str:
tokens = [token.text.lower() for token in spacy_zh(sentence)]
else:
tokens = [token.lower() for token in sentence]
# 加入開始符號跟結束符號,代表一個句子
tokens.insert(0, chinese.init_token)
tokens.append(chinese.eos_token)
# 然後把文字轉自 vactor
text_to_indices = [chinese.vocab.stoi[token] for token in tokens]
# 再把 vactor list 轉換成 Tensor
sentence_tensor = torch.LongTensor(text_to_indices).unsqueeze(1).to(device)
# 取消梯度修正
with torch.no_grad():
outputs_encoder, hiddens, cells = model.encoder(sentence_tensor)
# 先宣告 outputs ,然後裡面放一個開符號
outputs = [english.vocab.stoi["<sos>"]]
for _ in range(max_length):
previous_word = torch.LongTensor([outputs[-1]]).to(device)
# seq2seq 的decoder 會把上一個 hidden_state 跟 cell 當作input 這是觀念
# 然後output機率最大的
with torch.no_grad():
output, hiddens, cells = model.decoder(
previous_word, outputs_encoder, hiddens, cells
)
best_guess = output.argmax(1).item()
# 機率最大的數值再把它放進output
outputs.append(best_guess)
# 如果是結束字元 eos 的話就中斷不然會一直預測下去
if output.argmax(1).item() == english.vocab.stoi["<eos>"]:
break
# 再把 vactor 轉成文字, itos = integer to string
translated_sentence = [english.vocab.itos[idx] for idx in outputs]
# remove start token
return translated_sentence[1:]
encoder 的部分則是需要把它改為 bi-lstm 因為在一般的seq2seq 的 lstm 因為只需要考慮上一個的vector ,所以單向就可以,但是在加入attention 的話因為要計算 attention score 所以需要把完整的 sequence 都考慮進去,因此要改為雙向
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, embedding_size, hidden_size, num_layers, p):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, embedding_size)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embedding_size, hidden_size, num_layers, bidirectional=True)
self.fc_hidden = nn.Linear(hidden_size * 2, hidden_size)
self.fc_cell = nn.Linear(hidden_size * 2, hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p)
def forward(self, x):
# x: (seq_length, N) where N is batch size
embedding = self.dropout(self.embedding(x))
# embedding shape: (seq_length, N, embedding_size)
encoder_states, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(embedding)
# outputs shape: (seq_length, N, hidden_size)
# Use forward, backward cells and hidden through a linear layer
# so that it can be input to the decoder which is not bidirectional
# Also using index slicing ([idx:idx+1]) to keep the dimension
# 因為使用雙向的話會有 0 跟 1 ,所以這邊會需要cat起來
hidden = self.fc_hidden(torch.cat((hidden[0:1], hidden[1:2]), dim=2))
cell = self.fc_cell(torch.cat((cell[0:1], cell[1:2]), dim=2))
# encoder_states => 是最後的狀態, h1 h2 h3 放在hidden 裡面
return encoder_states, hidden, cell
如果不了解 decoder 的話,可以搭配這張截圖(來源Youtube)的部分,可以協助理解decoder 到底在做什麼
context vector = attention weight做 bmm(attention, encoder_state)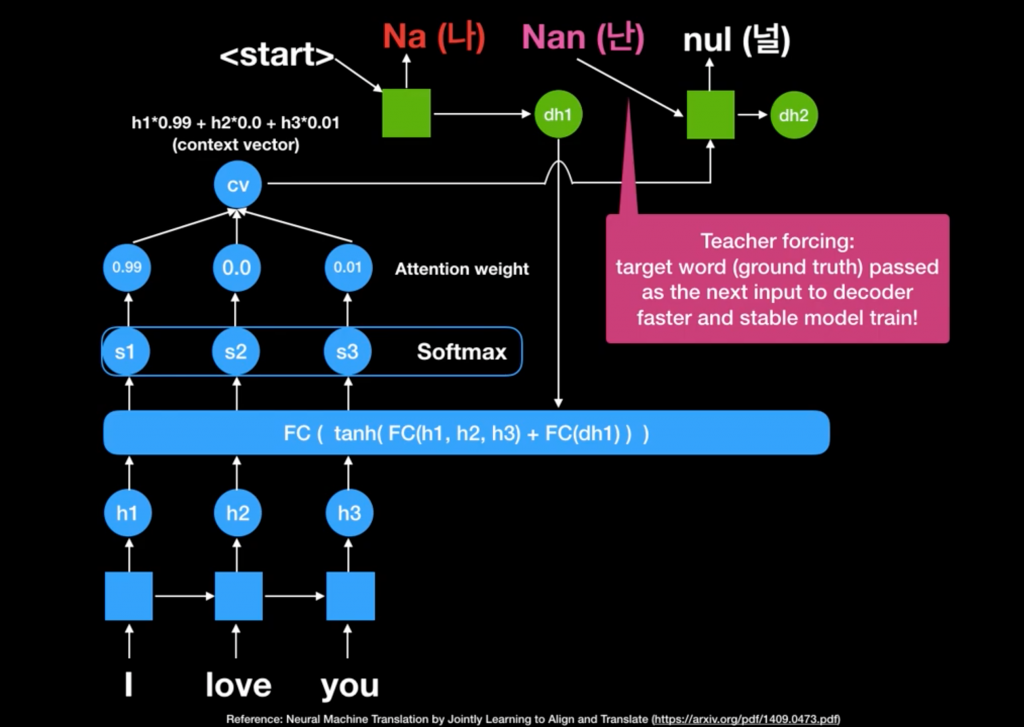
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self, input_size, embedding_size, hidden_size, output_size, num_layers, p
):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, embedding_size)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(hidden_size * 2 + embedding_size, hidden_size, num_layers)
self.energy = nn.Linear(hidden_size * 3, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=0)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x, encoder_states, hidden, cell):
x = x.unsqueeze(0)
# x: (1, N) where N is the batch size
embedding = self.dropout(self.embedding(x))
# embedding shape: (1, N, embedding_size
# hidden 應該要視為把encoder 的結果做 fc(h1 ,h2 h3)
sequence_length = encoder_states.shape[0]
h_reshaped = hidden.repeat(sequence_length, 1, 1)
# h_reshaped: (seq_length, N, hidden_size*2)
# encoder_states 應該為fc後的結果 = fc( final hidden state 3 or decoder_h1 h2 h3)
energy = self.relu(self.energy(torch.cat((h_reshaped, encoder_states), dim=2)))
# energy: (seq_length, N, 1)
# energy 應該為 s1 , s2 , s3,
attention = self.softmax(energy)
# attention: (seq_length, N, 1)
# attention score
# attention: (seq_length, N, 1), snk
# encoder_states: (seq_length, N, hidden_size*2), snl
# we want context_vector: (1, N, hidden_size*2), i.e knl
context_vector = torch.einsum("snk,snl->knl", attention, encoder_states)
# context_vector = attention weight * encoder_states
#### 原始寫法
# attention (seq_lens, N, 1)
# attention = attention.permute(1,2,0) # => attention (N, 1, seq_lens)
# encoder_state (seq_length, N, hidden_size*2)
# encoder_state = encoder_state.permute(1,0,2) # => (N, seq_lens, hidden_size*2)
# context_vector = torch.bmm(attention, encoder_state).permute(1,0,2) # 相乘
# torch.bmm(attention, encoder_state) => (N, 1, hidden_size*2) => permute 之後 (1, N, hidden_size*2)
rnn_input = torch.cat((context_vector, embedding), dim=2)
# rnn_input: (1, N, hidden_size*2 + embedding_size)
outputs, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(rnn_input, (hidden, cell))
# outputs shape: (1, N, hidden_size)
predictions = self.fc(outputs).squeeze(0)
# predictions: (N, hidden_size)
return predictions, hidden, cell
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder):
super(Seq2Seq, self).__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self, source, target, teacher_force_ratio=0.5):
# print(source.shape)
batch_size = source.shape[1]
target_len = target.shape[0]
target_vocab_size = len(english.vocab)
outputs = torch.zeros(target_len, batch_size, target_vocab_size).to(device)
# 這邊多一個output = encoder_states
encoder_states, hidden, cell = self.encoder(source)
# First input will be <SOS> token
x = target[0]
for t in range(1, target_len):
# At every time step use encoder_states and update hidden, cell
output, hidden, cell = self.decoder(x, encoder_states, hidden, cell)
# hidden 跟 cell 都是上個計算的結果導入這邊繼續計算
# Store prediction for current time step
outputs[t] = output
# Get the best word the Decoder predicted (index in the vocabulary)
best_guess = output.argmax(1)
# With probability of teacher_force_ratio we take the actual next word
# otherwise we take the word that the Decoder predicted it to be.
# Teacher Forcing is used so that the model gets used to seeing
# similar inputs at training and testing time, if teacher forcing is 1
# then inputs at test time might be completely different than what the
# network is used to. This was a long comment.
x = target[t] if random.random() < teacher_force_ratio else best_guess
# teacher force ratio 是用來協助訓練收斂的部分
return outputs
一樣checkpoint 很重要,hidden_size 會影響你訓練所使用的記憶體大小,但是太小記不住東西也沒用
checkPointPath = "/content/drive/MyDrive/Colab Notebooks/ithome/seq2seq_attention.pth.tar"
num_epochs = 100
learning_rate = 0.001
batch_size = 32
# Model hyperparameters
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
input_size_encoder = len(chinese.vocab)
input_size_decoder = len(english.vocab)
output_size = len(english.vocab)
encoder_embedding_size = 200
decoder_embedding_size = 200
hidden_size = 512 # Needs to be the same for both RNN's
num_layers = 1
enc_dropout = 0.0
dec_dropout = 0.0
# 先建立encoder net
encoder_net = Encoder(input_size_encoder, encoder_embedding_size, hidden_size, num_layers, enc_dropout).to(device)
# 再建立decoder net
decoder_net = Decoder(
input_size_decoder,
decoder_embedding_size,
hidden_size,
output_size,
num_layers,
dec_dropout,
).to(device)
# 兩個net丟進去seq2seq
model = Seq2Seq(encoder_net, decoder_net).to(device)
# 剩下的都一樣
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
pad_idx = english.vocab.stoi["<pad>"]
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=pad_idx)
# 如果有checkpoint的檔案就載入
if os.path.isfile(checkPointPath):
load_checkpoint(torch.load(checkPointPath ), model, optimizer)
# 可以看一下 bleu score 為多少(在尚未訓練之前)
score = bleu(test_data[1:100], model, chinese, english, device)
print(f"Bleu score {score*100:.2f}")
sentence = (
"你想不想要来我家看猫"
"一起看Netflix"
)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
print(f"[Epoch {epoch} / {num_epochs}]")
checkpoint = {"state_dict": model.state_dict(), "optimizer": optimizer.state_dict()}
save_checkpoint(checkpoint)
model.eval()
translated_sentence = translate_sentence(
model, sentence, chinese, english, device, max_length=50
)
print(f"Translated example sentence: \n {translated_sentence}")
model.train()
for batch_idx, batch in enumerate(train_iterator):
# Get input and targets and get to cuda
inp_data = batch.zh.to(device)
target = batch.eng.to(device)
# Forward prop
output = model(inp_data, target)
# Output is of shape (trg_len, batch_size, output_dim) but Cross Entropy Loss
# doesn't take input in that form. For example if we have MNIST we want to have
# output to be: (N, 10) and targets just (N). Here we can view it in a similar
# way that we have output_words * batch_size that we want to send in into
# our cost function, so we need to do some reshapin. While we're at it
# Let's also remove the start token while we're at it
output = output[1:].reshape(-1, output.shape[2])
target = target[1:].reshape(-1)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = criterion(output, target)
# Back prop
loss.backward()
# Clip to avoid exploding gradient issues, makes sure grads are
# within a healthy range
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1)
# Gradient descent step
optimizer.step()
# Plot to tensorboard
# writer.add_scalar("Training loss", loss, global_step=step)
step += 1
因為這個一個seqence 很大,所以對於大的句子和大的句子要直接做訓練的話,很容易造成記憶體不足,所以以我們範例的資料及要做訓練的話,其實不是那麼明智的選擇
反而用作者示範的 multi30k 這個資料及在訓練會輕鬆很多
