二元堆積(Binary Heap)為一有以下性質的二元樹:
1. 所有的parent nodes必須比下面的children nodes值都小(min heap)或都大(max heap)。也就是說,如果是min heap,root會是整個tree的最小值;如果是max heap,root會是整個tree的最大值。
2. 是個complete tree(除了最後一層外每一層皆被填滿)。因此,array/list適合用來表現binary heap。
這樣的性質,使得如果我們要找最大或最小值或是插入額外的數值,時間複雜度能大大的降低。(如圖1)實際使用的例子包含: Prim’s Algorithm, Heap Sort or Priority Queue。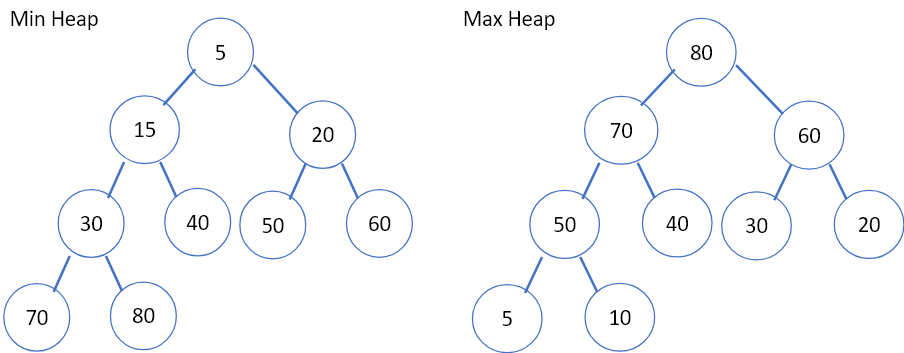
圖1. 左:為Min Heap,可以看到root以下的所有子孫都比自己大。所有parent都比自己的children小。右: 為Max Heap,所有children都比自己的parent小。
# 用python list建一個有限大小的Binary Heap,一樣因為index=0 不用,我們這裡寫作maxsize+1
# Time: O(1), Space: O(n)
class BinaryHeap:
def __init__(self, maxsize, heaptype):
self.customList = [None]*(maxsize+1)
self.maxsize = maxsize
self.heapsize = 0
self.heaptype = heaptype
# print function 其實跟level order traversal 一樣
# 讓他可以直接print出level order traversal的結果,用來檢查用
# time o(n), space: o(1)
def __str__(self):
if self.heapsize == 0:
return
else:
res = ''
for i in range(1, self.heapsize+1):
res += str(self.customList[i])
res += ' '
return res
# 先定義幾個function等等在寫的時候不至於很雜亂
def swap(customList, index1, index2):
customList[index1], customList[index2] = customList[index2], customList[index1]
return customList
# 在heap中插入節點,先插在最末端,然後再用heapifyinsertNode去調
# time:log(n), space:log(n)
def insertNode(rootNode, value):
if rootNode.heapsize >= rootNode.maxsize:
return 'The heap is full...'
else:
rootNode.heapsize += 1
rootNode.customList[rootNode.heapsize] = value
heapifyinsertNode(rootNode, rootNode.heapsize)
# 調整插入節點的位子,不斷跟parent node比較,始之符合binary heap的規則
def heapifyinsertNode(rootNode, index):
if not rootNode or index < 2:
return
parent = index//2
if rootNode.heaptype == 'Min':
if rootNode.customList[parent] > rootNode.customList[index]:
rootNode.customList = swap(rootNode.customList, parent, index)
heapifyinsertNode(rootNode, parent)
else:
return
elif rootNode.heaptype == 'Max':
if rootNode.customList[parent] < rootNode.customList[index]:
rootNode.customList = swap(rootNode.customList, parent, index)
heapifyinsertNode(rootNode, parent)
else:
return
# 根據index刪除節點,刪除的節點先用最末端節點取代,然後再用heapifydeleteNode跟後面節點調整位子
# time: O(logn), space: O(logn)
def deletebyindex(rootNode, index):
if rootNode.heapsize == 0:
return 'The heap is empty...'
else:
rootNode.customList[index] = rootNode.customList[rootNode.heapsize]
rootNode.customList[rootNode.heapsize] = None
rootNode.heapsize -= 1
heapifydeleteNode(rootNode, index)
# 再取代欲刪除節點後,調整節點的位子
# time:O(logn), space: O(logn)
def heapifydeleteNode(rootNode, index):
leftchild = 2*index
rightchild = 2*index+1
swapchild = 0
if leftchild > rootNode.heapsize:
return
# if there's only one child for the node
elif leftchild == rootNode.heapsize:
rootNode.customList = swap(rootNode.customList, index, leftchild)
# if it has both children
else:
if rootNode.heaptype == 'Min':
if rootNode.customList[leftchild] < rootNode.customList[rightchild]:
swapchild = leftchild
else:
swapchild = rightchild
else:
if rootNode.customList[leftchild] > rootNode.customList[rightchild]:
swapchild = leftchild
else:
swapchild = rightchild
rootNode.customList = swap(rootNode.customList, index, swapchild)
heapifydeleteNode(rootNode, swapchild)
# 取得節點的index,可以用在以value為基準刪除節點的時候
# time:O(n), space: O(1)
def getindex(rootNode, value):
if rootNode.heapsize == 0:
return
else:
for i in range(1, rootNode.heapsize+1):
if rootNode.customList[i] == value:
return i
# 根據value刪除節點
# time: O(n), space:O(logn) 主要是因為多了一個找value回傳index的動作
def deleteNode(rootNode, value):
if rootNode.heapsize == 0:
return 'The heap is empty...'
else:
index = getindex(rootNode, value)
rootNode.customList[index] = rootNode.customList[rootNode.heapsize]
rootNode.customList[rootNode.heapsize] = None
rootNode.heapsize -= 1
heapifydeleteNode(rootNode, index)
# 刪除整個binary heap
# time:O(1) space:O(1)
def deleteall(rootNode):
rootNode.customList = None
rootNode.maxsize = 0
rootNode.heapsize = 0
return 'Successfully delete the heap!'
直接來試試:
BH = BinaryHeap(10, 'Min')
insertNode(BH, 5)
insertNode(BH, 90)
insertNode(BH, 50)
insertNode(BH, 60)
insertNode(BH, 2)
print('== before deletion ==')
print(BH)
print('===after deletion===')
deletebyindex(BH, 1)
print(BH)
>> == before deletion ==
2 5 50 90 60
===after deletion===
5 90 50 60
剛發完文發現~今天應該是AVL Tree,那明天再來看AVL Tree吧 ~
參考資料:
The Complete Data Structures and Algorithms Course in Python (udemy)
