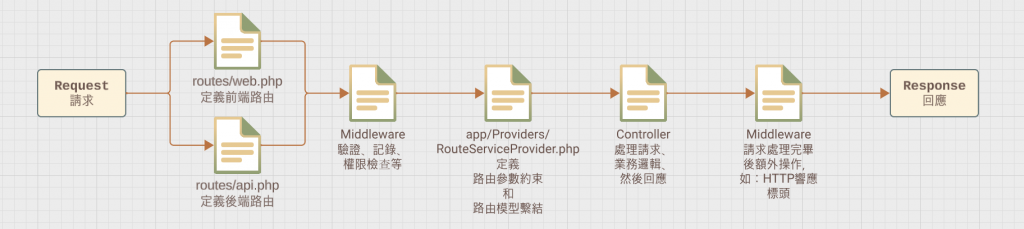
請求通常會經過路由定義、路由服務提供者、中介件、控制器、中介件和 HTTP 響應等階段,以完成請求處理過程。(當然還是要依照需求進行設計)
路由定義 (Route Definitions):
請求首先會被路由定義處理。根據您的請求 URL 和 HTTP 方法,Laravel 會查找匹配的路由定義。這可以包括 routes/web.php 或 routes/api.php 中的路由定義。
路由服務提供者 (Route Service Provider):
找到匹配的路由後,Laravel 會呼叫相關的控制器方法。在這個過程中,RouteServiceProvider 可以用來定義路由模型繫結,將 URL 參數綁定到相應的 Eloquent 模型。
中介件 (Middleware):
在執行控制器方法之前,請求通常會經過中介件。這些中介件可以在處理請求之前或之後執行一些操作,如驗證、記錄、權限檢查等。中介件可以在控制器方法中指定,也可以在路由群組中全局應用。
控制器 (Controller):
路由的控制器部分負責處理請求的邏輯。控制器方法接收請求,可能包含一些業務邏輯,然後返回一個響應。
中介件 (Middleware - 再次):
在控制器方法處理完請求後,請求還可以經過一個或多個中介件。這些中介件可以在請求處理完畢後執行額外的操作,如設定 HTTP 響應標頭等。
HTTP 響應 (Response):
最終,控制器方法將返回一個 HTTP 響應,該響應將根據您的應用程序邏輯生成,並最終返回給客戶端,以完成整個請求-響應流程。
前面有說明過前後端分離的差異,剛開啟 Laravel 專案,routes 資料夾裡面預設會有 web.php 及 api.php 兩個檔案:
web.php 主要用於處理與網站的前端頁面有關的請求,如果是將 Laravel 用於全端網站,需要處理包含 View 的部分,通常會將 routes 寫在 web.php。api.php 如果只負責撰寫後端程式,提供 JSON 或其他資料格式的 API 請求和響應,會將這部分的 routes 寫在api.php。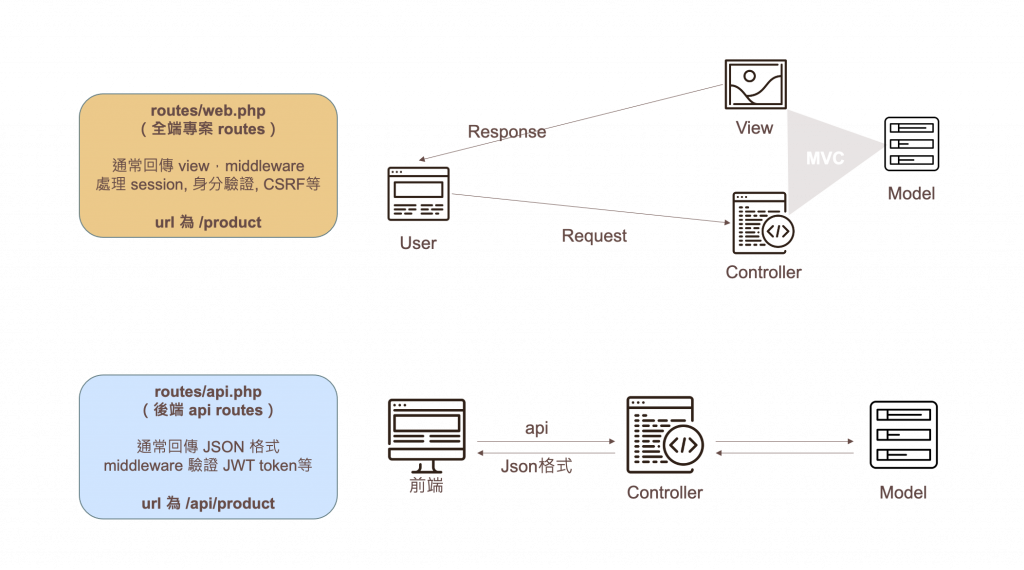
除此差異外, Laravel 內部對於這兩個檔案也有不同的處理,包括:
web.php 預設包含了一些與瀏覽器相關的中介層,例如 web 中介層組。這些中介層處理會話、身份驗證、CSRF 保護等功能,通常用於網頁應用程式。api.php 預設包含了一些與 API 相關的中介層,例如 api 中介層組。這些中介層通常用於處理 API 請求,並可能包括身份驗證、速率限制等功能。web.php 中的路由通常不需要指定前綴,因為它們預設位於根路由(例如 /home)。api.php 中的路由通常會使用 /api 作為路由前綴(例如 /api/users)。可以用 pattern() 方法在這邊定義整個專案通用的 route 規則
// App\Providers\**RouteServiceProvider** 中定義好後
/**
* Define your route model bindings, pattern filters, etc.
*/
public function boot(): void
{
Route::pattern('id', '[0-9]+');
}
// web.php 或 api.php
Route::get('/user/{id}', function ($id) {
// 只會在 {id} 為數字時執行...
});
// 定義一個 uri ,當網站接收到此 uri 時,會給予 $callback 回傳
Route::get($uri, $callback);
// 這裡回傳的 $callback 可以改成閉包
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
Route::get('/greeting', function () {
return 'Hello World';
});
// 或是傳入 controller 中指定的方法
Route::get('/greeting', [GreetingController::class, 'hello']);
// 搭配的 controller : GreetingController.php
public function hello()
{
return 'Hello World';
}

上面使用了閉包寫法,如果完全看不懂建議回去參考 closure 喔!
更詳細的 routes 寫法請參考官方文件
(再次附上這張圖讓大家參考)
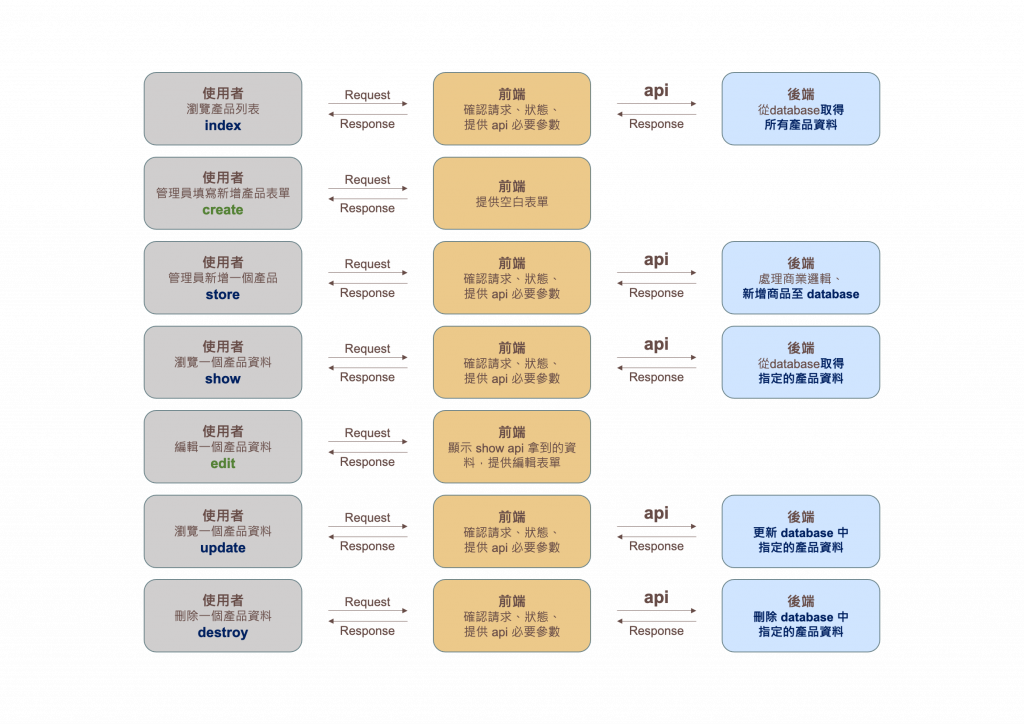
因為每個 controller 不外乎進行 index, store, create, show, update, destroy, edit 等動作,所以 Laravel 針對這些方法直接建立了 Route::resource() 方法,只要撰寫下面程式碼:
use App\Http\Controllers\ProductController;
Route::resource('product', ProductController::class);
就可以直接註冊下列 routes:
(terminal指令) php artisan route:list | grep product
GET|HEAD product .................................... product.index › ProductController@index
POST product .................................... product.store › ProductController@store
GET|HEAD product/create ........................... product.create › ProductController@create
GET|HEAD product/{product} ............................ product.show › ProductController@show
PUT|PATCH product/{product} ........................ product.update › ProductController@update
DELETE product/{product} ...................... product.destroy › ProductController@destroy
GET|HEAD product/{product}/edit ....................... product.edit › ProductController@edit
可以用 only() 方法限制要註冊的 routes
Route::resource('/product', ProductController::class)
->only('create', 'store', 'destroy');
(terminal指令) php artisan route:list | grep product
POST product .................................... product.store › ProductController@store
GET|HEAD product/create ........................... product.create › ProductController@create
DELETE product/{product} ...................... product.destroy › ProductController@destroy
而純後端的 api.php 不需要單純顯示頁面的 create、edit 方法,可改用 Route::apiresource() 進行排除:
use App\Http\Controllers\PhotoController;
Route::apiResource('photos', PhotoController::class);
Model Binding 是 Laravel routes 很大的重點,透過 Model Binding,後端小菜鳥可以輕鬆取得 Eloquent Model 的資料,Magic~~
User 模型,那該 route 參數名稱應該是 {user}。App\Models\User,型別提示(type-hint) 就是 User
// 直接用於 web.php 或 api.php
use App\Models\Product;
Route::get('/product/{product}', function (Product $product) {
return $product;
});
// 或是 route + Controller 方法定義...
Route::get('/product/{product}', [ Product::class, 'show' ]);
public function show(Product $product)
{
return $product;
}

在 Laravel 中,有兩種不同的路由模型繫結方式,分別是 Explicit Binding(明確綁定)和 Implicit Binding(隱式綁定),它們的主要差別如下:
| 隱式繫結 Implicit Binding (菜鳥用這個) | 顯式繫結 Explicit Binding |
|---|---|
| 自動綁定 Model Binding | 手動設定關聯 |
| 自動處理例外 | 手動處理例外 |
| 簡化配置 | 使用自定義邏輯 |
| 適用於常見情況 | 更多控制權和彈性 |
Route::model 方法或在 RouteServiceProvider 中的 bind 方法中進行設定。ModelNotFoundException 來處理。本文介紹了 routes 的流程與前後端差異,也比較了 隱式 和 顯式 的 Model Binding。
但若是在使用 Model Binding 時,Model 裡面根本沒有這筆資料怎麼辦?難道直接讓他回 Laravel 自訂的 404 錯誤頁面?明天就來講講如何解決這個問題~~
