
當談到APIs 的測時,有些人可能選擇連接到真實的資料庫,而有些人則認為使用 mocking 較好,原因如下:
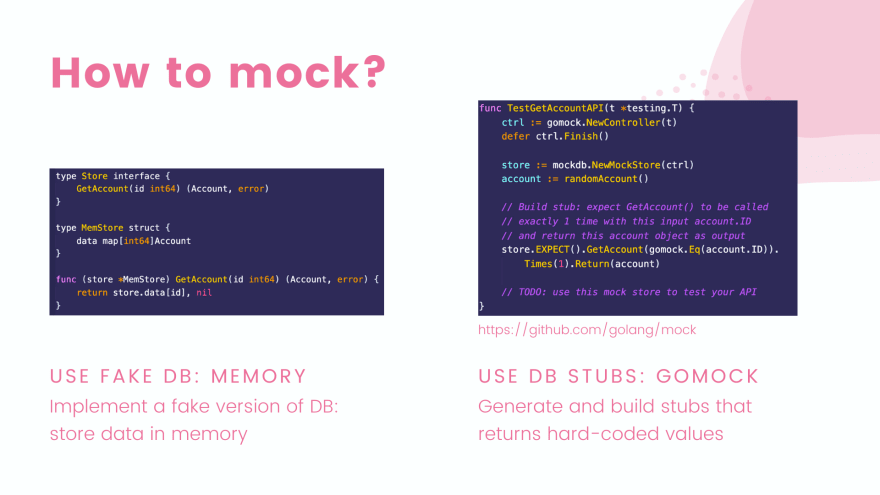
MemStore struct,它實現了 Store interface 的所有操作,但僅使用 map 來讀寫數據。gomock package 生成並建立為我們想要測試的每個場景返回hard-coded values的 stubs。gomockgo install github.com/golang/mock/mockgen@v1.6.0
mockgen 的二進制文件將存在於 go/bin 資料夾中。❯ ls -l
total 311448
-rwxr-xr-x@ 1 avery_yang staff 8723440 Aug 31 09:48 air
-rwxr-xr-x 1 avery_yang staff 16250656 Sep 3 14:03 dlv
-rwxr-xr-x@ 1 avery_yang staff 5797096 Aug 5 16:29 goimports
-rwxr-xr-x 1 avery_yang staff 3583488 Sep 3 14:03 gomodifytags
--rwxr-xr-x@ 1 avery_yang staff 9356912 Sep 3 14:03 mockgen
mockgen,通過 which mockgen 來檢查。which mockgen
mockgen not found
若出現 "mockgen not found",這是因為當前的 go/bin 資料夾不在 PATH 環境變數中。
為將它加入 PATH,根據你的 shell 編輯相應的檔案加入此 export 命令:
◦ zsh 使用者編輯 .zshrc 文件
◦ bash 使用者則編輯 .bash_profile 或 .bashrc 文件。
export PATH=$PATH:~/go/bin
儲存並退出編輯器後,執行 source ~/.zshrc 命令以重新載入 .zshrc 文件。
再次執行 which mockgen,我們可以看到它現在已在 go/bin 資料夾中。
which mockgen
/Users/avery_yang/Workplace/go/bin/mockgen
需要注意的是,每次開啟新的終端視窗時,.zshrc 文件會自動載入,因此我們不需要每次都執行 source 命令。
為了使用 mockgen 來生成 mock DB,我們需要更新我們的程式碼:
**type Store interface** : 定義了所有操作Database的MethodSQLStore : 是一個 struct,它具體實現了如何使用 SQL 數據庫來執行那些功能。目前,在 api/server.go 文件中,NewServer() 函數接受一個 db.Store 物件:
type Server struct {
store *db.Store
router *gin.Engine
}
func NewServer(store *db.Store) *Server {
...
}
這個 db.Store 在 db/sqlc/store.go 文件中定義。它是一個結構,總是連接到真實的資料庫:
type Store struct {
db *sql.DB
*Queries
}
為了在 API 伺服器測試中使用 mock DB,我們必須用一個介面來替換那個存儲物件。因此,我將複製這個 Store 結構定義,並將其類型改為Interface:
type Store interface {
// TODO: add functions to this interface
}
type SQLStore struct {
db *sql.DB
*Queries
}
原始的 Store 結構將被重命名為 SQLStore。它將是 Store interface的真實實現,連接到 SQL 資料庫,這裡是 PostgreSQL。
更新 NewStore() 函數
Store 介面而不是指針。內部返回的是真正的數據庫實現,即 SQLStore。db/sqlc/store.go
func NewStore(db *sql.DB) Store {
return &SQLStore{
db: db,
Queries: New(db),
}
}
func (store *SQLStore) execTx(ctx context.Context, fn func(*Queries) error) error {
...
}
func (store *SQLStore) TransferTx(ctx context.Context, arg TransferTxParams) (TransferTxResult, error) {
}
定義 Store 介面的功能
type Store interface {
Querier
TransferTx(ctx context.Context, arg TransferTxParams) (TransferTxResult, error)
}
介面應包括所有 Queries 結構的功能,以及執行轉帳事務的額外功能。
sqlc 套件也允許我們生成一個包含所有Querier 的interface,所以我們只需要在 sqlc.yaml 文件中設置 emit_interface 為 true。
**sqlc.yaml**
version: '2'
sql:
- schema: './db/migration'
queries: './db/query'
engine: 'postgresql'
gen:
go:
package: 'db'
out: './db/sqlc'
emit_json_tags: true
emit_empty_slices: true
emit_interface: true
設定完成再透過make sqlc 來Generate出Querier interface:
make sqlc
db/sqlc/querier.go
// Code generated by sqlc. DO NOT EDIT.
// versions:
// sqlc v1.20.0
package db
import (
"context"
)
type Querier interface {
AddAccountBalance(ctx context.Context, arg AddAccountBalanceParams) (Account, error)
CreateAccount(ctx context.Context, arg CreateAccountParams) (Account, error)
CreateEntry(ctx context.Context, arg CreateEntryParams) (Entry, error)
CreateTransfer(ctx context.Context, arg CreateTransferParams) (Transfer, error)
DeleteAccount(ctx context.Context, id int64) error
GetAccount(ctx context.Context, id int64) (Account, error)
GetAccountForUpdate(ctx context.Context, id int64) (Account, error)
GetEntry(ctx context.Context, id int64) (Entry, error)
GetTransfer(ctx context.Context, id int64) (Transfer, error)
ListAccounts(ctx context.Context, arg ListAccountsParams) ([]Account, error)
ListEntries(ctx context.Context, arg ListEntriesParams) ([]Entry, error)
ListTransfers(ctx context.Context, arg ListTransfersParams) ([]Transfer, error)
UpdateAccount(ctx context.Context, arg UpdateAccountParams) (Account, error)
}
var _ Querier = (*Queries)(nil)
更新 api/server.go 中的類型
Store 現在是一個介面而不是結構指針,所以我們需要更新 NewServer() 函數中的類型。api/server.go
type Server struct {
store db.Store
router *gin.Engine
}
func NewServer(store db.Store) *Server {
...
}
確保主代碼不變
儘管我們將Store從Strut更改為Interface,但我們的main.go仍然能夠正常運行,因為 db.NewStore() 現在也返回一個 Store 介面,其實際實現是連接到真實的 SQL DB 的 SQLStore。
func main() {
config, err := util.LoadConfig(".")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("cannot load config:", err)
}
conn, err := sql.Open(config.DBDriver, config.DBSource)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("cannot connect to db:", err)
}
store := db.NewStore(conn)
server := api.NewServer(store)
err = server.Start(config.ServerAddress)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("cannot start server:", err)
}
}
struct 和interface之間是什麼關係呢?
struct 是一種聚合多種不同類型數據的方式。想像它就像一個模板,用於描述一個物件的特點。
例如,我們可以有一個 Person 結構體,用來描述一個人的基本資訊:
type Person struct {
Name string
Age int
Height float64
}
這裡,Person 結構體有三個字段:名字 (Name)、年齡 (Age) 和身高 (Height)。
interface 是一種定義行為的方式。它指定了某個物件應該具備哪些功能,但不會說明這些功能是如何實現的。
例如,我們可以定義一個 Speaker 接口,代表任何能夠說話的物件:
type Speaker interface {
Speak() string
}
這裡,任何實現了 Speak 方法的結構體都可以認為是一個 Speaker。
現在,假設我們想要讓 Person 成為一個 Speaker。我們可以為 Person 實現 Speak 方法:
func (p Person) Speak() string {
return "Hello, my name is " + p.Name
}
這樣,Person 就實現了 Speaker 接口,因為它有了 Speak 方法。
現在,我們可以創建一個 Person 物件,並讓它說話:
p := Person{Name: "John", Age: 30, Height: 175.5}
fmt.Println(p.Speak()) // 輸出: Hello, my name is John
同時,如果我們有其他物件,如 Robot 或 Bird,只要它們也實現了 Speak 方法,它們也可以被認為是 Speaker。
總結:struct 用於定義和描述物件的特點,而 interface 用於定義物件的行為或功能。透過 interface,我們可以確保不同的物件具有相同的行為或功能,而不管它們的內部結構是如何的。
SQLStore struct 和 Store Interface的關係和作用?
type Store interface {
// TODO: add functions to this interface
}
type SQLStore struct {
db *sql.DB
*Queries
}
這裡的 Store 是一個 interface,它定義了一組方法,這組方法描述了一個存儲機制應具備的功能。例如,可能有 CreateAccount, GetAccountByID 等方法。
SQLStore 是一個 struct,它具體實現了如何使用 SQL 數據庫來執行那些功能。在這個結構體中,您可以看到它包含了一個數據庫連接 (db *sql.DB) 和一組查詢方法 (*Queries)。這意味著 SQLStore 將具體地使用 SQL 語句和數據庫操作來執行那些功能。
Store 接口允許我們有多種不同的存儲實現。除了 SQLStore(針對 SQL 數據庫)之外,我們還可以有其他實現,例如 MemoryStore(使用內存存儲數據)或 NoSQLStore(針對 NoSQL 數據庫)。Store 接口,我們可以輕鬆地創建模擬的存儲實現,以便進行測試,而不需要實際連接到數據庫。假設 Store 接口定義了一個 GetAccountByID 方法,該方法返回一個帳戶:
type Store interface {
GetAccountByID(id int64) (*Account, error)
}
現在,我們的 SQLStore 可以具體實現這個方法,使用 SQL 語句去查詢數據庫:
func (s *SQLStore) GetAccountByID(id int64) (*Account, error) {
// 使用 SQL 語句從數據庫查詢帳戶
}
同時,我們還可以有一個模擬的存儲實現,用於測試:
type MockStore struct {}
func (m *MockStore) GetAccountByID(id int64) (*Account, error) {
// 直接返回一個模擬的帳戶,不真的去查詢數據庫
}
這樣,不論是真正的 SQLStore 還是模擬的 MockStore,只要它們都實現了 Store 接口中的方法,它們都可以被當作 Store 使用。這提供了極大的靈活性和可擴展性。
