
延續在本系列開始的 Dart 3 解說與實用範例,目的是希望系列結束前能再讓大家複習和更熟悉 Dart 3 新版帶來的方便性,有效運用在目前的專案上,甚至能優化以前的程式碼,相信它們能夠給予一定的協助。
Dart 3 相關文章:
本文從第二篇的 Dart 3 文章接棒,繼續分享更多的實際案例與技巧,我們不只是要知道如何使用外,也要慢慢內化它,不靠死背記下來。而後面我也準備了小測驗,驗證大家對於 Dart 的熟悉程度,順便學習一些觀念。建議在閱讀文章的同時打開 IDE,同步跟著撰寫程式碼,這種方式學習速度會大大提升哦。
isMale 命名參數,記得大括號包裹。(int, String, {bool isMale}) student = (18, isMale: true, 'Yii');
print(student);
// (18, Yii, isMale: true)
final (isMale: isMale, age, name) = student;
print('$isMale, $age, $name');
// true, 18, Yii
這裡創建了一個方法 waitTwoTask(),返回一個 Record 結果,可以很簡單地處理多回傳值。以這個範例,當我有兩個非同步操作要同時處理時,就能使用 waitTwoTask() 協助我們,外部再順取兩個結果變數。
final Future<int> futureAge = getAge();
final Future<String> futureName = getName();
final (int age, String name) = await waitTwoTask(futureAge, futureName);
print('$age, $name');
// 18, Yii
---
Future<int> getAge() async {
return 18;
}
Future<String> getName() async {
return 'Yii';
}
Future<(T1, T2)> waitTwoTask<T1, T2>(Future<T1> func1, Future<T2> func2) async {
final data = await Future.wait([func1, func2]);
return (data[0] as T1, data[1] as T2);
}
在 Dart 3 更新後,針對 Iterable 的 Extension 有在優化,新增了幾個常用 API,其中一個為 indexed getter,直接回傳一個 Record Iterable,內容為 index 和原有元素,多了索引讓我們在使用上更為方便。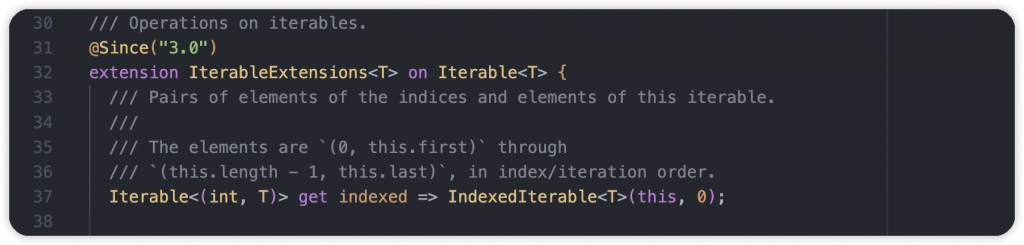
indexed 搭配 for loop,將每個 Record 拿出來處理/// 1.
final students = ['Amy', 'Berry', 'Alan', 'Hank'];
for (final (index, element) in students.indexed) {
print('$index, $element');
}
// 0, Amy
// 1, Berry
// 2, Alan
// 3, Hank
/// 2.
const names = ['Jack', 'Tina', 'Doodle'];
final result = [
for (final (index, word) in names.indexed) '$index is $word',
];
result.forEach(print);
// 0 is Jack
// 1 is Tina
// 2 is Doodle
此範例使用到 Switch Expression,可以運用在日常的 Flutter 場景。目的是取得設備類型,所以首先有個 DeviceType enum,接著撰寫新的 BuildContext 擴充 API,根據目前的寬度根據每個設備條件來確認,完成一個 deviceType getter。接著在 UI code 就能透過 deviceType 處理每個場景。
enum DeviceType {
mobile,
tablet,
desktop,
tv4k,
giant,
}
extension BuildContextExtension on BuildContext {
double get width => MediaQuery.sizeOf(this).width;
DeviceType get deviceType => switch (width) {
< 450 => DeviceType.mobile,
< 800 => DeviceType.tablet,
< 2160 => DeviceType.desktop,
< 3840 => DeviceType.tv4k,
_ => DeviceType.giant,
};
}

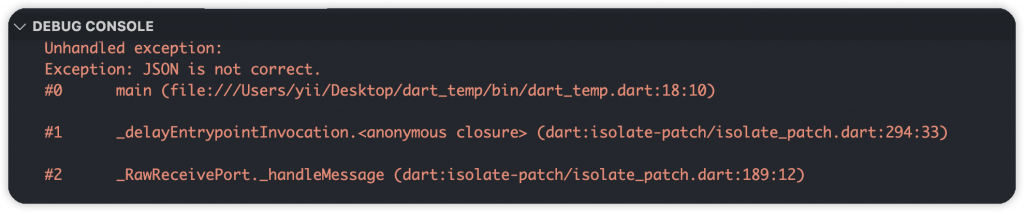
使用 Switch Expression、Pattern Matching 和 Destructuring。此範例需要解析 Json 並取得指定的 title 字串, 其中檢查格式是否有 name 這個 Key,而且 Value 不是空值,這時候就安全地拿 title 來使用,否則就拋出例外。
final jsonMap = {
'student': {
'name': 'Jay',
}
};
final title = switch (jsonMap) {
{'student': {'name': final String title}} => title,
_ => throw Exception('JSON is not correct.'),
};
print(title);
// Jay
在寫 UI 時,大家對於 FutureBuilder 應該非常熟悉,等待 future function 處理完後反應 UI,這時候針對 AsyncSnapshot 的各種狀態就能使用 Switch Expression 來協助,透過 when 進行第二層檢查,精簡、快速的處理成功、載入、錯誤三種情況,可讀性也因此提高了你說是吧。
FutureBuilder<String>(
future: Future.delayed(
const Duration(seconds: 10),
() {
return 'Dart 3 is awesome.';
},
),
builder: (context, snapshot) => switch (snapshot) {
final snapshot when snapshot.hasData => Text(snapshot.data ?? ''),
final AsyncSnapshot<String> snapshot when !snapshot.hasError => const CircularProgressIndicator(),
_ => const Text('Oops!')
},
),
此範例使用 sealed Class、If-Case Matching、Destructuring,目的要快速的確認 sub class 並存取屬性。首先有一個 Car 跟 Tesla 兩個父子類別,經由 getCar() 取得子類別實體,這時候外部拿到的是 Car,需要檢查是否為我們要的 Tesla。
final car = getCar();
if (car case Tesla(name: 'Red')) {
print('I am Red.');
} else if (car case Tesla(:final name)) {
print('I am $name.');
// I am Blue.
} else if (car case Tesla(name: final name)) {
print('I am $name.');
// I am Blue.
}
---
sealed class Car {
final String name;
Car(this.name);
}
class Tesla extends Car {
Tesla(super.name);
}
Car getCar() {
return Tesla('Blue');
}
從此圖範例可以表達 Switch Expression 的方便性,功用就跟 freezed 的 union-class 相同,針對多種情境和資料的使用方式都吃不啊多,透過 Dart 3 解構用法可以幫我們提高效率。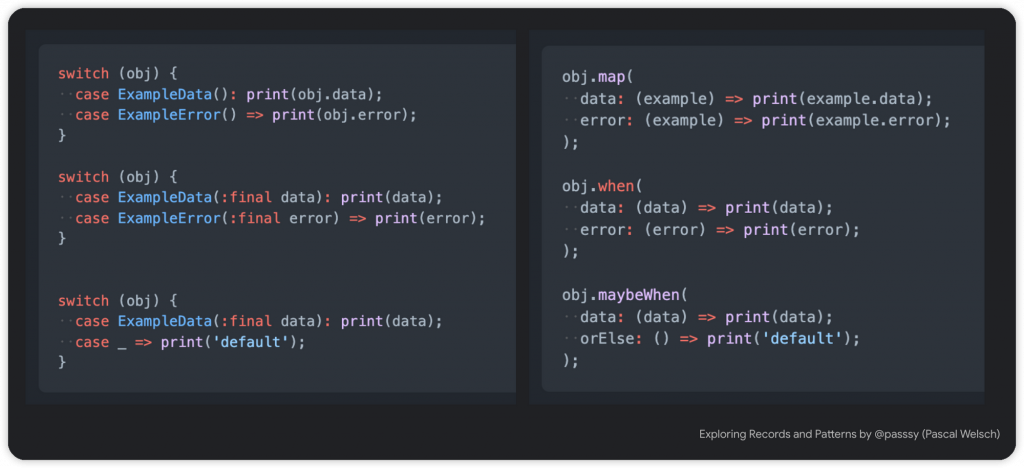
by Pascal Welsch
再次複習 indexed 新用法,有個 Map 需要有索引進行一些操作,搭配 for loop,在當中將每個 Item 轉成 Record 形式,並進行 MapEntry 解構,拿出 Key 名稱跟 Value 價格。在解構當中,方式不只一種,可以透**前綴:**取值,也可以透過命名參數取值,根據自己的使用習慣和規範。
final cars = {
'Tesla': 100,
'Benz': 200,
'BMW': 300,
};
for (final (index, MapEntry(:key, value: value)) in cars.entries.indexed) {
print('$index - ($key, $value)');
}
// 0 - (Tesla, 100)
// 1 - (Benz, 200)
// 2 - (BMW, 300)
本題主要是考驗 Pattern Matching 中的 If-Case Matching,哪幾個 Pattern 會符合而且印出結果?
結果:
int? age;
void main(List<String> arguments) {
// 1.
if (age case final int age) {
printAge(age);
}
// 2.
if (age case final int? age) {
printAge(age);
}
// 3.
if (age case final age) {
printAge(age);
}
// 4.
if (age case final age?) {
printAge(age);
}
}
void printAge(int age) {
print('Age is $age.');
}
對於以下的 Records 操作,它們個別印出什麼結果呢?
這個測驗過程很有趣,以 Record 來說,當我們有加上逗號,代表可能有多值要記錄,實際上就會是 Record,儘管只有一個參數。
final one = 42;
print(one.runtimeType); // int
final one = (42);
print(one.runtimeType); // int
final two = (42,);
print(two.runtimeType); // (int)
final (int) two = (42,);
print(two.runtimeType); // (int)
final (int,) two = (42,);
print(two.runtimeType); // (int)
by Pascal Welsch
對於以下的 Destructuring 操作,它們個別印出什麼結果呢?
首先提供一個 Record,它附有一個參數並多加了一個逗號誘導,當解構後的 Record 存取時,裡面的變數就是獨立的,在有逗號的情況下,元素就能期待它是原有型別。沒有逗號的情況下,取出的元素為 Record。
final (int,) item = (42,);
final (one,) = item;
print(one.runtimeType); // int
final (two) = item;
print(two.runtimeType); // (int), Record!
final two = item;
print(two.runtimeType); // (int), Record!
by Pascal Welsch
相信跟著操作過這些實際例子的你們,應該已經懂得如何正確使用新的語法特性,其實不會很難對吧。也建議有時間的話去閱讀官方文件以及 Dart Repository,裡面有更詳細的設計說明。而現在社群很多人也已經有提供相關的 Dart 3 文章和影片解說,可以的話也鼓勵把開發經驗跟大家分享,多看多練習,你才會發現 Dart 語言其實越來越豐富、越來越強大了。
