定位元素 + 模擬操作,已經能夠真實呈現使用者的操作流程,不過,測試最重要的核心價值在於驗證結果是否與預期相符,因此,就必須談到測試當中非常重要的一環:Assertion (斷言)。
斷言是一個邏輯判斷式,會回傳驗證結果是否如預期結果的布林值,如果為 true(符合預期),程式繼續往下執行,如果為 false(不符預期),則中止執行,並回傳錯誤。
撰寫斷言的方式為,呼叫expect()函式,傳入比對目標,比對目標可以是 locator、page 或變數,再選擇反映期望的比對器(matcher):
await expect(target).matcher(options)
Playwright 官方提供的斷言 API - expect(),它是一個函數,接收 locator 作為參數,它的機制為:
首先,我們透過印出結果來觀察 Playwright 斷言是否回傳布林值:
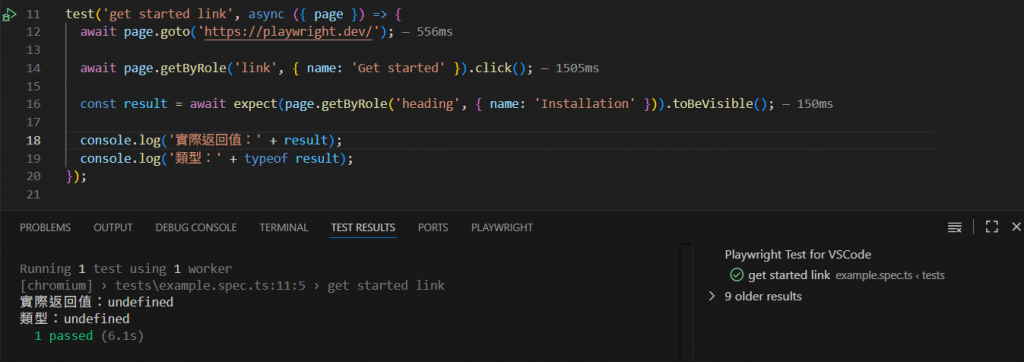
以上可以看到返回值與型別都是 undefiend,表示 Playwright 的斷言不回傳布林值,這是 Playwright 斷言與其他傳統斷言不同之處。
再來,如果找不到預期元素時,Playwright 會自動重試直到超時,如下方測試的結果:
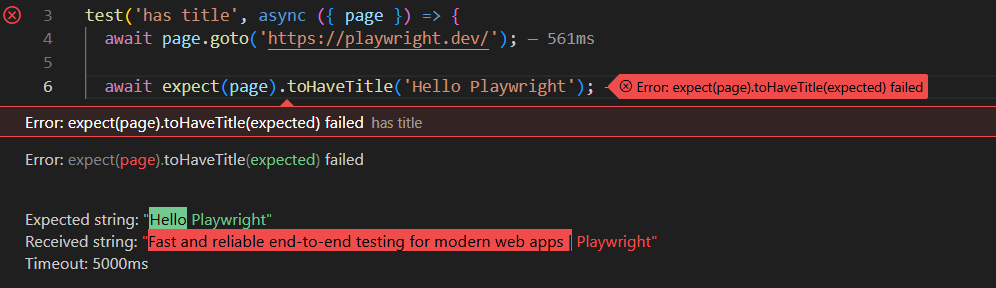
我們可以看到斷言驗證失敗時,Playwright 會報告錯誤:
Error: expect(page).toHaveTitle(expected) failed
Expected string: "Hello Playwright"
Received string: "Fast and reliable end-to-end testing for modern web apps | Playwright"
Timeout: 5000ms
預期應為"Hello Playwright"字串,但接收到的是 "Fast and reliable end-to-end testing for modern web apps | Playwright" 字串,並且 Timeout 為 5 秒(預設值),表示 Playwright 在這 5 秒之間不斷尋找預期的正規式,但直到 5 秒結束,都沒有找到目標。
Playwright 具有完整且豐富的斷言比對器供我們使用,比對器分為兩大類型:自動重試與非自動重試,自動重試比對器的 timeout 預設為 5 秒,如果有需要延長或縮短,可自行加入參數調整時間,這邊建議優先選擇重試斷言比對器,由於非自動重試比對器為立即斷言,如果在這一刻,遇到網路延遲、動畫還沒跑完或是後端回應較慢,測試可能會立即失敗,而如果下一次測試,網路較順暢或者後端回應較快,測試又通過了,如此可能會導致測試的不穩定。
接下來我們來初步認識一下基本的比對器:
所有自動重試比對器
元素狀態:檢查元素是否可見、可互動,或狀態是否正確
toBeVisible() / toBeHidden() → 可見 / 隱藏
await expect(locator).toBeVisible();
await expect(locator).not.toBeVisible();
await expect(locator).toBeHidden();
toBeEnabled() / toBeDisabled() → 可用 / 不可用
await expect(locator).toBeEnabled();
await expect(locator).toBeDisabled();
toBeChecked() → 是否勾選
await expect(locator).toBeChecked();
await expect(locator).not.toBeChecked();
toBeEditable() → 是否可編輯
await expect(locator).toBeEditable()
await expect(locator).not.toBeEditable()
toBeFocused() → 是否為焦點
await expect(locator).toBeFocused();
await expect(locator).not.toBeFocused();
toBeAttached() → 是否存在於 DOM
await expect(locator).toBeAttached();
await expect(locator).not.toBeAttached();
toBeEmpty() → 內容是否為空
await expect(locator).toBeEmpty();
await expect(locator).not.toBeEmpty();
💡Tips:
Playwright 支援反向斷言,也就是.not
預期可見toBeVisible()→ 加上.not→ 預期不可見.not.toBeVisible()
元素內容:檢查元素的文字、輸入值
toHaveText() → 完整比對文字
await expect(locator).toHaveText(text: string);
toContainText() → 包含文字
await expect(locator).toContainText(text: string);
toHaveValue() → 單一輸入框值
await expect(locator).toHaveValue(value: string);
toHaveValues() → 多個輸入值(例如 )
await expect(locator).toHaveValue([value: string, value: string]);
元素屬性 / 樣式:用於檢查 HTML 屬性、CSS 樣式或 JS 屬性
toHaveAttribute() → 具有指定的 HTML 屬性
await expect(locator).toHaveAttribute(name: string, value: string);
toHaveClass() → 檢查元素是否具有相應的 class 類別
await expect(locator).toHaveClass(className: string);
toHaveCSS() → 檢查元素是否具有指定的 CSS 樣式
await expect(locator).toHaveCSS(property: string, value: string);
toHaveId() → 檢查元素的 id name
await expect(locator).toHaveId(idName: string);
toHaveJSProperty() → 檢查元素是否具有指定的 JS 屬性
await expect(locator).toHaveJSProperty(name: string, value: string);
可存取性 / ARIA:用於檢查無障礙(Accessibility)
toHaveRole() → 檢查元素是否具有 ARIA Role
await expect(locator).toHaveRole(aria-role: string);
toHaveAccessibleName() → 檢查元素是否具有無障礙 name
await expect(locator).toHaveAccessibleName(name: string);
toHaveAccessibleDescription() → 檢查元素是否具有無障礙描述
await expect(locator).toHaveAccessibleDescription(description: string);
toMatchAriaSnapshot() → 檢查元素是否符合無障礙快照
await expect(locator).toMatchAriaSnapshot(string);
頁面層級:用於檢查 page 相關內容,而非檢查單一元素
toHaveURL() → 檢查頁面 Url
await expect(page).toHaveURL(url: string);
toHaveTitle() → 檢查頁面 title
await expect(page).toHaveTitle(title: string);
數量:檢查數量是否符合預期
toHaveCount() → 檢查元素數量
await expect(locator).toHaveCount(number: number);
可視範圍:檢查元素是否出現在可見範圍內
toBeInViewport() → 檢查元素是否在 Viewport 內
await expect(locator).toBeInViewport();
視覺回歸測試:檢查畫面或元素截圖
toHaveScreenshot() → 檢查截圖畫面
await expect(page).toHaveScreenshot();
await expect(locator).toHaveScreenshot();
常用非自動重試比對器
toBe() → 值是否相等(必須嚴格相等 ===)
await expect(target value).toBe(expected value);
toContain() → 字串是否包含指定的字串
await expect(target string).toContain(specified string);
toBeGreaterThan() → 驗證值是否大於指定數字
await expect(target number).toBeGreaterThan(specified number);
toBeLessThan() → 驗證值是否小於指定數字
await expect(target number).toBeLessThan(specified number);
toBeTruthy() → 判斷布林值是否為 true
await expect(target).toBeTruthy();
toBeFalsy() → 判斷布林值是否為 false
await expect(target).toBeFalsy();
到這裡,我們認識了 Playwright 的斷言設計與常用方法,並了解在測試中的基本應用,接下來,將更進一步探討這些斷言的進階技巧以及撰寫重點,並藉由實際範例來體驗斷言在戰場(測試情境)上如何發揮作用。
