嗨大家,我是 Debuguy。
昨天我們聊完了如何讓 LLM 知道「自己是誰」,System Prompt 的重要性。今天想來聊聊一個很實務的問題:當 Prompt 越來越複雜時,該怎麼管理?
讓我們回顧一下昨天的程式碼:
const chatFlow = ai.defineFlow(
{
name: 'chatFlow',
inputSchema: z.object({
text: z.string(),
user: z.string(),
ts: z.string(),
}),
},
async ({ user, ts, text }) => (await ai.generate({
model: googleAI.model('gemini-2.5-flash-lite'),
system: `
You are a helpful AI assistant operating as a Slack bot.
Your Slack ID is U09BASU9P6K.
The user who mentioned you is the one you must address in your reply.
// ... 一大串 system prompt
`,
prompt: `${user}@${ts}: ${text}`,
})).text
);
乍看之下還好,但仔細想想:
「咦?這個 System Prompt 如果要改怎麼辦?」
「如果我想測試不同的 prompt 版本呢?」 _
「模型參數寫死在程式碼裡,要調整不就要重新部署?」_
更麻煩的是,隨著功能增加,這個 system prompt 會變得越來越複雜:
// 想像一下如果變成這樣...
system: `
You are a helpful AI assistant operating as a Slack bot.
Your Slack ID is ${process.env.SLACK_BOT_USER_ID}.
Your name is ${botConfig.name}.
You are currently in ${channel.name} channel.
The current time is ${new Date().toISOString()}.
Available tools: ${availableTools.join(', ')}.
Company name: ${companyConfig.name}.
Working hours: ${companyConfig.workingHours}.
Today's weather: ${weatherData.summary}.
// ... 還有更多變數
`,
「天啊,如果有這麼多變數需要放進去,程式碼會充滿 ${var} 的字串插值!」
「更慘的是,如果我要 A/B 測試不同的 prompt,難道要寫兩套程式碼?」
突然意識到,我把 Prompt 直接寫在程式碼裡,這不就是Hard Code 的一種嗎?
程式碼的邏輯相對穩定,但 Prompt 需要不斷調整:
我光是昨天的 System Prompt 就已經改了至少 5 版:
v1: "You are a helpful AI assistant."
v2: "You are a helpful AI assistant operating as a Slack bot."
v3: "You are a helpful AI assistant operating as a Slack bot. Your Slack ID is U09BASU9P6K."
v4: "...加上互動規則..."
v5: "...加上 Response Style..."
「天啊,新版本的 prompt 讓 Bot 變得很奇怪,快退回上一版!」
如果 Prompt 寫死在程式碼裡,回滾就意味著:
這個流程至少要 20-30 分鐘,但如果 Prompt 是獨立管理的,rollback 可能只需要幾分鐘。
當團隊裡有多個人在優化 Prompt 時:
如果 Prompt 寫在程式碼裡,每個人都需要懂程式碼才能參與優化,這會大大降低協作效率。
一開始,我以為「Prompt 版本控制」就是把 System Prompt 的文字另外存起來。
但實際開發後發現,需要版本控制的不只是文字內容,還包括:
1. 模型選擇
model: googleai/gemini-2.5-flash-lite # 還是 gemini-2.5-pro?
2. 模型參數
config:
temperature: 0.2
topP: 0.95
topK: 30
3. 其他配置
config:
thinkingConfig:
includeThoughts: true # 要不要顯示思考過程?
thinkingBudget: -1 # 思考的預算限制
這些參數的任何一個改變,都會影響 LLM 的行為表現。如果沒有一起做版本控制,你永遠不知道某次的改進是因為 Prompt 調整,還是參數的調整。
GenKit 的 dotPrompt 是一個很棒的設計,它把所有相關的配置都放在一個檔案裡:
---
model: googleai/gemini-2.5-flash-lite
config:
temperature: 0.2
topP: 0.95
topK: 30
thinkingConfig:
includeThoughts: true
thinkingBudget: -1
input:
schema:
botUserId: string
prompt: string
---
{{role "system"}}
You are a helpful AI assistant operating as a Slack bot.
Your Slack ID is {{botUserId}}.
// ... rest of system prompt
{{role "user"}}
{{prompt}}
這個設計的優雅之處:
原本的複雜程式碼:
const chatFlow = ai.defineFlow(
{
name: 'chatFlow',
inputSchema: z.object({
text: z.string(),
user: z.string(),
ts: z.string(),
}),
},
async ({ user, ts, text }) => (await ai.generate({
model: googleAI.model('gemini-2.5-flash-lite'),
system: `
You are a helpful AI assistant operating as a Slack bot.
Your Slack ID is U09BASU9P6K.
The user who mentioned you is the one you must address in your reply.
// ... 一大串 system prompt
`,
prompt: `${user}@${ts}: ${text}`,
})).text
);
變成了優雅的新版本:
const chatFlow = ai.defineFlow(
{
name: 'chatFlow',
inputSchema: z.object({
text: z.string(),
user: z.string(),
ts: z.string(),
}),
},
async ({ user, ts, text }) => (await ai.prompt('chatbot')({
botUserId: process.env['SLACK_BOT_USER_ID']!,
prompt: `${user}@${ts}: ${text}`,
})).text
);
差異立見:
可以利用 {{role "system"}} {{role "user"}} 來定義區塊
dotPrompt 採用了 Handlebars 樣板語言,所以想要寫 condition, loop 都不是問題
{{#if isLoggedIn}}
歡迎回來,{{username}}!
{{else}}
請先登入
{{/if}}
{{#unless isGuest}}
你有 {{messageCount}} 則未讀訊息
{{/unless}}
購物清單:
{{#each items}}
{{@index}}. {{name}} - ${{price}}
{{/each}}
團隊成員:
{{#each team}}
- {{name}} ({{role}})
{{#if isActive}}✅ 在線中{{else}}⏸️ 離線{{/if}}
{{/each}}
{{#with user}}
姓名:{{firstName}} {{lastName}}
Email:{{email}}
{{/with}}
這些基本的 Handlebars 語法在 dotPrompt 中都可以使用,讓你的 prompt 變得更加動態和靈活!
GenKit 提供了一個超好用的 Development UI,讓 prompt tuning 變得像玩遊戲一樣簡單!
原本啟動的 command 是這樣的話
bun run --watch src/index.ts
只需要改成
genkit start -- bun run --watch src/index.ts
開啟瀏覽器的 http://localhost:4000,你會看到一個漂亮的介面。
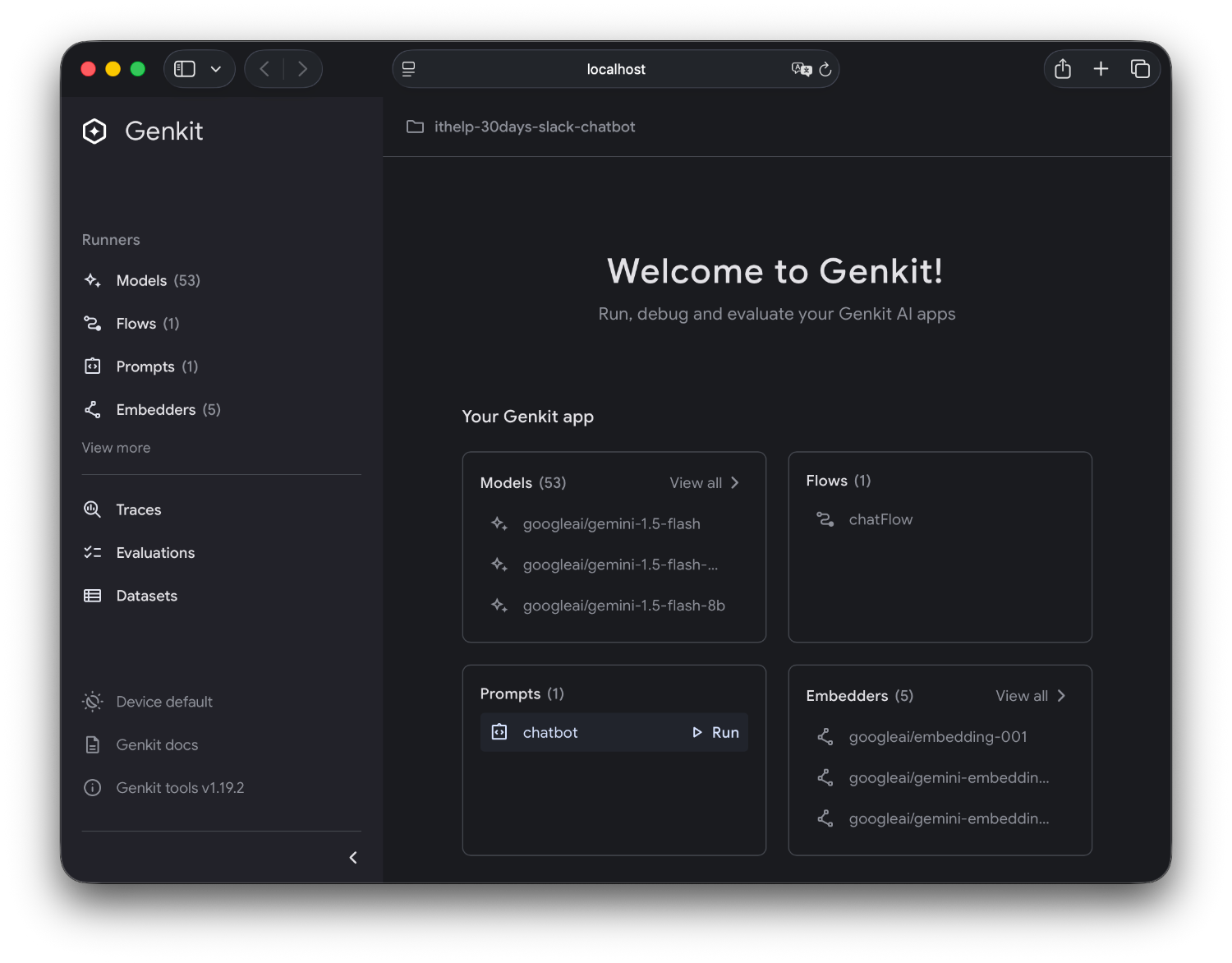
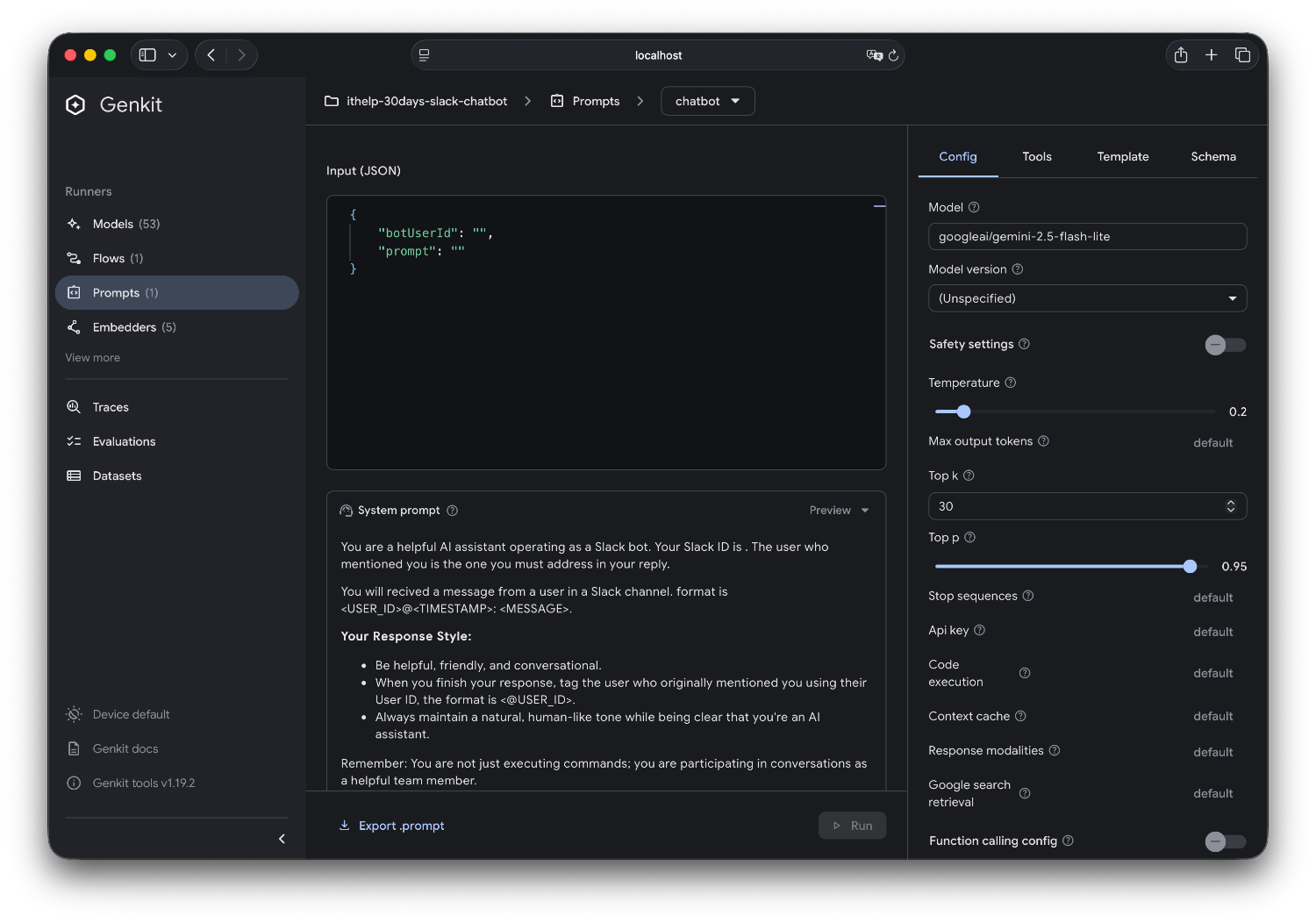
1. 測試不同的 Prompt 版本
2. 調整模型參數
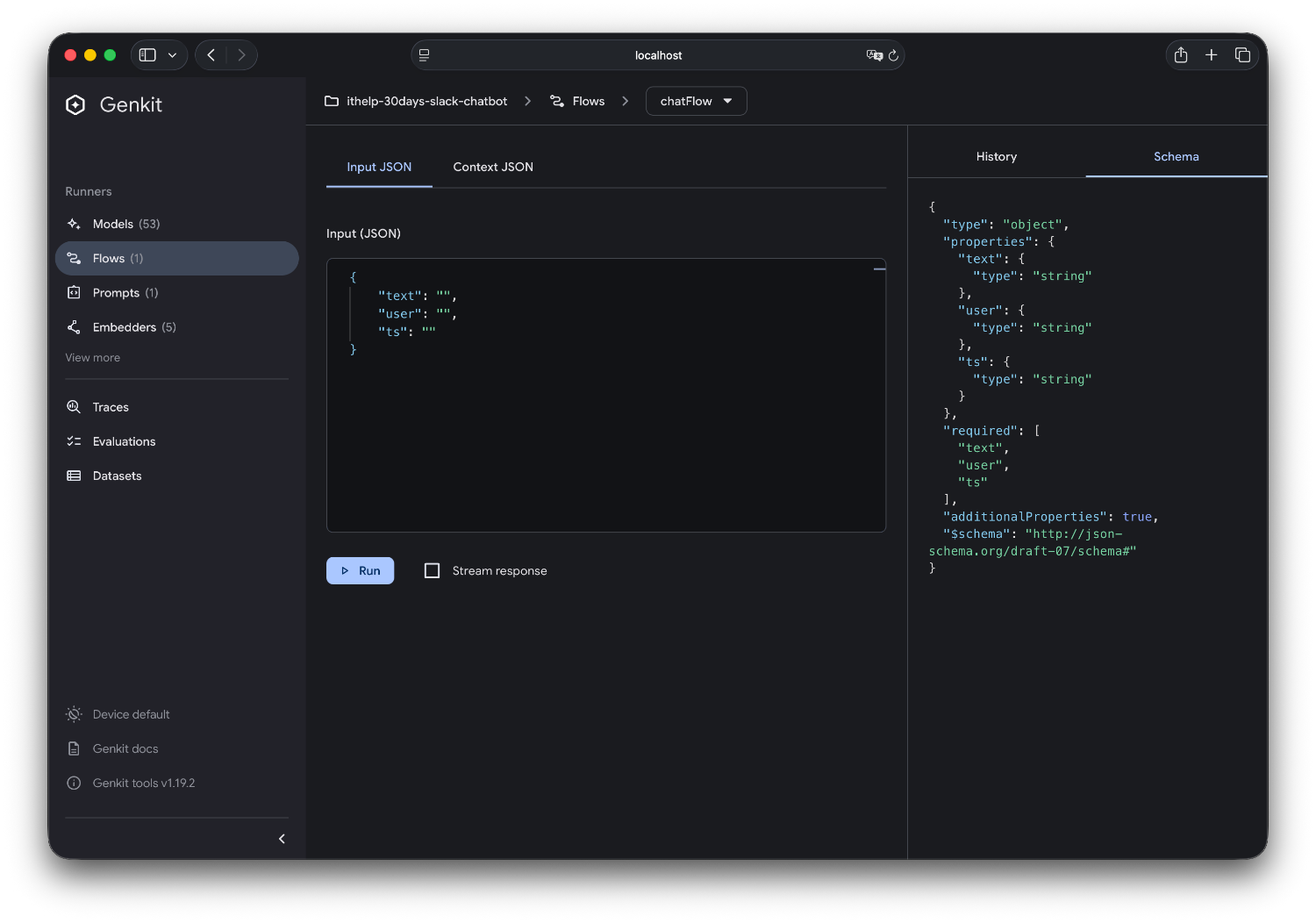
1. 視覺化 Flow 執行流程
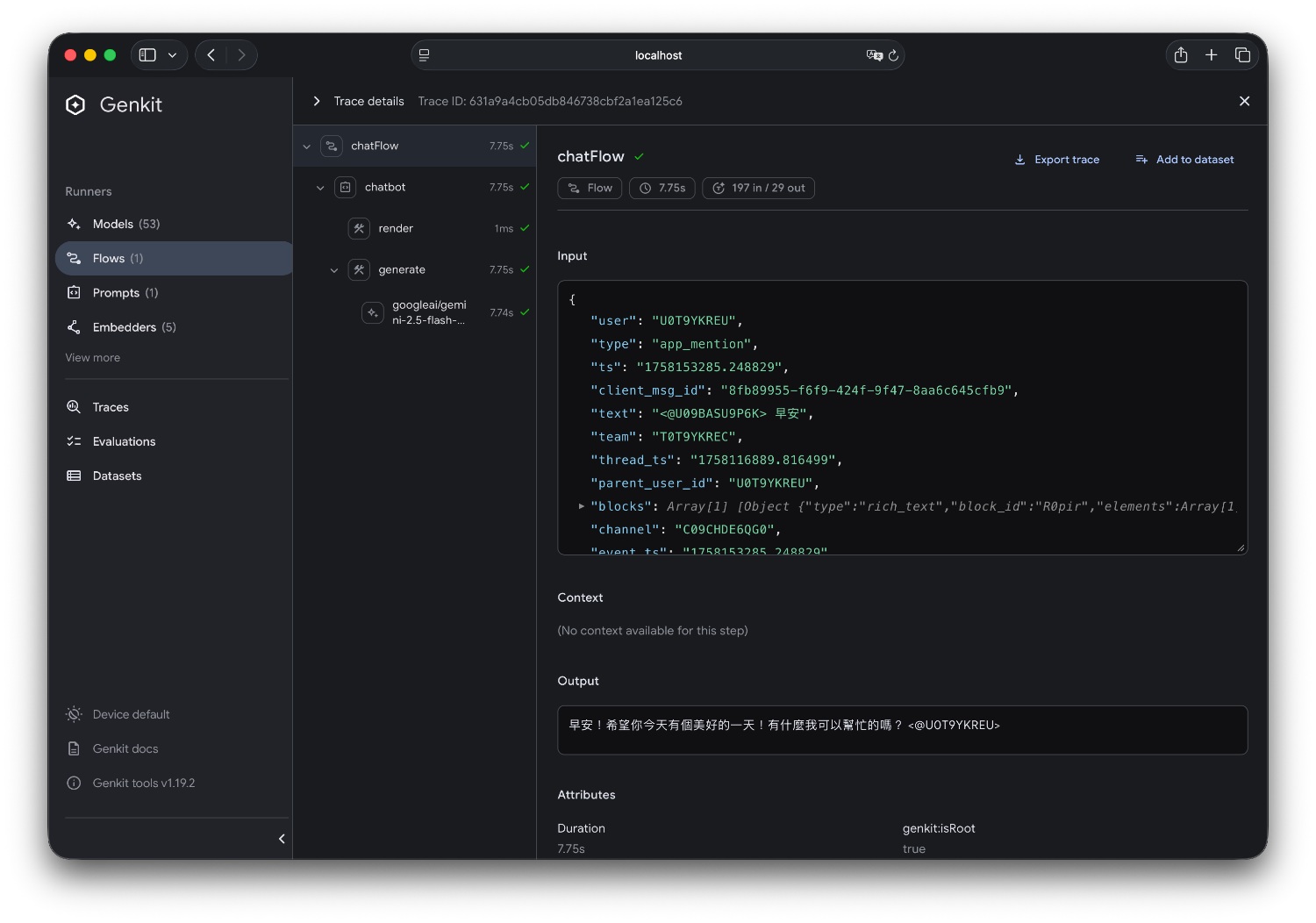
2. 即時測試 Flow
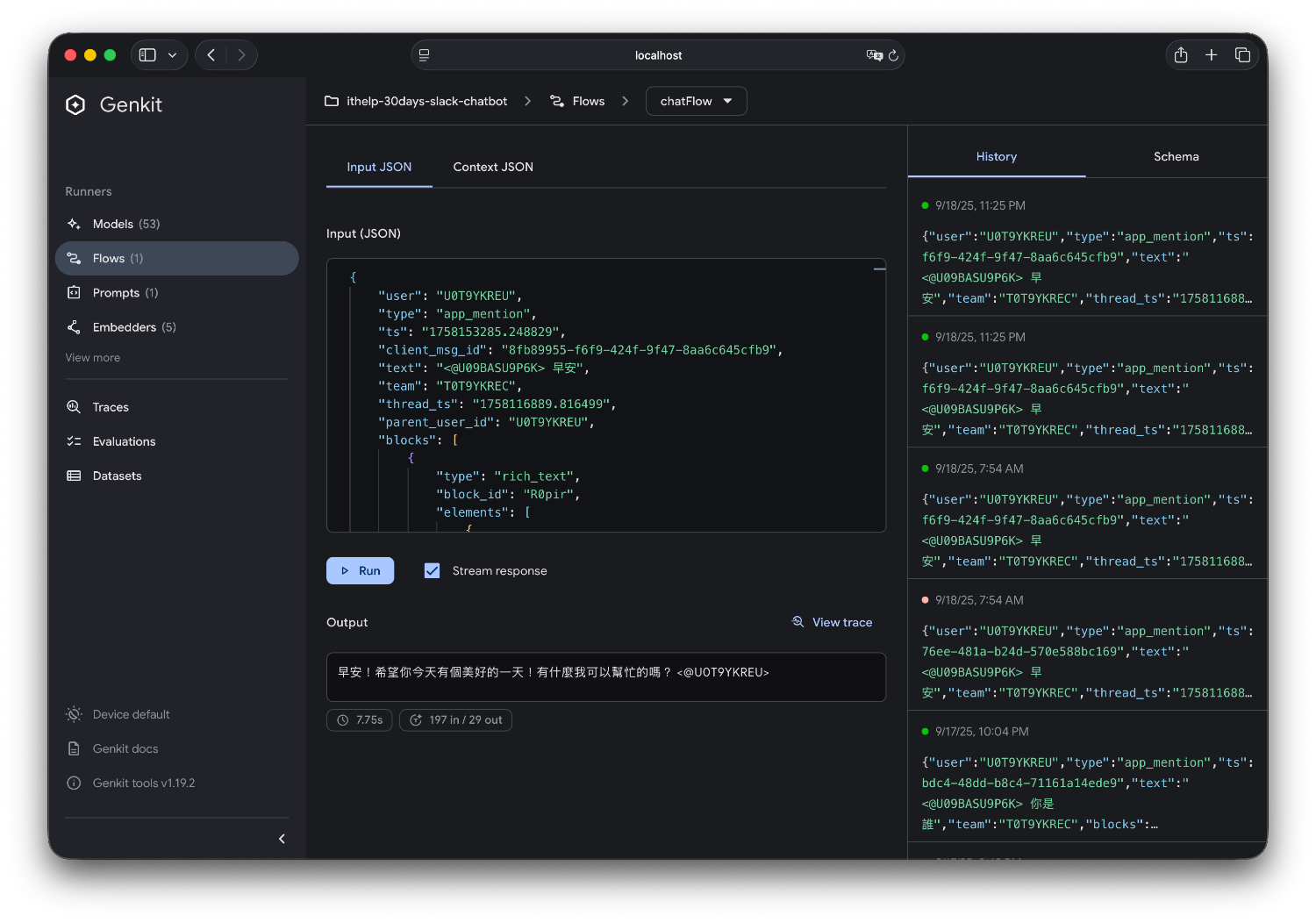
3. Flow 執行歷史
經過這段時間的實驗,我得出幾個 Prompt 管理的最佳實踐:
既使沒有要做 prompt / flow tuning 都要用 genkit start 作為啟動指令
在我的範例程式碼中 bun run dev 就是如此
原因是因為 genkit 會幫我們記錄所有的執行 history
所以當我們需要 tuning 的時候
直接打開 Developer UI 就可以用相同的 input 來做回歸測試
這樣一來就不用一直從 Slack trigger 來測試結果
Prompt 可能看起來只是「一些文字」,但實際上它是 AI 產品的核心邏輯。用管理程式碼的標準來管理 Prompt,你的 AI 產品才能健康成長。
今天我們聊完工具
明天我們來回到產品面:如何從單輪對話升級到多輪對話或是持續對話,這是另一個從「工具」到「夥伴」的重要轉換點。
完整的原始碼在這裡,有興趣的人可以下載玩玩看!
AI 的發展變化很快,目前這個想法以及專案也還在實驗中。但也許透過這個過程大家可以有一些經驗和想法互相交流,歡迎大家追蹤這個系列。
也歡迎追蹤我的 Threads @debuguy.dev
